Table (.dat)
Background & Context
-
- Generic tabular data.
- Stores numerical and textual information, formatted as a table.
- Supports user-defined field and record separators, field delimiters, currency tokens, and number formats.
- Plain text format.
Import & Export
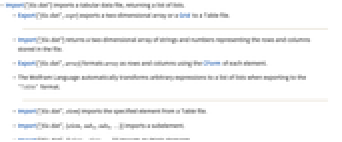
- Import["file.dat"] returns a list of lists containing strings and numbers representing the rows and columns stored in the file.
- Import["file.dat",elem] imports the specified element from a Table file.
- Import["file.dat",{elem,subelem1,…}] imports subelements subelemi, useful for partial data import.
- Import["file.dat",{{elem1,elem2,…}}] imports multiple elements.
- The import format can be specified with Import["file","Table"] or Import["file",{"Table",elem,…}].
- Export["file.dat",expr] creates a Table file from expr.
- Supported expressions expr include:
-
{v1,v2,…} a single column of data {{v11,v12,…},{v21,v22,…},…} lists of rows of data array an array such as SparseArray, QuantityArray, etc. tseries a TimeSeries, EventSeries or a TemporalData object Dataset[…] a dataset Tabular[…] a tabular object - See the following reference pages for full general information:
-
Import, Export import from or export to a file CloudImport, CloudExport import from or export to a cloud object ImportString, ExportString import from or export to a string ImportByteArray, ExportByteArray import from or export to a byte array
Import Elements

- General Import elements:
-
"Elements" list of elements and options available in this file "Summary" summary of the file "Rules" list of rules for all available elements - Data representation elements:
-
"Data" two-dimensional array, representing the rows and columns "Grid" table data as a Grid object "Tabular" table data as a Tabular object - Import and Export use the "Data" element by default.
Options

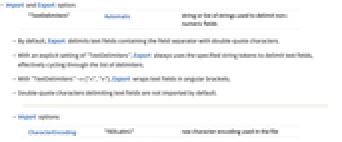

- Import and Export option:
-
"TextDelimiters" Automatic string or list of strings used to delimit non-numeric fields - By default, Export delimits text fields containing the field separator with double-quote characters.
- With an explicit setting of "TextDelimiters", Export always uses the specified string tokens to delimit text fields, effectively cycling through the list of delimiters.
- With "TextDelimiters"->{"<",">"}, Export wraps text fields in angular brackets.
- Double-quote characters delimiting text fields are not imported by default.
- Import options:
-
CharacterEncoding "ISOLatin1" raw character encoding used in the file "CurrencyTokens" {{"$", " 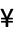 ", "
", "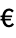 ", "
", "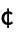 "}, {"c", "
"}, {"c", "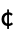 ", "p", "F"}}
", "p", "F"}}currency units to be skipped when importing numerical values "DateStringFormat" None date format, given as a DateString specification "FieldSeparators" {" ","∖t"} string tokens taken to separate columns "HeaderLines" 0 number of lines to skip at the beginning of the file "IgnoreEmptyLines" False whether to ignore empty lines "LineSeparators" {"∖r\n","∖n","\r"} string tokens taken to separate rows "NumberPoint" "." decimal point string "NumberSigns" {"-","+"} strings to use for signs of negative and positive numbers "Numeric" True whether to import data fields as numbers if possible "RepeatedSeparators" True whether to parse a sequence of field separators as a single separator - With CharacterEncoding -> Automatic, Import attempts to infer the character encoding of the file.
- Import converts table entries formatted as specified by the "DateStringFormat" option to a DateObject.
- Empty lines and lines containing only whitespace characters are converted to an empty list by default. With "IgnoreEmptyLines" set to True, Import will skip empty lines.
- With "Numeric"->False, numbers will be imported as strings in the form they appear in the file.
- With the default setting for "LineSeparators", Import automatically recognizes all common conventions for the encoding of line-separator characters.
- Export options:
-
Alignment None how data is aligned within table columns CharacterEncoding "UTF8" raw character encoding used in the file "FieldSeparators" "\t" string token used to separate columns "TableHeadings" None headings for table columns and rows - Possible settings for Alignment are None, Left, Center, and Right.
- "TableHeadings" can be set to the following values:
-
None no labels Automatic gives successive integer labels for columns and rows {"col1","col2",…} list of column labels {rhead,chead} specifies separate labels for the rows and columns - Export encodes line separator characters using the convention of the computer system on which the Wolfram Language is being run.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (8)
Import (3)
Show all elements available in the file:
Import a tabular data file that uses vertical bars as field separators:
Import converts dates to a Wolfram Language DateObject specification if the date format is specified:
Export (5)
Create a UTF-8 encoded text file that contains currency tokens:
When importing this file, currency tokens are automatically skipped:
The Wolfram Language automatically converts expressions to a list of lists when exporting to the Table format:
Table export uses the CForm for Real values:
Export an array of random numbers as a table:
Export a table formatted as a grid:
Use ExportString to create a formatted version of an array:
Import Elements (5)
Import Options (11)
CharacterEncoding (1)
The character encoding can be set to any value from $CharacterEncodings:
"CurrencyTokens" (1)
"DateStringFormat" (1)
By default, no date conversion is happening:
Convert dates to a DateObject using the date format specified:
"FieldSeparators" (1)
"HeaderLines" (1)
"NumberPoint" (1)
"NumberSigns" (1)
"Numeric" (1)
By default, Import interprets numbers:
Export Options (4)
Alignment (1)
CharacterEncoding (1)
The character encoding can be set to any value from $CharacterEncodings:
"FieldSeparators" (1)
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1999 (4.0) | Updated in 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2025 (14.2)