



PolyLog
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
![TemplateBox[{n, z}, PolyLog]=sum_(k=1)^(infty)z^k/k^n TemplateBox[{n, z}, PolyLog]=sum_(k=1)^(infty)z^k/k^n](Files/PolyLog.en/3.png) .
. ![TemplateBox[{n, p, z}, PolyLog3]=(-1)^(n+p-1)/((n-1)!p!)int_0^1log^(n-1)(t)log^p(1-zt)/t dt TemplateBox[{n, p, z}, PolyLog3]=(-1)^(n+p-1)/((n-1)!p!)int_0^1log^(n-1)(t)log^p(1-zt)/t dt](Files/PolyLog.en/4.png) .
. ![TemplateBox[{{n, -, 1}, 1, z}, PolyLog3]=TemplateBox[{n, z}, PolyLog] TemplateBox[{{n, -, 1}, 1, z}, PolyLog3]=TemplateBox[{n, z}, PolyLog]](Files/PolyLog.en/5.png) .
. - PolyLog[n,z] has a branch cut discontinuity in the complex
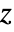 plane running from 1 to
plane running from 1 to 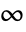 .
. - For certain special arguments, PolyLog automatically evaluates to exact values.
- PolyLog can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- PolyLog automatically threads over lists.
- PolyLog can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (33)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix PolyLog function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (5)
Visualization (3)
Function Properties (11)
Real domain of PolyLog:
PolyLog threads elementwise over lists:
PolyLog is not an analytic function:
PolyLog is not meromorphic:
![]() is non-decreasing on its real domain for
is non-decreasing on its real domain for ![]() :
:
For other values of ![]() , it might or might not be monotonic:
, it might or might not be monotonic:
PolyLog is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
PolyLog has both singularity and discontinuity for x≥1:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (2)
Series Expansions (2)
Find the Taylor expansion using Series:
Function Identities and Simplifications (4)
PolyLog is defined through the identity:
For positive integer ![]() ,
, ![]() can be expressed in terms of hypergeometric functions:
can be expressed in terms of hypergeometric functions:
Generalizations & Extensions (7)
Ordinary Polylogarithm Function (5)
Infinite arguments give symbolic results:
PolyLog can be applied to power series:
Applications (5)
Plot of the absolute value of the dilogarithm function in the complex plane:
Calculate integrals over Bose–Einstein distributions:
Calculate integrals over Fermi–Dirac distributions:
Volume of a hyperbolic ideal tetrahedron with vertices at ![]() , 0, 1,
, 0, 1, ![]() (subject to
(subject to ![]() ):
):
Plot the volume as a function of the vertex ![]() :
:
Mahler measure of the trivariate polynomial ![]() as a function of
as a function of ![]() :
:
Generate the Eulerian numbers [MathWorld]:
Properties & Relations (6)
Use FullSimplify to simplify polylogarithms:
Use FunctionExpand to expand polylogarithms:
Numerically find a root of a transcendental equation:
Generate from integrals and sums:
PolyLog appears in special cases of various mathematical functions:
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 1999 (4.0) ▪ 2000 (4.1) ▪ 2002 (4.2) ▪ 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2022 (13.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), PolyLog, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PolyLog.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "PolyLog." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PolyLog.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). PolyLog. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PolyLog.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_polylog, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PolyLog}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PolyLog.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_polylog, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PolyLog}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PolyLog.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}