WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
MeasureDemoMeasure demo |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["PlanarMechanics.Examples.MeasureDemo"]
Information
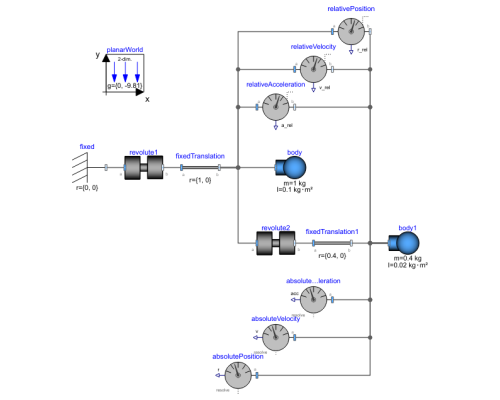
This example shows how to use absolute and relative sensors for position, velocity and acceleration. For demonstration purposes a double pendulum is used.
Components (14)
| body |
Type: Body Description: Body component with mass and inertia |
|
|---|---|---|
| fixedTranslation |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: A fixed translation between two components (rigid rod) |
|
| fixed |
Type: Fixed Description: Frame fixed in the planar world frame at a given position and orientation |
|
| body1 |
Type: Body Description: Body component with mass and inertia |
|
| fixedTranslation1 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: A fixed translation between two components (rigid rod) |
|
| planarWorld |
Type: PlanarWorld Description: Planar world coordinate system + gravity field + default animation definition |
|
| absolutePosition |
Type: AbsolutePosition Description: Measure absolute position and orientation of the origin of frame connector |
|
| relativePosition |
Type: RelativePosition Description: Measure relative position and orientation between the origins of two frame connectors |
|
| revolute1 |
Type: Revolute Description: A revolute joint |
|
| absoluteVelocity |
Type: AbsoluteVelocity Description: Measure absolute velocity of origin of frame connector |
|
| relativeVelocity |
Type: RelativeVelocity Description: Measure relative velocity between the origins of two frame connectors |
|
| absoluteAcceleration |
Type: AbsoluteAcceleration Description: Measure absolute acceleration of origin of frame connector |
|
| relativeAcceleration |
Type: RelativeAcceleration Description: Measure relative acceleration between the origins of two frame connectors |
|
| revolute2 |
Type: Revolute Description: A revolute joint |
Revisions
 Developed 2010 at the DLR Institute of System Dynamics and Control
Developed 2010 at the DLR Institute of System Dynamics and Control