BandstopFilter
BandstopFilter[data,{ω1,ω2}]
applies a bandstop filter with cutoff frequencies ω1 and ω2 to an array of data.
BandstopFilter[data,{{ω,q}}]
uses center frequency ω and quality factor q.
BandstopFilter[data,spec,n]
uses a filter kernel of length n.
BandstopFilter[data,spec,n,wfun]
applies a smoothing window wfun to the filter kernel.
Details and Options


- Bandstop filtering is used in audio amplifiers, hearing aids and public address systems to attenuate mid-range frequencies in a signal while leaving the low and high frequencies unchanged.
- BandstopFilter convolves a digital signal with a finite impulse response (FIR) kernel created using the window method.
- Longer kernels result in a better frequency discrimination.
- The data can be any of the following:
-
list arbitrary-rank numerical array tseries temporal data such as TimeSeries and TemporalData image arbitrary Image or Image3D object audio an Audio or Sound object - The range of frequencies that are attenuated is dependent on the values of the cutoff frequencies ω1 and ω2, with ω2>ω1.
- When applied to images and multidimensional arrays, filtering is applied successively to each dimension starting at level 1. BandstopFilter[data,{{ω11,ω21},…}] uses the frequency {ω1i,ω2i} for the i
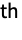 dimension.
dimension. - The frequency values ωi should be between 0 and
 .
. - BandstopFilter[data,{ω1,ω2}] uses a filter kernel length and smoothing window suitable for the cutoff frequencies {ω1,ω2} and the input data.
- Typical smoothing windows wfun include:
-
BlackmanWindow smoothing with a Blackman window DirichletWindow no smoothing HammingWindow smoothing with a Hamming window {v1,v2,…} use a window with values vi f create a window by sampling f between  and
and 
- The following options can be given:
-
Padding "Fixed" the padding value to use SampleRate Automatic sample rate assumed for the input - By default, SampleRate->1 is assumed for images as well as data. For audio signals and time series, the sample rate is either extracted or computed from the input data.
- With SampleRatesr, the cutoff frequency ωc should be between 0 and sr
 .
.

Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (12)
Data (7)
Filter a TimeSeries:
Bandstop filtering of a Sound object of a tri-tone signal:
Eliminate the middle tone using a bandstop filter with a Blackman window of length 101:
Bandstop filtering of a halftone image:
Parameters (5)
A numeric cutoff frequency is interpreted as a quantity in units of radians per second:
Filter a white noise signal using a bandstop filter with cutoff frequencies of ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Use center frequency of 8660 Hz and a ![]() factor of 1:
factor of 1:
Make the quality factor smaller:
Increase frequency discrimination by using a longer kernel:
Vary the amount of attenuation by using different window functions:
Vary the amount of attenuation by using the adjustable Kaiser window:
Options (3)
Applications (1)
On a modern 88-key piano, key 55 (note C5) has a fundamental frequency of approximately 523 Hz. Use BandstopFilter to effectively remove the first harmonic (1046 Hz) of this key while retaining the remaining frequencies in the following audio clip:
Use a narrow filter (Q=3) of length 101 centered on frequency 1046 Hz:
Properties & Relations (5)
Using cutoff frequencies of 0 and π returns a zero sequence:
Create a bandstop filter using LeastSquaresFilterKernel and a Hamming window:
Compare with the result of BandstopFilter:
Impulse response of a bandstop filter of length 21:
Magnitude spectrum of the filter:
Impulse response of a bandstop filter of length 21 without a smoothing window:
Magnitude spectrum of the filter:
The frequency discrimination of the bandstop filter improves as the length of the filter is increased:
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), BandstopFilter, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BandstopFilter.html (updated 2017).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "BandstopFilter." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2017. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BandstopFilter.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). BandstopFilter. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BandstopFilter.html