

Encrypt
Details and Options



- Encrypt yields EncryptedObject[…], suitable for decryption with Decrypt.
- Encrypt[key,"string"] yields an EncryptedObject containing the encrypted version of the contents of the string as encoded in UTF-8.
- Encrypt[key,ByteArray[…]] yields an EncryptedObject containing the encrypted version of the raw bytes in the ByteArray object.
- For a general expression, Encrypt[key,expr] yields an EncryptedObject essentially containing an encrypted version of Compress[expr].
- The encryption method is based on the cipher and parameters of the key. See GenerateSymmetricKey and GenerateAsymmetricKeyPair for details.
- In a notebook interface, Encrypt[expr] generates a dialog box; in a textual interface it generates a textual prompt.
- Encrypt has the following option:
-
Method Automatic details of encryption method - With the setting Methodassoc, the association assoc gives details of the encryption method to use.
- The following elements can be given in the association assoc:
-
"Padding" Automatic padding mode "InitializationVector" Automatic initialization vector for block ciphers "BlockMode" "CBC" block chaining mode ("ECB","CBC", "OFB", "CFB", "CTR") - The "Padding" element in the association assoc specifies the padding method to pad incomplete input.
- Encryption with symmetric key supports the following padding methods: Automatic and None.
- Encryption with a public key and decryption with a private key support the following padding methods: "PKCS1", "OAEP", None.
- Encryption with a private key and decryption with a public key support the following padding methods: "PKCS1", None.
- The "PKCS1" padding method is used as a default for asymmetric encryption.
- All ciphers except RC4 and RSA can use the block modes "ECB", "CBC", "CFB", "OFB". "RC4" can only use None.
- Possible settings for "InitializationVector" include:
-
Automatic generate an appropriate initialization vector ByteArray[…] use an explicitly specified initialization vector - With "InitializationVector"->Automatic, Encrypt will generate a new initialization vector whenever it is run. Later, the vector can be obtained from the EncryptedObject that was produced.
- Supported ciphers, together with default initialization vector size, include:
-
"Blowfish" 64 bits "CAST5" 64 bits "DES" 64 bits "IDEA" 64 bits "AES128" 128 bits "AES192" 128 bits "AES256" 128 bits - For RSA cipher, the maximum length of data that can be encrypted is determined by the number of bytes
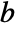 in the modulus, and the padding mode, according to:
in the modulus, and the padding mode, according to: -
"PKCS1" < 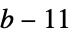
"OAEP" < 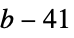
None 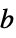
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (2)
Options (5)
Method (5)
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (2)
The returned encrypted object stores all aspects of the encrypted result:
Extract the bytes in the ciphertext:
Extract the bytes in the initialization vector used for encryption:
Some block modes are more secure than others:
There is a noticeable repeating pattern when encrypting uniform data using ECB:
Possible Issues (5)
Timing (1)
Incompatible Padding Modes (1)
History
Introduced in 2015 (10.1) | Updated in 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2021 (12.3) ▪ 2023 (13.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), Encrypt, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Encrypt.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "Encrypt." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Encrypt.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). Encrypt. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Encrypt.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_encrypt, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Encrypt}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Encrypt.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_encrypt, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Encrypt}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Encrypt.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}