

Comap
Details and Options
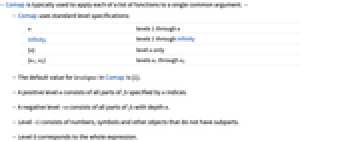
- Comap is typically used to apply each of a list of functions to a single common argument. »
- Comap uses standard level specifications:
-
n levels 1 through n Infinity levels 1 through Infinity {n} level n only {n1,n2} levels n1 through n2 - The default value for levelspec in Comap is {1}.
- A positive level n consists of all parts of fs specified by n indices.
- A negative level -n consists of all parts of fs with depth n.
- Level –1 consists of numbers, symbols and other objects that do not have subparts.
- Level 0 corresponds to the whole expression.
- With the option setting Heads->True, Comap includes heads of expressions and their parts. »
- Comap always effectively constructs a complete new expression and then evaluates it. »
- The head of fs in Comap[fs,x,…] need not be List.
- If fs is an Association object, Comap[fs,x] applies the values in the association to x. »
- Comap[fs][x] is equivalent to Comap[fs,x].
- Parallelize[Comap[fs,x]] computes Comap[fs,x] in parallel on all subkernels. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Wrap x with each element of a list:
Use the operator form of Comap:
Scope (6)
Comap can be used on expressions with any head:
Comap on the second level of a nested Association:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (9)
Comap wraps parts of an expression around another expression:
Map wraps an expression around parts of another expression:
Query[list] is equivalent to Comap[list]:
Query[assoc] is also equivalent to Comap[assoc]:
Through[p[f,g,…][x]] is equivalent to Comap[p[f,g,…],x]:
Compare this to the operator form of Comap:
Comap[p[f,g,…],x] can be used even when p[f,g,…][x] has a value:
When p[f,g,…][x] has a value, Through cannot be used:
Comap[{f1,f2,…},x] is equivalent to Map[f|->f[x],{f1,f2,…}] when the fi have no attributes:
Comap can apply parts inside held expressions to an expression without allowing evaluation to proceed:
Use ReleaseHold to allow evaluation to proceed:
If only some arguments are held, only those arguments will not evaluate further:
Use Unevaluated to apply a list of functions to an expression without evaluating it first:
The expression is evaluated first by default:
Use Unevaluated to comap an expression into the parts of an expression without evaluating it first:
The expression is evaluated first by default:
Comap can be parallelized automatically:
Possible Issues (1)
Comap by default starts at level 1, so does not apply the whole expression to the expression:
Tech Notes
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), Comap, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Comap.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "Comap." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Comap.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). Comap. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Comap.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_comap, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Comap}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Comap.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_comap, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Comap}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Comap.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}