HilbertFilter[data,ωc]
applies a Hilbert filter with a cutoff frequency ωc to an array of data.
HilbertFilter[data,ωc,n]
uses a filter kernel of length n.
HilbertFilter[data,ωc,n,wfun]
applies a smoothing window wfun to the filter kernel.


HilbertFilter
HilbertFilter[data,ωc]
applies a Hilbert filter with a cutoff frequency ωc to an array of data.
HilbertFilter[data,ωc,n]
uses a filter kernel of length n.
HilbertFilter[data,ωc,n,wfun]
applies a smoothing window wfun to the filter kernel.
Details and Options


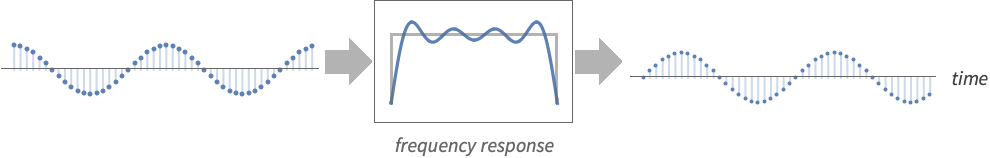
- HilbertFilter is a finite-impulse response (FIR) discrete-time filter typically used to apply a 90-degree phase shift to a signal.
- The data can be any of the following:
-
list arbitrary-rank numerical array tseries temporal data such as TimeSeries and TemporalData image arbitrary Image or Image3D object audio an Audio or Sound object video a Video object - Data smoothing with cutoff frequency ωc reduces the susceptibility of the evaluation to signal noise with the amount of smoothing dependent on the value of the cutoff frequency ωc.
- The cutoff frequency ωc should be between 0 and
 . Smaller values of ωc result in greater smoothing.
. Smaller values of ωc result in greater smoothing. - When applied to images and multidimensional arrays, filtering is applied successively to each dimension, starting at level 1. HilbertFilter[data,{ωc1,ωc2,…}] uses the frequency ωci for the

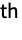 dimension.
dimension. - HilbertFilter[data,ωc] uses a filter kernel length and smoothing window suitable for the cutoff frequency ωc and the input data.
- Typical smoothing windows wfun include:
-
BlackmanWindow smoothing with a Blackman window DirichletWindow no smoothing HammingWindow smoothing with a Hamming window {v1,v2,…} use a window with values vi f create a window by sampling f between  and
and 
- The following options can be given:
-
Padding "Fixed" the padding value to use SampleRate Automatic sample rate assumed for the input - By default, SampleRate->1 is assumed for images as well as data. For a sampled sound object of sample rate of r, SampleRate->r is used.
- With SampleRate->r, the cutoff frequency ωc should be between 0 and r×
 .
.
Examples
open all close allScope (10)
Data (7)
Filter a TimeSeries:
Hilbert filtering of a square wave audio signal:
Options (5)
Padding (3)
Applications (1)
Properties & Relations (7)
Using a cutoff frequency of 0 returns a zero sequence:
Create a Hilbert filter using LeastSquaresFilterKernel and a Hamming window:
Compare with the result of HilbertFilter:
Impulse response of a Hilbert filter of length 21:
Impulse response of a Hilbert filter of length 21 without a smoothing window:
Magnitude spectrum of the filter:
Impulse response of even-length Hilbert filter:
The magnitude response of the Hilbert filter improves as the length of the filter is increased:
The magnitude response of a half-band Hilbert filter of length 21:
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2015 (10.2) ▪ 2016 (11.0) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), HilbertFilter, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HilbertFilter.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "HilbertFilter." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HilbertFilter.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). HilbertFilter. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HilbertFilter.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hilbertfilter, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HilbertFilter}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HilbertFilter.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hilbertfilter, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HilbertFilter}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HilbertFilter.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}