WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
ForwardWhirlingFinding whirling frequencies of a rotating shaft: Part I |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["RotatingMachinery.Examples.StabilityAnalysis.ForwardWhirling"]
Information
Campbell Diagram Part I: Forward Whirling Frequency
This example shows the first part of how to find critical speeds of a simple rotor, i.e. finding forward whirling frequency.
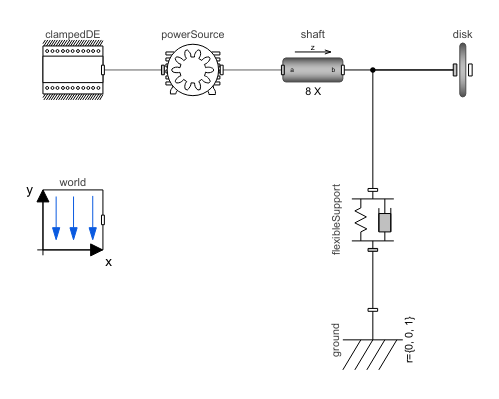
The example consists of a rotating shaft that is clamped at one end and has a disk attached to the other end. Additionally, there is a flexibleSupport system that includes damping. This makes it possible to operate the machinery at resonance frequencies. This type of setup is common in many types of machinery, such as pulleys and flywheels.
Figure 1: Clamped shaft with a disk.
The natural frequencies of a rotating shaft are influenced by gyroscopic effects and depend on the rotational speed. These frequencies can be categorized as forward and backward mode frequencies. When the machinery reaches these frequencies, it starts to whirl. Forward mode frequencies increase with speed, while backward mode frequencies decrease. The Campbell diagram, [1], is created by using Mathematica to identify critical speeds, or whirling frequencies, where resonance may occur.
The rotor is ramping up in angular velocity during the simulation, starting at 0 rad/s and ending at over 90 rad/s. It can be seen in the animation that at around 1000 s, the rotor whirls a lot.
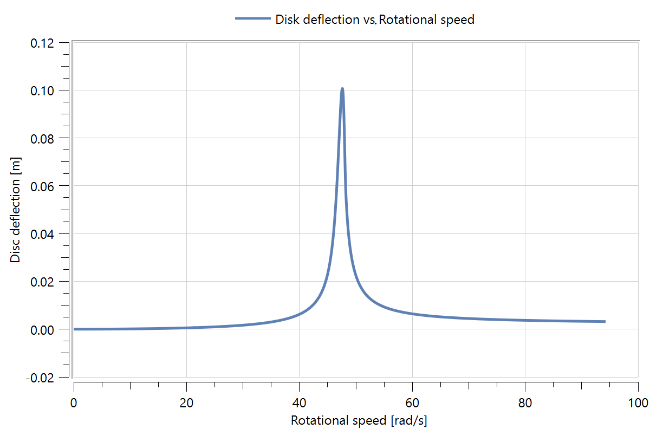
Figure 2: Disk deflection vs. Rotational speed.
Figure 2 shows the deflection of the disk versus the angular velocity of the shaft. The resonance is observed at an angular velocity of 47.6 rad/s. This peak deflection frequency is the forward whirling speed of the rotor.
References
[1] Campbell, W. "Protection of Steam Turbine Disk Wheels from Axial Vibration." Transactions of the ASME 46 (1924): 31–160.
Components (7)
| world |
Type: World Description: World coordinate system + gravity field + default animation definition |
|
|---|---|---|
| disk |
Type: Disk Description: Class with a disk and unblances |
|
| shaft |
Type: CylindricalBeam Description: Class with a flexible cylindrical beam |
|
| ground |
Type: Fixed Description: Frame fixed in the world frame at a given position |
|
| flexibleSupport |
Type: SupportStiffnessDamping Description: Support that acts as a translational two-dimensional coupled spring damper |
|
| powerSource |
Type: Motor Description: Class for applying a torque to generate a desired angular velocity |
|
| clampedDE |
Type: ClampedDriveEnd Description: Component that can act as a clamped drive end to a beam, containing different options |