ChatSubmit[chat,prompt]
submits prompt to be appended with its follow-ups to the ChatObject chat asynchronously.


ChatSubmit
ChatSubmit[chat,prompt]
submits prompt to be appended with its follow-ups to the ChatObject chat asynchronously.
Details and Options







- ChatSubmit is used to continue the conversation in a ChatObject asynchronously.
- ChatSubmit requires external service authentication, billing and internet connectivity.
- Possible values for prompt include:
-
"text" static text LLMPrompt["name"] a repository prompt StringTemplate[…] templated text TemplateObject[…] template for creating a prompt Image[…] an image {prompt1,…} a list of prompts - Prompt created with TemplateObject can contain text and images. Not every LLM supports image input.
- ChatSubmit returns a TaskObject[…].
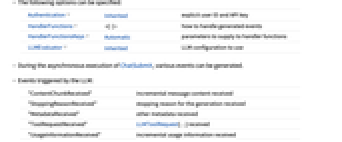
- The following options can be specified:
-
Authentication Inherited explicit user ID and API key HandlerFunctions how to handle generated events HandlerFunctionsKeys Automatic parameters to supply to handler functions LLMEvaluator Inherited LLM configuration to use - During the asynchronous execution of ChatSubmit, various events can be generated.
- Events triggered by the LLM:
-
"ContentChunkReceived" incremental message content received "StoppingReasonReceived" stopping reason for the generation received "MetadataReceived" other metadata received "ToolRequestReceived" LLMToolRequest[…] received "UsageInformationReceived" incremental usage information received - Events triggered by local processing:
-
"ChatObjectGenerated" the final ChatObject[…] generated "ToolResponseGenerated" an LLMToolResponse[…] generated - Events triggered by the task framework:
-
"FailureOccurred" failure generated during the computation "TaskFinished" task completely finished "TaskRemoved" task being removed "TaskStarted" task started "TaskStatusChanged" task status changed - HandlerFunctionsf uses f for all the events.
- With the specification HandlerFunctions-><|…,"eventi"->fi,…|>, fi[assoc] is evaluated whenever eventi is generated. The elements of assoc have keys specified by the setting for HandlerFunctionsKeys.
- Possible keys specified by HandlerFunctionsKeys include:
-
"ChatObject" modified ChatObject[…] "ContentChunk" a message part "EventName" the name of the event being handled "Failure" failure object generated if task failed "Model" model used to generate the message "Role" role of the message author "StoppingReason" why the generation has stopped "Task" the task object generated by ChatSubmit "TaskStatus" the status of the task "TaskUUID" unique task identifier "Timestamp" timestamp of the message "ToolRequest" received LLMToolRequest[…] "ToolResponse" last generated LLMToolResponse[…] "UsageIncrement" token usage update {key1,…} a list of keys All all the keys Automatic keys lexically present in HandlerFunctions - Values that have not yet been received are given as Missing["NotAvailable"].
- If LLMEvaluator is set to Inherited, the LLM configuration specified in chat is used.
- LLMEvaluator can be set to an LLMConfiguration object or an association with any of the following keys:
-
"MaxTokens" maximum amount of tokens to generate "Model" base model "PromptDelimiter" string to insert between prompts "Prompts" initial prompts or LLMPromptGenerator objects "StopTokens" tokens on which to stop generation "Temperature" sampling temperature "ToolMethod" method to use for tool calling "Tools" list of LLMTool objects to make available "TopProbabilities" sampling classes cutoff "TotalProbabilityCutoff" sampling probability cutoff (nucleus sampling) - Valid forms of "Model" include:
-
name named model {service,name} named model from service <|"Service"service,"Name"name|> fully specified model - Prompts specified in "Prompts" are prepended to the messages in chat with role set as "System".
- Multiple prompts are separated by the "PromptDelimiter" property.
- The generated text is sampled from a distribution. Details of the sampling can be specified using the following properties of the LLMEvaluator:
-
"Temperature"t Automatic sample using a positive temperature t "TopProbabilities"k Automatic sample only among the k highest-probability classes "TotalProbabilityCutoff"p Automatic sample among the most probable choices with an accumulated probability of at least p (nucleus sampling) - The Automatic value of these parameters uses the default for the specified "Model".
- Possible values for "ToolMethod" include:
-
"Service" rely on the tool mechanism of service "Textual" use prompt-based tool calling - Possible values for Authentication are:
-
Automatic choose the authentication scheme automatically Inherited inherit settings from chat Environment check for a key in the environment variables SystemCredential check for a key in the system keychain ServiceObject[…] inherit the authentication from a service object assoc provide explicit key and user ID - With AuthenticationAutomatic, the function checks the variable ToUpperCase[service]<>"_API_KEY" in Environment and SystemCredential; otherwise, it uses ServiceConnect[service].
- When using Authenticationassoc, assoc can contain the following keys:
-
"ID" user identity "APIKey" API key used to authenticate - ChatSubmit uses machine learning. Its methods, training sets and biases included therein may change and yield varied results in different versions of the Wolfram Language.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (2)
Options (14)
Authentication (4)
HandlerFunctions (2)
HandlerFunctionsKeys (3)
List explicitly the handler function keys to be passed to the handler functions:
Set HandlerFunctionsKeys values to be inferred lexically from the slots present in the handler functions (default):
Include all available handler function keys in the handler function argument:
LLMEvaluator (5)
Specify the service used to generate the answer:
Specify both the service and the model:
By default, the text generation continues until a termination token is generated:
Limit the amount of generated samples (tokens):
Specify that the sampling should be performed at zero temperature:
Specify a high temperature to get more variation in the generation:
Specify the maximum cumulative probability before cutting off the distribution:
Specify a prompt to be automatically added to the conversation:
See Also
ChatEvaluate ChatObject LLMSynthesizeSubmit LLMConfiguration LLMTool LLMPrompt LLMPromptGenerator
Service Connections: OpenAI Anthropic GoogleGemini AlephAlpha Cohere DeepSeek Groq MistralAI TogetherAI
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), ChatSubmit, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChatSubmit.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "ChatSubmit." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChatSubmit.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). ChatSubmit. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChatSubmit.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_chatsubmit, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ChatSubmit}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChatSubmit.html}", note=[Accessed: 07-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_chatsubmit, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ChatSubmit}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChatSubmit.html}, note=[Accessed: 07-March-2026]}