Set a Cloud Object’s Permissions
Access to a cloud object is controlled by the setting of its Permissions option. Set permissions so that only you have access, or share a cloud object with the world.
So That Only You Have Access...
With the default setting of $Permissions, a newly created cloud object has Permissions->"Private", which prevents anyone but its owner from accessing it:

The object’s permissions show that only the owner can read, write and execute the cloud object:

To Share It with the World...
To give anyone access to a cloud object, set Permissions->"Public":

The object’s permissions show that anyone can read the object, but only the owner can write and execute it:
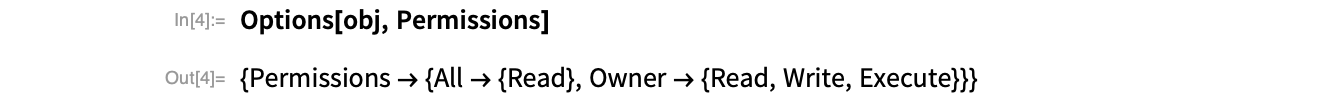
To Share It with Particular People...
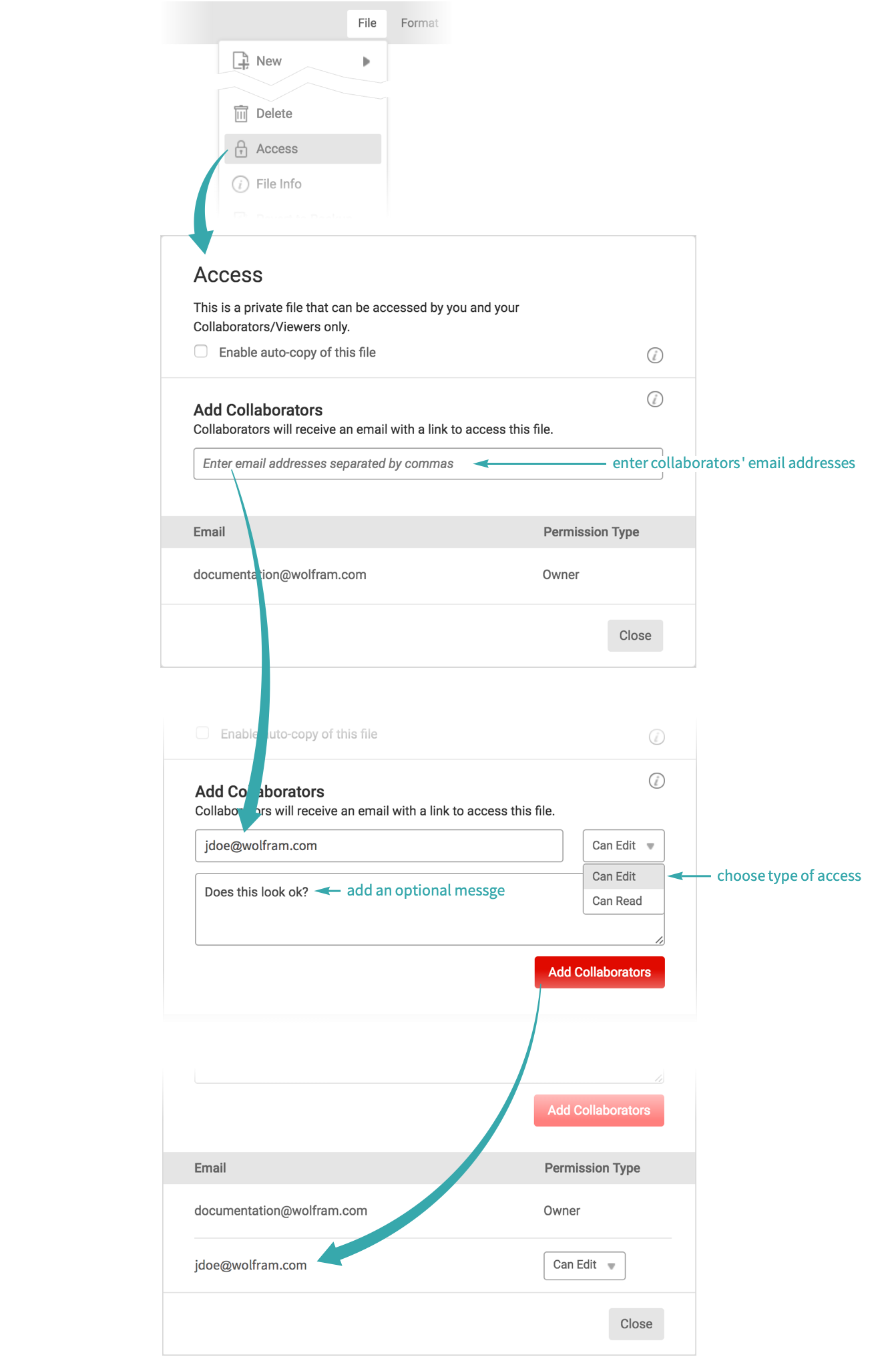
To share a cloud object with particular people, specify their email addresses, Wolfram IDs or Wolfram UUIDs in the Permissions option:

- The Wolfram ID of the currently logged-in user is given by $WolframID, and the Wolfram UUID is given by $WolframUUID.
- Specified users must have Wolfram IDs. Giving email addresses that do not have Wolfram IDs will result in an error.
When the Cloud Object Already Exists...
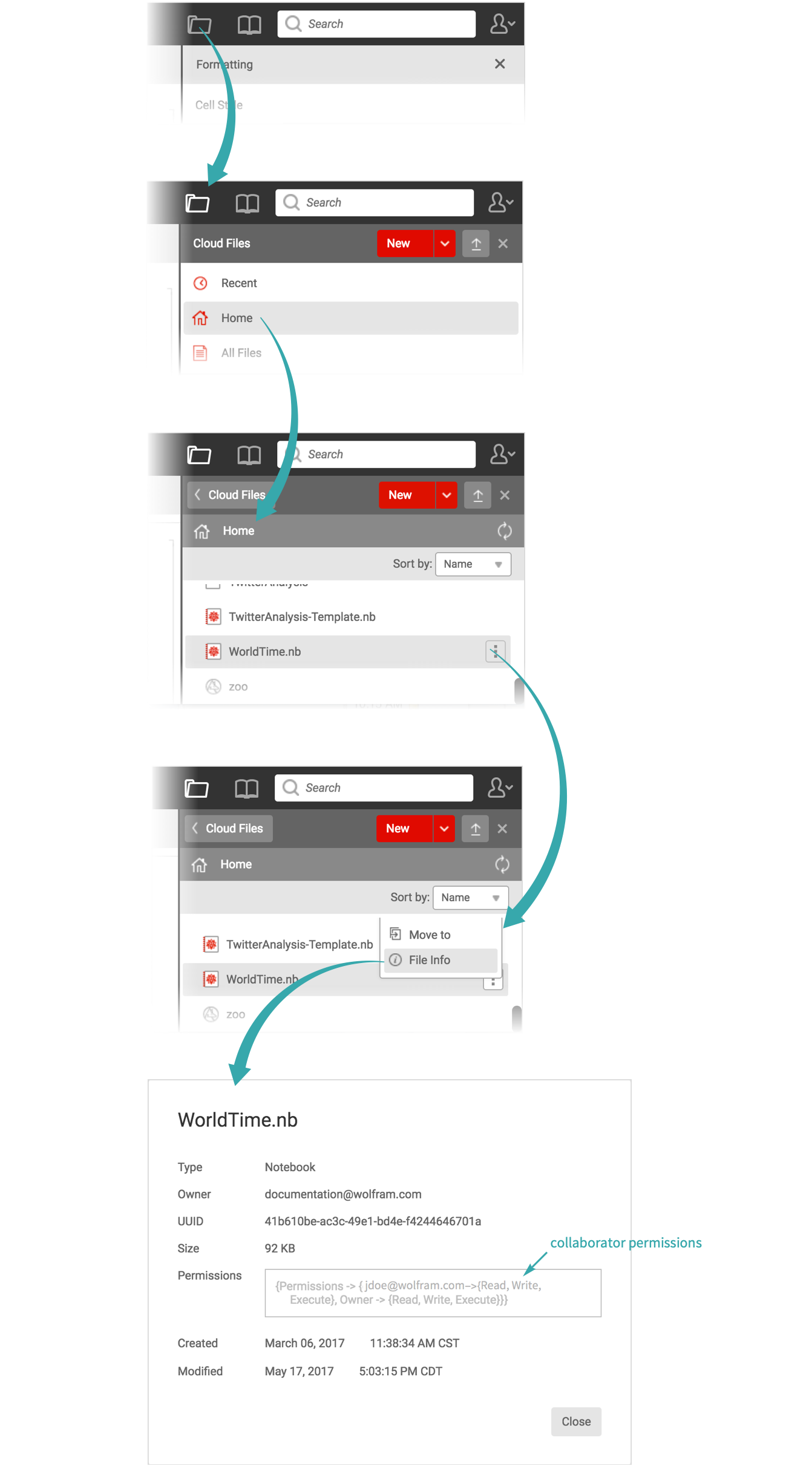
Set the permissions of an existing cloud object with SetPermissions.
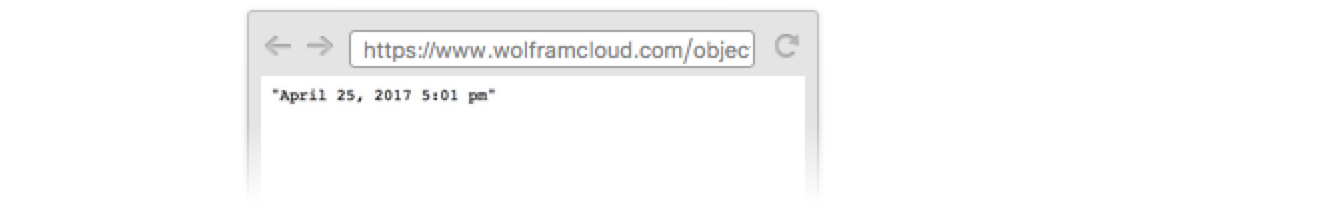
Deploy an APIFunction:
With the default permissions, anyone but the owner who visits the URL will be denied access:
Set the object’s permissions to give anyone access:

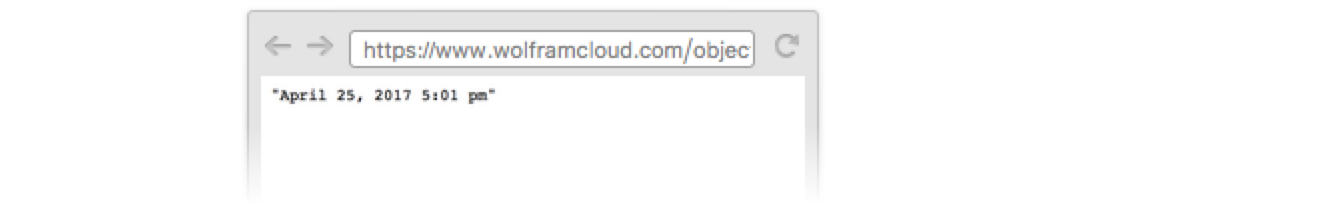
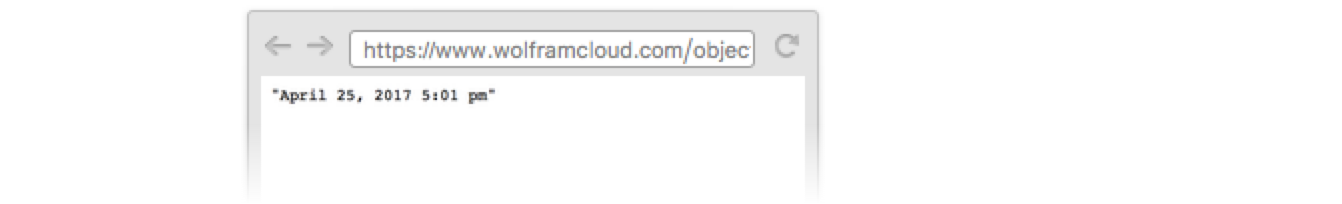
Now anyone can access the API:
So That Only You Have Access...
With the default setting of $Permissions, a newly created cloud object has Permissions->"Private", which prevents anyone but its owner from accessing it:

The object’s permissions show that only the owner can read, write and execute the cloud object:

To Share It with the World...
To give anyone access to a cloud object, set Permissions->"Public":

The object’s permissions show that anyone can read the object, but only the owner can write and execute it:
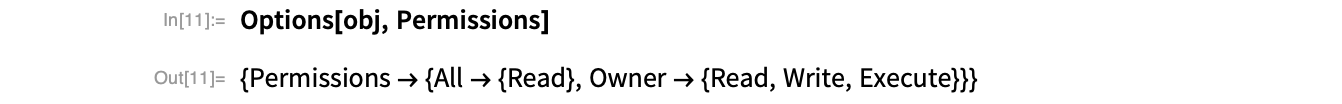
To Share It with Particular People...
To share a cloud object with particular people, specify their email addresses, Wolfram IDs or Wolfram UUIDs in the Permissions option:

- The Wolfram ID of the currently logged-in user is given by $WolframID, and the Wolfram UUID is given by $WolframUUID.
- Specified users must have Wolfram IDs. Giving email addresses that do not have Wolfram IDs will result in an error.
When the Cloud Object Already Exists...
Set the permissions of an existing cloud object with SetPermissions.
Deploy an APIFunction:
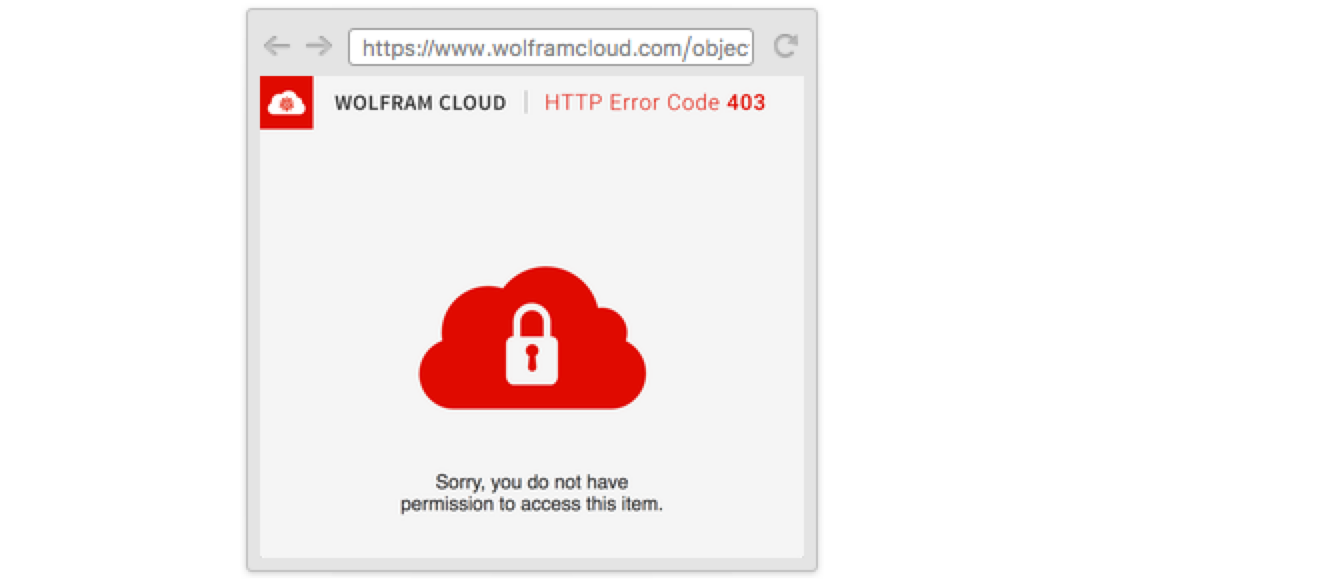
With the default permissions, anyone but the owner who visits the URL will be denied access:
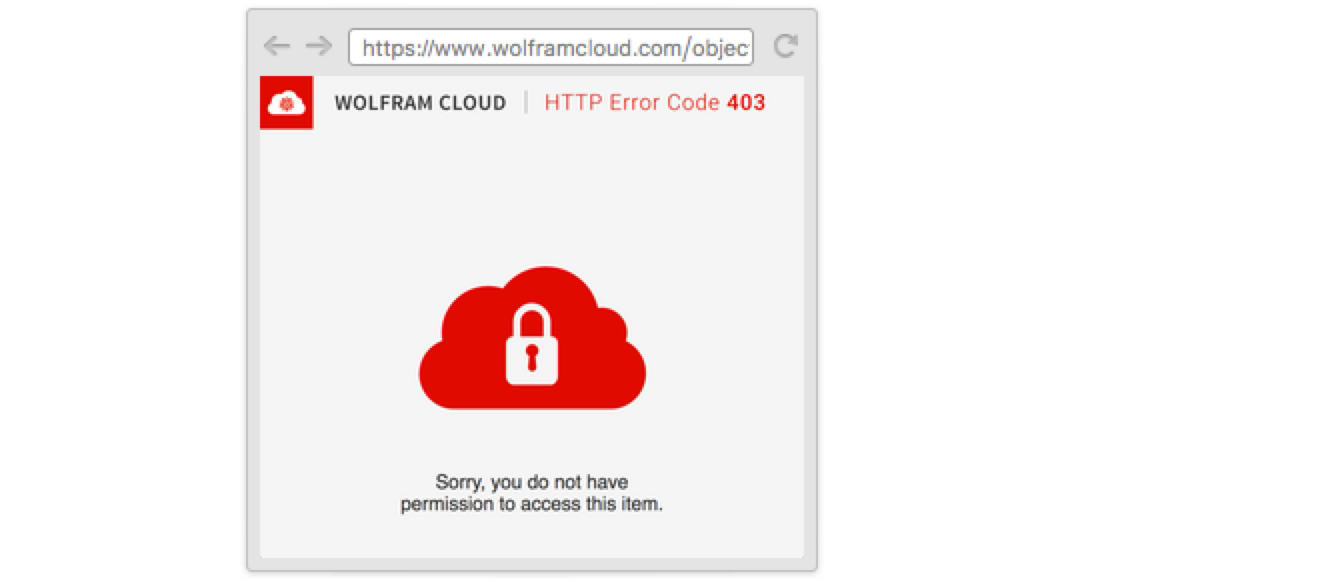
Set the object’s permissions to give anyone access:

Now anyone can access the API:
So That Only You Have Access...
With the default setting of $Permissions, a newly created cloud object has Permissions->"Private", which prevents anyone but its owner from accessing it:

The object’s permissions show that only the owner can read, write and execute the cloud object:

To Share It with the World...
To give anyone access to a cloud object, set Permissions->"Public":

The object’s permissions show that anyone can read the object, but only the owner can write and execute it:
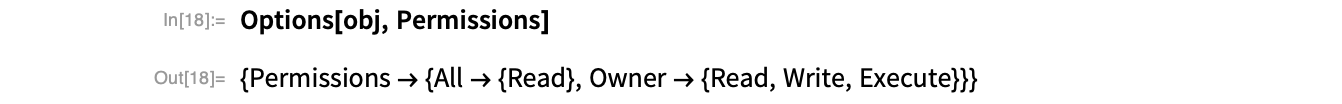
To Share It with Particular People...
To share a cloud object with particular people, specify their email addresses, Wolfram IDs or Wolfram UUIDs in the Permissions option:

- The Wolfram ID of the currently logged-in user is given by $WolframID, and the Wolfram UUID is given by $WolframUUID.
- Specified users must have Wolfram IDs. Giving email addresses that do not have Wolfram IDs will result in an error.
When the Cloud Object Already Exists...
Set the permissions of an existing cloud object with SetPermissions.
Deploy an APIFunction:
With the default permissions, anyone but the owner who visits the URL will be denied access:
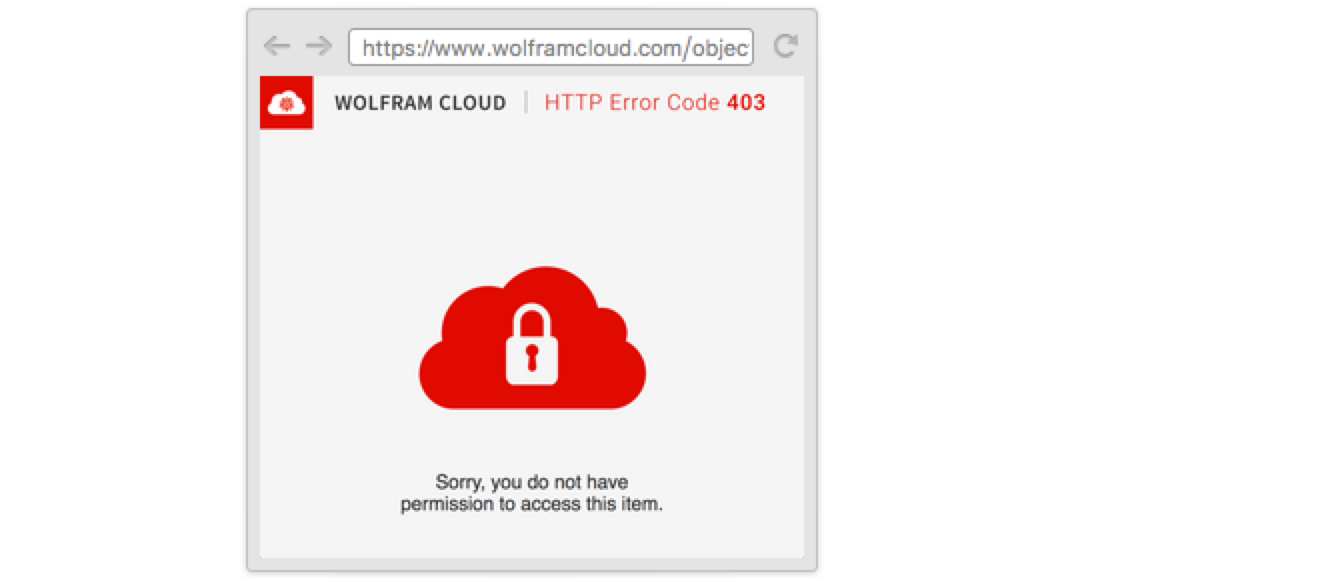
Set the object’s permissions to give anyone access:

Now anyone can access the API: