NotebookRead
NotebookRead[notebook]
gives the expression corresponding to the current selection in the specified notebook object.
NotebookRead[obj]
gives the expression corresponding to the given cell or box object.
NotebookRead[{obj1,obj2,…}]
gives a list of expressions corresponding to the obji.
Details and Options

- NotebookRead is the basic way to get into the kernel pieces of notebooks that are being manipulated by the front end.
- NotebookRead can take a NotebookObject, CellObject, or BoxObject.
- If a list of CellObject or BoxObject expressions is given, then a list of equal length will be returned, with the expressions corresponding to each object.
- If an object is no longer valid, NotebookRead returns $Failed. If a list of objects is given, then $Failed will be returned for each of the invalid objects.
- The following options can be given:
-
CellContext None context to substitute for $CellContext` StripCellGrouping False whether to strip cell grouping when reading contiguously selected cells - When NotebookRead[notebook] reads a contiguous selection of cells, selected cell groups are returned as Cell[CellGroupData[…]] expressions by default. The option setting StripCellGroupingTrue will force selected cells to be returned as a flat list regardless of grouping.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
This creates a document notebook:
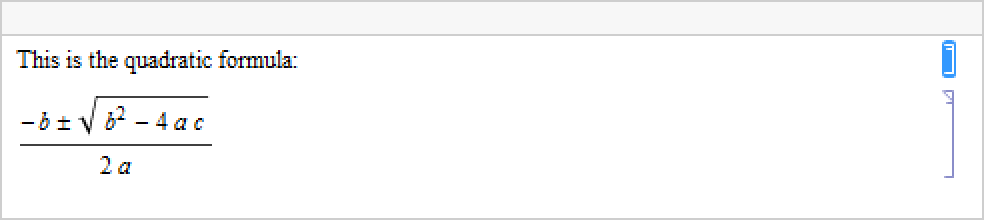
This reads the cell and returns its Cell expression:
Read a CellObject:
Read a BoxObject:
Scope (1)
Options (2)
CellContext (1)
Create a target cell with a raw expression in it:
Read the cell using NotebookRead:
Use CellContext to substitute a value for the $CellContext` context:
StripCellGrouping (1)
Reading a group of cells includes CellGroupData constructs by default:
Use StripCellGrouping to remove the grouping information:
Text
Wolfram Research (1996), NotebookRead, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NotebookRead.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1996. "NotebookRead." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NotebookRead.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1996). NotebookRead. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NotebookRead.html