PoissonPDEComponent[vars,pars]
yields a Poisson PDE term ![]() with model variables vars and model parameters pars.
with model variables vars and model parameters pars.


PoissonPDEComponent
PoissonPDEComponent[vars,pars]
yields a Poisson PDE term ![]() with model variables vars and model parameters pars.
with model variables vars and model parameters pars.
Details

- PoissonPDEComponent returns a sum of differential operators to be used as a part of partial differential equations:
- PoissonPDEComponent can be used to model Poisson equations with dependent variable
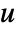 , independent variables
, independent variables 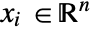 and time variable
and time variable 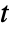 .
. - Stationary model variables vars are vars={u[x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}.
- Time-dependent model variables vars are vars={u[t,x1,…,xn],t,{x1,…,xn}}.
- The PoissonPDEComponent is based on a diffusion and source term:
- The Poisson PDE term
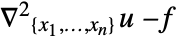 is realized as a DiffusionPDETerm with –1 as a diffusion coefficient and a SourcePDETerm with coefficient
is realized as a DiffusionPDETerm with –1 as a diffusion coefficient and a SourcePDETerm with coefficient 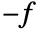 resulting in
resulting in 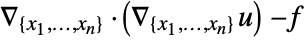 .
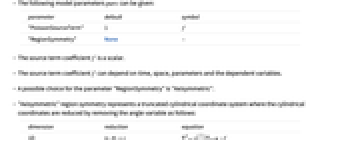
. - The following model parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "PoissonSourceTerm" 1 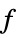
"RegionSymmetry" None 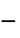
- The source term coefficient
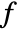 is a scalar.
is a scalar. - The source term coefficient
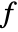 can depend on time, space, parameters and the dependent variables.
can depend on time, space, parameters and the dependent variables. - A possible choice for the parameter "RegionSymmetry" is "Axisymmetric".
- "Axisymmetric" region symmetry represents a truncated cylindrical coordinate system where the cylindrical coordinates are reduced by removing the angle variable as follows:
-
dimension reduction equation 1D 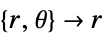
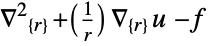
2D 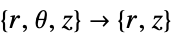
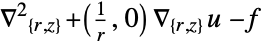
- The diffusion coefficient 1 affects the meaning of NeumannValue.
- If the PoissonPDEComponent depends on parameters
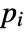 that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters
that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters 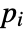 are replaced with
are replaced with 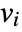 .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Applications (1)
Solve an axisymmetric Poisson problem in a solid cylinder. Define the variables and parameters:
The solid cylinder can be approximated by a 2D rectangle that represents a cross section of the solid. Create the 2D rectangle using Polygon:
Set up the boundary conditions:
Visualize the solution with DensityPlot:
The exact solution is given by ![]() . Visualize the error between the exact solution and the 2D axisymmetric solution:
. Visualize the error between the exact solution and the 2D axisymmetric solution:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), PoissonPDEComponent, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoissonPDEComponent.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "PoissonPDEComponent." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoissonPDEComponent.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). PoissonPDEComponent. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoissonPDEComponent.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_poissonpdecomponent, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PoissonPDEComponent}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoissonPDEComponent.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_poissonpdecomponent, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PoissonPDEComponent}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PoissonPDEComponent.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}