"NodeJS" (External Evaluation System)
Details
- Node.js Version 7.10.1 and higher is supported.
- Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine.
- To configure Node.js for use in the Wolfram Language, follow the instructions from the Configure NodeJS for ExternalEvaluate workflow.
ExternalEvaluate Usage
- ExternalEvaluate["NodeJS",code] executes the code string in a Node.js REPL and returns the results as a Wolfram Language expression.
- ExternalEvaluate["NodeJS""String",code] executes the code string in a Node.js REPL and does not interpret the results.
- Possible settings for "type" in ExternalEvaluate["NodeJS""type",code] include:
-
"Expression" attempt to convert to a Wolfram Language expression "String" give the raw string output by the external evaluator "ExternalObject" return the result as ExternalObject
Data Types
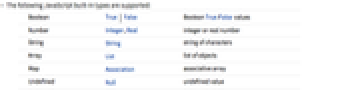
- The following JavaScript built-in types are supported:
-
Boolean True | False Boolean True/False values Number Integer,Real integer or real number String String string of characters Array List list of objects Map Association associative array Undefined Null undefined value - Any unsupported NodeJS type that is a function returns an ExternalFunction; any other unsupported NodeJS type returns an ExternalObject.
Supported External Operations
- ExternalOperation["Eval","code"] represents an external evaluation of "code".
- ExternalOperation["Eval","code",assoc] represents an external evaluation of "code" with parameters given by assoc.
- ExternalOperation["Call",func,arg1,arg2,…] calls the function func with the given arguments arg1, arg2, ….
- ExternalOperation["GetAttribute",obj,"attr"] gets the attribute "attr" of obj.
- ExternalOperation["SetAttribute",obj,"attr",val] sets the attribute "attr" of obj to the given value val.
- ExternalOperation["Cast",obj,"type"]casts obj to the given "type".
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Use the File wrapper to execute code contained in a file:
Deploy code using CloudDeploy and then run the code directly from a CloudObject:
Use a URL wrapper to directly run code hosted online:
Scope (27)
Evaluate a Boolean statement in NodeJS and return it:
Concatenate strings in NodeJS and return the result:
Create an ExternalFunction with NodeJS:
Session Options (8)
"ReturnType" (3)
For NodeJS, the default return type is "Expression":
Numbers, strings, lists and associations are automatically imported for the "Expression" return type:
The return type of "String" returns a string, using JSON:
Command Options (10)
"Command" (4)
When a string is provided, the command is directly executed:
The above is equivalent to writing the command using this form:
Use a File wrapper to run the code from a file:
The above is equivalent to writing the command using this form:
Use a URL wrapper to directly run code hosted online:
The above is equivalent to writing the command using this form:
Put code in a CloudObject:
Evaluate directly from the cloud:
The above is equivalent to writing the command using this form:
"ReturnType" (1)
"Arguments" (2)
Use "Arguments" to call the command with arguments:
For a single argument, you do not need to use a list:
If you need to pass a list as the first argument, wrap it with an extra list explicitly:
You can name a function in "Command" and directly call it with "Arguments":
The same result can be archived by using a Rule:
An alternative method is to define an ExternalFunction:
"TemplateArguments" (2)
When running a command, you can inline a TemplateExpression:
You can explicitly fill TemplateSlot using "TemplateArguments":
If you need to pass a list as the first argument, wrap it with an extra list explicitly:
You can name template slots and use an Association to pass named arguments to the template:
External Operations (8)
"Eval" (1)
Run an ExternalOperation that represents arbitrary code evaluation in Python:
"Call" (3)
Define an ExternalOperation that creates a function in NodeJS:
Call the function by running the ExternalOperation "Call":
Run the operation using ExternalEvaluate:
Any argument of the "Call" operation can be an ExternalOperation:
Arguments can also be passed directly in ExternalEvaluate by doing the following:
The result is equivalent to running the following NodeJS code:
Create an ExternalFunction for the NodeJS function max:
Call the function by running the operation "Call":
The same result can be achieved by doing the following:
Create an ExternalFunction for a NodeJS function:
Call the function by running the operation "Call":
The same result can be achieved by doing the following:
Or by using ExternalObject subvalues:
"GetAttribute" (2)
Start a NodeJS session to work with dates:
Return an ExternalObject for a "Math" object:
Extract a function by using "GetAttribute":
The result is equivalent to running the following NodeJS code:
Create an ExternalObject that represents the "Math" object:
Use ExternalOperation to get a function:
For most evaluators, "GetAttribute" is the default operation, and ExternalOperation can be omitted:
The function can be called directly by chaining a "Call" operation:
"SetAttribute" (1)
"Cast" (1)
Create an ExternalObject that represents an array:
Use "Expression" to return the object as a Wolfram Language expression:
The Cast operation can also run in ExternalObject subvalues:
The symbol Expression is a shortcut for the same:
Return the object as a string:
The symbol String is a shortcut for the same:
Return the object as an ExternalObject:
The symbol ExternalObject is a shortcut for the same:
The same can be achieved by using "ReturnType" in ExternalEvaluate:
Applications (2)
Define the Range function in NodeJS:
Related Guides
Related Workflows
- Configure NodeJS for ExternalEvaluate
History
Introduced in 2018 (11.3)