KernelModelFit[data]
fits the given dataset data using a default local kernel.
KernelModelFit[data,bw]
uses bandwidth bw for the kernel function.
KernelModelFit[data,bw,f]
uses the specified local kernel f.


KernelModelFit
KernelModelFit[data]
fits the given dataset data using a default local kernel.
KernelModelFit[data,bw]
uses bandwidth bw for the kernel function.
KernelModelFit[data,bw,f]
uses the specified local kernel f.
Details




- The KernelModelFit function performs localized data fitting using a specified kernel function.
- KernelModelFit uses fixed basis expansion, which is commonly used in data analysis fields like signal processing and financial modeling, where capturing local variations is essential.
- Possible forms of data are:
-
{y1,y2,…} equivalent to the form {{1,y1},{2,y2},…} {{x11,x12,…,y1},…} a list of independent values xij and the responses yi {{x11,x12,…}y1,…} a list of rules between input values and responses {{x11,x12,…},…}{y1,y2,…} a rule between a list of input values and a list of responses {{x11,…,y1,…},…}n fit the n 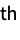 column of a matrix
column of a matrixTabular[…]name fit the column name in a tabular object - The following bandwidth specifications bw can be given:
-
Automatic automatically computed bandwidth (default) h bandwidth to use {bw1,bw2,…} use a bandwidth bwi in dimension i {{n1, bw1},…} use ni kernel functions in dimension i - With multivariate data such as
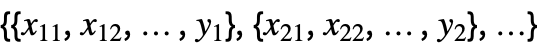 , the number of coordinates xi1, xi2, … should equal the number of input arguments of f.
, the number of coordinates xi1, xi2, … should equal the number of input arguments of f. - The kernel function f can be an arbitrary expression or one of the following values:
-
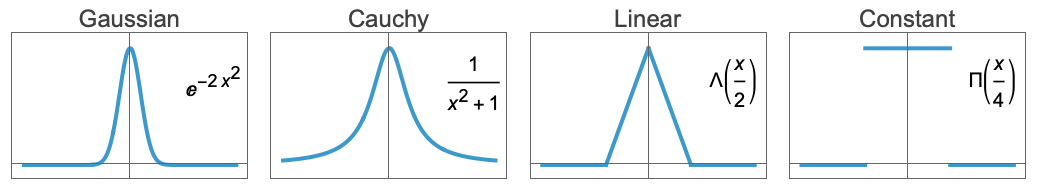
Automatic automatically pick the basis function (default) "Cauchy" 1/(1+x)2 fit a Cauchy mixture model "Constant" ![TemplateBox[{{x, /, 4}}, UnitBoxSeq] TemplateBox[{{x, /, 4}}, UnitBoxSeq]](Files/KernelModelFit.en/4.png)
fit a piecewise constant combination "Gaussian" -2 x2 fit a Gaussian mixture model "Linear" ![TemplateBox[{{x, /, 2}}, HeavisideLambdaSeq] TemplateBox[{{x, /, 2}}, HeavisideLambdaSeq]](Files/KernelModelFit.en/5.png)
fit a linear piecewise combination fun explicit function - If an explicit kernel function f is specified, this function will receive arguments r of the form dist[x,x0]/d, with dist a distance metric, x the prediction point, x0 the central point of the local kernel function and d a scaling factor. Typically, the function f[r] should be positive for 0<=r<=1 to work well. For example, the "Gaussian" mixture model corresponds to f[r]== Exp[-2r2].
- KernelModelFit has the following options:
-
DistanceFunction Automatic distance metric to use IncludeConstantBasis True whether to include a constant basis function WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision to use -
ConfidenceLevel 95/100 confidence level to use for parameters and predictions IncludeConstantBasis True whether to include a constant basis function LinearOffsetFunction None known offset in the linear predictor NominalVariables None variables considered as nominal or categorical VarianceEstimatorFunction Automatic function for estimating the error variance Weights Automatic weights for data elements WorkingPrecision Automatic precision used in internal computations
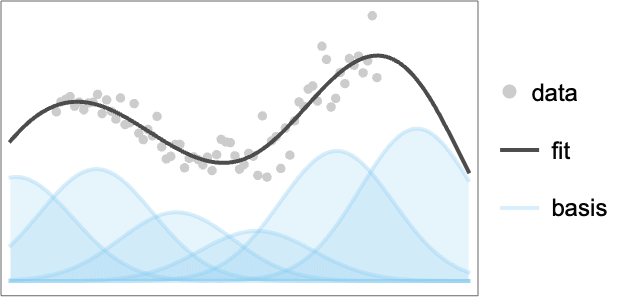
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
See Also
FittedModel LocalModelFit Fit LinearModelFit SmoothKernelDistribution
Methods: GaussianMixture
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), KernelModelFit, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KernelModelFit.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "KernelModelFit." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KernelModelFit.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). KernelModelFit. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KernelModelFit.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_kernelmodelfit, author="Wolfram Research", title="{KernelModelFit}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KernelModelFit.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_kernelmodelfit, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={KernelModelFit}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KernelModelFit.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}