



FindFaces
Details and Options


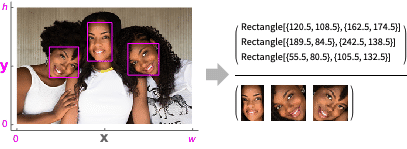
- FindFaces is also known as face detection, which is a common computer vision technique that returns detected faces.
- FindFaces returns faces as a list of bounding boxes, each given as a Rectangle object.
- Coordinates {x,y} are assumed to be in the standard image coordinate system.
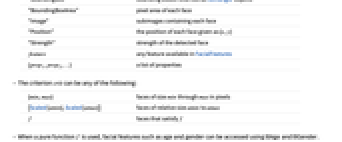
- The property prop can be any of the following:
-
"BoundingBox" bounding boxes returned as Rectangle objects "BoundingBoxArea" pixel area of each face "Confidence" strength of the detected face "Image" subimages containing each face "Position" the position of each face given as {x,y} feature any feature available in FacialFeatures {prop1,prop2,…} a list of properties - The criterion crit can be any of the following:
-
{min,max} faces of size min through max in pixels {Scaled[amin],Scaled[amax]} faces of relative size amin to amax f faces that satisfy f - When a pure function f is used, facial features such as age and gender can be accessed using #Age and #Gender. A face is returned if f returns True.
- For the complete list of facial features, see the reference page for FacialFeatures.
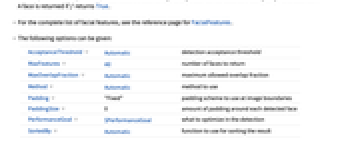
- The following options can be given:
-
AcceptanceThreshold Automatic detection acceptance threshold MaxFeatures All number of faces to return MaxOverlapFraction Automatic maximum allowed overlap fraction Method Automatic method to use Padding "Fixed" padding scheme to use at image boundaries PaddingSize 0 amount of padding around each detected face PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal what to optimize in the detection SortedBy Automatic function to use for sorting the result TargetDevice "CPU" the target device to use - With PaddingSize->x, each detected face is padded by x pixels on each side. Using PaddingSize->Scaled[s], each face is padded by a fraction s of its bounding box.
- If available, faces are padded with image content. At the boundaries, the setting of Padding is used.
- By default, detected faces are sorted based on their strength. Use SortedBy->f to specify a different sorting function. The function f can access available properties using the pattern #prop.
- Possible settings for Method include:
-
"Haar" cascade detector based on Haar features "LocalBinaryPatterns" cascade detector based on LBP features "SingleShotDetector" neural network detector based on SSD architecture {method1,method2,…} aggregates the result of all methodi - For multichannel images, the "Haar" and "LocalBinaryPatterns" methods operate on grayscale intensities.
- FindFaces uses machine learning. Its methods, training sets and biases included therein may change and yield varied results in different versions of the Wolfram Language.
- FindFaces may download resources that will be stored in your local object store at $LocalBase, and that can be listed using LocalObjects[] and removed using ResourceRemove.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (9)
Data (2)
Properties (4)
Compute the face bounding box:
Extract the portion of the image corresponding to the bounding box:
Extract features available in FacialFeatures:
Criteria (3)
Use a computable property as a test argument:
Some test results can be used as shortcuts for the whole test:
Specify a maximum face size in pixels:
Specify a minimum face size in pixels:
Use Scaled to specify the face size relative to the image dimensions:
Options (10)
AcceptanceThreshold (1)
By default, all the detected faces are returned:
Use AcceptanceThresholdt to return only detections with strength greater than t:
Use AcceptanceThreshold0 to return all the detected faces:
MaxFeatures (1)
By default, all the detected faces are returned:
Use MaxFeaturesn to return only the n strongest detections:
MaxOverlapFraction (1)
Method (2)
FindFaces automatically picks the detection method:
Use the combined result from multiple methods:
The "LocalBinaryPatterns" method is a cascade classifier that works on a histogram of the gradients (HoG) features. It is a very fast and lightweight multiscale method:
The "Haar" method is a cascade classifier working on Haar features. It is more robust than "LocalBinaryPatterns" but generally slower:
The "SingleShotDetector" method is based on a single neural net evaluation, and it is very stable with respect to variations in pose, illumination, occlusion and subjects. It is slower compared to two other methods:
Padding (1)
PaddingSize (2)
FindFaces by default returns a fairly tight crop around each face:
Specify a padding size to be added around each face:
PerformanceGoal (1)
Use PerformanceGoal"Quality" to emphasize the quality of the result:
Use PerformanceGoal"Speed" to emphasize the speed of computation:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (2)
See Also
FacialFeatures FaceAlign FaceRecognize ImageIdentify ImageContents ImageBoundingBoxes HighlightImage HighlightVideo Classify CurrentImage ImageKeypoints
Classifiers: FacialAge FacialGender FacialExpression NotablePerson
Function Repository: OccludeFaces
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2018 (11.3) ▪ 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2024 (14.1) ▪ 2025 (14.2)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), FindFaces, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFaces.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "FindFaces." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFaces.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). FindFaces. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFaces.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_findfaces, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FindFaces}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFaces.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_findfaces, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FindFaces}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFaces.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}