"MeanShift" (Machine Learning Method)
- Method for FindClusters, ClusterClassify and ClusteringComponents.
- Partitions data into clusters of similar elements using "MeanShift" clustering algorithm.
Details & Suboptions
- "MeanShift" is a density-based clustering method where the density is estimated using a neighbor-based approach. "MeanShift" works for arbitrary cluster shapes and sizes; however, it can fail when clusters have different densities or are intertwined.
- The following plots show the results of the "MeanShift" method applied to toy datasets:
-
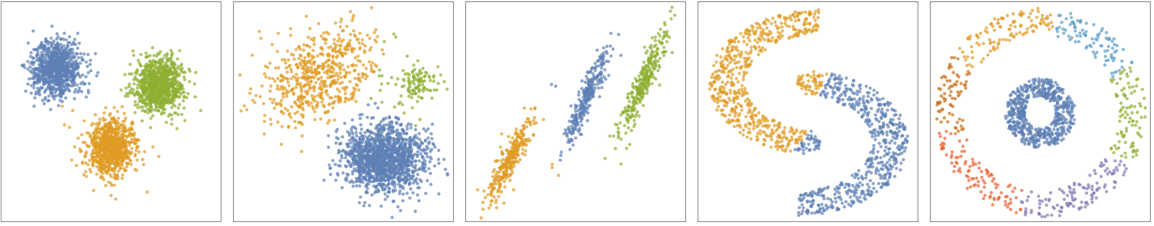
- The "MeanShift" method iteratively shifts data points toward higher-density regions. During this procedure, data points tend to collapse to different fixed points, each of them representing a cluster.
- Formally, at each step, each data point
 is set to
is set to 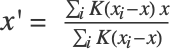 with
with  ,
, 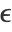 defining an effective neighborhood radius. The difference
defining an effective neighborhood radius. The difference  is called mean shift. The algorithm repeats the mean-shift updates until points stop moving; all points belonging to a cluster are then collapsed (up to a tolerance). This algorithm is equivalent to the "NeighborhoodContraction" method but with a different neighborhood definition.
is called mean shift. The algorithm repeats the mean-shift updates until points stop moving; all points belonging to a cluster are then collapsed (up to a tolerance). This algorithm is equivalent to the "NeighborhoodContraction" method but with a different neighborhood definition. - The option DistanceFunction can be used to define which distance to use.
- The following suboption can be given:
-
"NeighborhoodRadius" Automatic radius ϵ
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Find clusters of nearby values using the "MeanShift" clustering method:
Train the ClassifierFunction on a list of colors using the "MeanShift" method:
Gather the elements by their class number:
Train a ClassifierFunction on a list of strings:
Find the cluster assignments and gather the elements by their cluster: