RadonTransform[expr,{x,y},{p,ϕ}]
gives the Radon transform of expr.


RadonTransform
RadonTransform[expr,{x,y},{p,ϕ}]
gives the Radon transform of expr.
Details and Options

- The Radon transform of a function
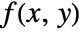 is defined to be
is defined to be 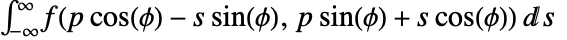 .
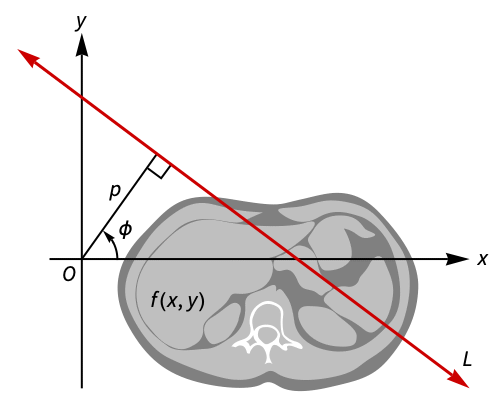
. - Geometrically, the Radon transform represents the integral of
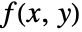 along a line
along a line 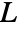 given in normal form by the equation
given in normal form by the equation 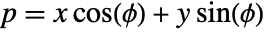 , with -∞<p<∞ and -π/2<ϕ<π/2.
, with -∞<p<∞ and -π/2<ϕ<π/2. - The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions on parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate results that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic what method to use - In TraditionalForm, RadonTransform is output using
![TemplateBox[{{f, (, {x, ,, y}, )}, x, y, p, phi}, RadonTransform] TemplateBox[{{f, (, {x, ,, y}, )}, x, y, p, phi}, RadonTransform]](Files/RadonTransform.en/7.png) .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (10)
Basic Uses (2)
Gaussian Functions (5)
Radon transform of a circular Gaussian function:
Plot the function along with the transform:
Radon transform of an elliptic Gaussian function:
Plot the function along with the transform:
Product of a polynomial with a Gaussian function:
Product of Hermite polynomials and a Gaussian function:
Products of trigonometric functions with Gaussian functions:
Piecewise and Generalized Functions (3)
Radon transform of the characteristic function for the unit disk:
Products of polynomials with the characteristic function for the unit disk:
Radon transforms for expressions involving DiracDelta:
Options (2)
Applications (2)
Compute the symbolic Radon transform for the characteristic function of a disk:
Obtain the same result using Radon:
Use the Radon transform to solve a Poisson equation:
Apply RadonTransform to the equation:
Solve the ordinary differential equation using DSolveValue:
Set the arbitrary constants in the solution to 0:
Obtain the solution for the original equation using InverseRadonTransform:
Properties & Relations (10)
RadonTransform computes the integral ![]() :
:
Obtain the same result using Integrate:
RadonTransform and InverseRadonTransform are mutual inverses:
RadonTransform is a linear operator:
The shifting property for RadonTransform:
The symmetry property for RadonTransform:
Express the Radon transform of ![]() in terms of a unit vector:
in terms of a unit vector:
The homogeneity property for RadonTransform:
Express the Radon transform of ![]() in terms of a unit vector:
in terms of a unit vector:
Verify the homogeneity property:
The scaling property for RadonTransform:
Express the Radon transform of ![]() in terms of a unit vector:
in terms of a unit vector:
Express the Radon transform of ![]() in terms of a unit vector:
in terms of a unit vector:
RadonTransform of derivatives:
RadonTransform of the Laplacian:
RadonTransform can be computed using Fourier transforms:
Compute the Fourier transform of f in polar coordinates:
Compute the inverse Fourier transform to obtain the Radon transform:
Obtain the same result directly using RadonTransform:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), RadonTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RadonTransform.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "RadonTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RadonTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). RadonTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RadonTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_radontransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{RadonTransform}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RadonTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_radontransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={RadonTransform}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RadonTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}