WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
ClampedDriveEndComponent that can act as a clamped drive end to a beam, containing different options |
|
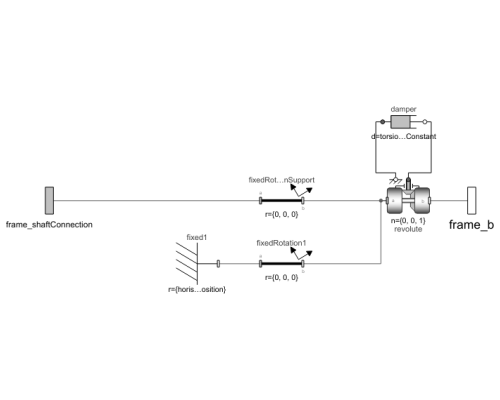
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["RotatingMachinery.Supports.ClampedDriveEnd"]
Information
Clamped Drive End Support
This component acts as support to a beam/shaft. Depending on the settings of the parameters, the support will act as a clamped support with a built-in fixed point or a clamped support that connects to another frame (activated by setting useFlangeSupport to true). The default setting is a clamped support with a built-in fixed point.
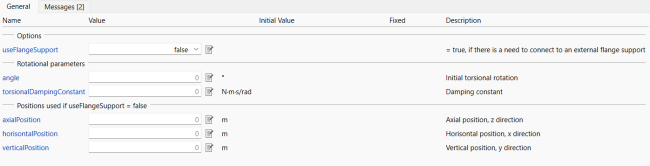 Figure 1: Clamped support parameters tab.
Figure 1: Clamped support parameters tab.
A clamped support only enables rotation around the beam axis (z axis). If a translational movement in the beam axis should be allowed, use the useFlangeSupport and connect to a prismatic joint that allows for that movement.
References
[1] Schmid, S. R., B. J. Hamrock and Bo. O. Jacobson. Fundamentals of Machine Elements. CRC Press, 2013.
Parameters (6)
| useFlangeSupport |
Value: Type: Boolean Description: = true, if there is a need to connect to an external flange support |
|---|---|
| angle |
Value: 0 Type: Angle_deg (°) Description: Initial torsional rotation |
| torsionalDampingConstant |
Value: 0 Type: RotationalDampingConstant (N⋅m⋅s/rad) Description: Damping constant |
| axialPosition |
Value: 0 Type: Length (m) Description: Axial position, z direction |
| horisontalPosition |
Value: 0 Type: Length (m) Description: Horisontal position, x direction |
| verticalPosition |
Value: 0 Type: Length (m) Description: Vertical position, y direction |
Connectors (2)
Components (5)
| fixedRotation1 |
Type: FixedRotation Description: Fixed translation followed by a fixed rotation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
|---|---|---|
| fixed1 |
Type: Fixed Description: Frame fixed in the world frame at a given position |
|
| fixedRotationSupport |
Type: FixedRotation Description: Fixed translation followed by a fixed rotation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| revolute |
Type: Revolute Description: Revolute joint (1 rotational degree-of-freedom, 2 potential states, optional axis flange) |
|
| damper |
Type: Damper Description: Linear 1D rotational damper |
Used in Examples (10)
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.StabilityAnalysis Finding whirling frequencies of a rotating shaft: Part I |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.StabilityAnalysis Finding whirling frequencies of a rotating shaft: Part II |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.Gears.PlanetaryGears A basic planetary gear application; WindTurbine Part I |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.Gears.PlanetaryGears Building a three-shaft gearbox; WindTurbine Part II |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.Gears.PlanetaryGears Assembly of a planetary gear and a three-shafted gearbox; Part I and Part II |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.ContactAnalysis Study of contact forces between a disk and a housing |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.ContactAnalysis Study of a running up clamped free rotor |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.ContactAnalysis Inspection of deflection of a free rotor without clearance |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.ContactAnalysis Calculation of deflection for a rotor with a surrounding and a clearance |
|
|
RotatingMachinery.Examples.ContactAnalysis Application of a running down rotor deflection with a clearance |