RecurrenceFilter[{α,β},x]
filters x using a linear recurrence equation with coefficients α and β.
RecurrenceFilter[tf,x]
uses a discrete-time filter defined by the TransferFunctionModel tf.
RecurrenceFilter[…,x,{y0,y-1,…}]
uses a specified list {y0,y-1,…} as the initial condition.
RecurrenceFilter[…,image]
filters image.
RecurrenceFilter[…,sound]
filters sampled sound object.


RecurrenceFilter
RecurrenceFilter[{α,β},x]
filters x using a linear recurrence equation with coefficients α and β.
RecurrenceFilter[tf,x]
uses a discrete-time filter defined by the TransferFunctionModel tf.
RecurrenceFilter[…,x,{y0,y-1,…}]
uses a specified list {y0,y-1,…} as the initial condition.
RecurrenceFilter[…,image]
filters image.
RecurrenceFilter[…,sound]
filters sampled sound object.
Details and Options

- RecurrenceFilter[{α,β},x] gives the response y to the causal input x by solving the recurrence equation
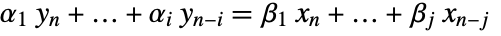 for n from 1 to Length[x], where i is Length[α] and j is Length[β].
for n from 1 to Length[x], where i is Length[α] and j is Length[β]. - RecurrenceFilter[{α,β},x] uses an initial condition
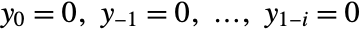 .
. - RecurrenceFilter[{α,β},x] pads the input x so that
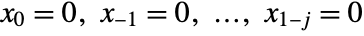 . The values can be changed with the Padding option. With Padding->None, the response y effectively starts at yj, and the output dimensions are normally smaller than the input. »
. The values can be changed with the Padding option. With Padding->None, the response y effectively starts at yj, and the output dimensions are normally smaller than the input. » - The specified coefficients α and β are respectively the denominator and numerator polynomial coefficients of the desired transfer function model.
- In RecurrenceFilter[tf,…], tf should be a single-input single-output (SISO) system.
- RecurrenceFilter works with arbitrary-rank numerical arrays, 2D and 3D images, and sampled sound objects, operating separately on each channel.
- Possible sound objects include:
-
SampledSoundList[{a1,a2,…},r] amplitude levels given in a list SampledSoundFunction[f,n,r] amplitude levels generated by a function Sound[prims,…] excluding SoundNote objects in prims - When applied to images and multidimensional arrays, the specified filter is applied successively to each dimension, starting at level 1.
- For multichannel image and sound objects, RecurrenceFilter is applied to each channel separately.
Examples
open all close allScope (5)
Use symbolic values for filter coefficients:
Apply a filter specified using a transfer function model:
Filter a TimeSeries:
Options (1)
Padding (1)
By default, RecurrenceFilter uses zero padding:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (5)
Impulse response of first-order recursive filter:
Step response of a non-recursive filter:
In 2D, the filter is applied successively to rows and columns:
Use Map to apply the filter to rows only:
For 1D arrays, OutputResponse is equivalent to RecurrenceFilter:
Use RecurrenceTable when describing the filter using a difference equation:
ListConvolve and RecurrenceFilter return equivalent results for non-recursive digital filters:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), RecurrenceFilter, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RecurrenceFilter.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "RecurrenceFilter." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RecurrenceFilter.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). RecurrenceFilter. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RecurrenceFilter.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_recurrencefilter, author="Wolfram Research", title="{RecurrenceFilter}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RecurrenceFilter.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_recurrencefilter, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={RecurrenceFilter}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RecurrenceFilter.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}