

ArgMax
Details and Options


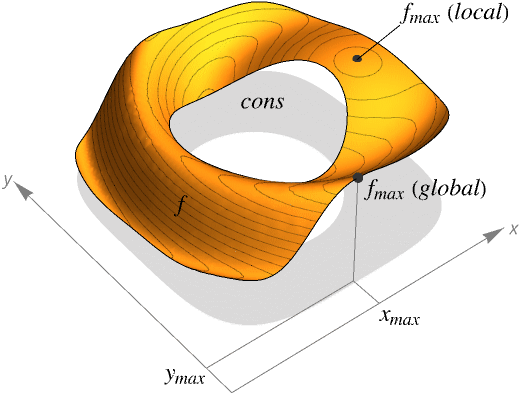
- ArgMax finds the global maximum of f subject to the constraints given.
- ArgMax is typically used to find the largest possible values given constraints. In different areas, this may be called the best strategy, best fit, best configuration and so on.
- If f and cons are linear or polynomial, ArgMax will always find a global maximum.
- The constraints cons can be any logical combination of:
-
lhs==rhs equations lhs>rhs, lhs≥rhs, lhs<rhs, lhs≤rhs inequalities (LessEqual,…) lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs vector inequalities (VectorLessEqual,…) Exists[…], ForAll[…] quantified conditions {x,y,…}∈rdom region or domain specification - ArgMax[{f,cons},x∈rdom] is effectively equivalent to ArgMax[{f,cons∧x∈rdom},x].
- For x∈rdom, the different coordinates can be referred to using Indexed[x,i].
- Possible domains rdom include:
-
Reals real scalar variable Integers integer scalar variable Vectors[n,dom] vector variable in 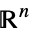
Matrices[{m,n},dom] matrix variable in 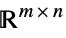
ℛ vector variable restricted to the geometric region 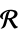
- By default, all variables are assumed to be real.
- ArgMax will return exact results if given exact input. With approximate input, it automatically calls NArgMax.
- If the maximum is achieved only infinitesimally outside the region defined by the constraints, or only asymptotically, ArgMax will return the closest specifiable point.
- Even if the same maximum is achieved at several points, only one is returned.
- If the constraints cannot be satisfied, ArgMax returns {Indeterminate,Indeterminate,…}.
- N[ArgMax[…]] calls NArgMax for optimization problems that cannot be solved symbolically.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Scope (36)
Basic Uses (7)
Univariate Problems (7)
Multivariate Problems (9)
Multivariate linear constrained maximization:
Linear-fractional constrained maximization:
Unconstrained polynomial maximization:
Constrained polynomial optimization can always be solved:
The maximum value may not be attained:
The objective function may be unbounded:
There may be no points satisfying the constraints:
Quantified polynomial constraints:
Bounded transcendental maximization:
Maximize concave objective function ![]() such that
such that ![]() is positive semidefinite and
is positive semidefinite and ![]() :
:
Parametric Problems (4)
Optimization over Integers (3)
Optimization over Regions (6)
Options (1)
WorkingPrecision (1)
Finding an exact maximum point can take a long time:
With WorkingPrecision->200, you get an approximate maximum point:
Applications (15)
Basic Applications (3)
Geometric Distances (9)
The point q in a region ℛ that is farthest from a given point p is given by ArgMax[{Norm[p-q],q∈ℛ},q]. Find the farthest point in Disk[] from {1,1}:
Find the farthest point from {1,2} in the standard unit simplex Simplex[2]:
Find the farthest point from {1,1,1} in the standard unit sphere Sphere[]:
Find the farthest point from {-1,1,1} in the standard unit simplex Simplex[3]:
The diameter of a region ℛ is given by the distance between the farthest points in ℛ, which can be computed through ArgMax[Norm[p-q],{q∈ℛ,p∈ℛ}]. Find the diameter of Circle[]:
Find the diameter of the standard unit simplex Simplex[2]:
Find the diameter of the standard unit cube Cuboid[]:
The farthest points p∈ and q∈ can be found through ArgMax[Norm[p-q],{p∈,q∈}]. Find the farthest points in Disk[{0,0}] and Rectangle[{3,3}]:
Find the farthest points in Line[{{0,0,0},{1,1,1}}] and Ball[{5,5,0},1]:
Geometric Centers (3)
If ℛ⊆n is a region that is full dimensional, then the Chebyshev center is the point p∈ℛ that maximizes -SignedRegionDistance[ℛ,p], i.e. the distance to the complement region. Find the Chebyshev center for Disk[]:
Find the Chebyshev center for Rectangle[]:
The analytic center of a region defined by inequalities ℛ=ImplicitRegion[f1[x]≥0∧⋯∧fm[x]≥0,x] is given by ArgMax[{Log[f1[x]⋯ fm[x]],x∈ℛ},x]. Find the analytic center for Triangle[{{0,0},{1,0},{0,1}}]:
From the conditions above you have an inequality representation:
Find the analytic center for Cylinder[]:
Properties & Relations (4)
Maximize gives both the value of the maximum and the maximizer point:
ArgMax gives an exact global maximizer point:
NArgMax attempts to find a global maximizer numerically, but may find a local maximizer:
FindArgMax finds a local maximizer point depending on the starting point:
The maximum point satisfies the constraints, unless messages say otherwise:
The given point maximizes the distance from the point {2,![]() }:
}:
When the maximum is not attained, ArgMax may give a point on the boundary:
Here the objective function tends to the maximum value when y tends to infinity:
ArgMax can solve linear optimization problems:
LinearOptimization can be used to solve the same problem by negating the objective:
Possible Issues (2)
The maximum value may not be attained:
The objective function may be unbounded:
There may be no points satisfying the constraints:
ArgMax requires that all functions present in the input be real valued:
Values for which the equation is satisfied but the square roots are not real are disallowed:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), ArgMax, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArgMax.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "ArgMax." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArgMax.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). ArgMax. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArgMax.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_argmax, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ArgMax}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArgMax.html}", note=[Accessed: 07-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_argmax, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ArgMax}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArgMax.html}, note=[Accessed: 07-March-2026]}