XML (.xml)
- Import fully supports the XML standard version 1.1.
- Special converters are used for the following XML-based formats: "ExpressionML", "JVX", "MathML", "ODS", "SXC", "XHTML", and "XHTMLMathML".
Background & Context

-
- MIME type: text/xml
- XML general-purpose markup language and structured document format.
- Primarily used for the exchange of data across different systems in computer networks.
- Uses a hierarchical model for the representation of structured data.
- Stores data in a tree-based structure consisting of markup tags, attributes, and character contents.
- Plain text file, normally encoded as UTF-8.
- XML is an acronym derived from Extensible Markup Language.
- Is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML).
- Developed since 1996 by the XML Working Group.
- Published in 2001 as W3C standard recommendation RFC 3076.
Import & Export

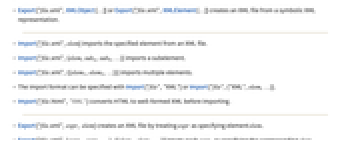
- Import["file.xml"] uses a specific converter for XML-based file formats if possible; otherwise, it imports the file as generic XML and returns an XMLObject expression.
- The XMLObject expression represents the entire XML document in symbolic form as a tree of XMLElement expressions.
- Import["file.xml","XML"] always imports as generic XML.
- Import["file.xml",elements] imports the specified element.
- Since both XML and the Wolfram Language represent data as a tree structure, there is a natural mapping from one to the other. The Wolfram Language stores XML data structures as nested XMLElement objects, and an entire XML document as XML data embedded in an XMLObject.
- Import by default returns numeric data stored in XML as strings.
- The import format can be specified with Import["file","XML"] or Import["file",{"XML",elem,…}].
- Import["file.html","XML"] converts HTML to well-formed XML before importing.
- Export["file.xml",expr] creates an XML file from expr.
- Supported expressions expr include:
-
XMLElement[…] exports a symbolic XML element XMLObject[…] exports a symbolic XML object - Expressions of types other than XMLObject or XMLElement are exported as ExpressionML.
- Export["file.xml",expr, elem] creates an XML file by treating expr as specifying element elem.
- Export["file.xml",{expr1,expr2,…},{{elem1,elem2,…}}] treats each expri as specifying the corresponding elemi.
- Export["file.xml",expr,opt1->val1,…] exports expr with the specified option elements taken to have the specified values.
- Export["file.xml",{elem1->expr1,elem2->expr2,…},"Rules"] uses rules to specify the elements to be exported.
- See the following reference pages for full general information:
-
Import, Export import from or export to a file CloudImport, CloudExport import from or export to a cloud object ImportString, ExportString import from or export to a string ImportByteArray, ExportByteArray import from or export to a byte array
Import Elements

- General Import elements:
-
"Elements" list of elements and options available in this file "Summary" summary of the file "Rules" list of rules for all available elements - Data representation elements:
-
"CDATA" CDATA sections as a list of strings "Comments" XML comments as a list of strings "EmbeddedDTD" embedded document type definition (DTD) "Plaintext" a plain text representation of the file "Tags" list of all tags occurring in the file "XMLObject" entire document as a symbolic XML expression "XMLElement" nested XMLElement objects - Import uses the "XMLObject" element by default.
Options

- Import options:
-
"AllowRemoteDTDAccess" True whether to attempt to retrieve an external DTD over a network "AllowUnrecognizedEntities" Automatic whether to allow parsing to work around unrecognized entities in the XML document "IncludeDefaultedAttributes" False whether to fill in default values for attributes "IncludeEmbeddedObjects" None embedded objects (of "Comments" and "ProcessingInstructions") to include "IncludeNamespaces" Automatic whether to return fully qualified tag and attribute names "NormalizeWhitespace" True whether to remove leading and trailing whitespace and reduce consecutive spaces to a single space in character data "PreserveCDATASections" False whether to preserve character data sections as special objects "ReadDTD" True whether to read an external DTD "ValidateAgainstDTD" Automatic whether to validate the document against the specified DTD - Export options:
-
"AttributeQuoting" "'" specifies the delimiter for attribute values "ElementFormatting" Automatic indentation of elements and line breaking of long strings in the exported document "Entities" None rules for replacing characters with named entities "NamespacePrefixes" {} namespace prefix designations, of the form "namespace"->"prefix"
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (1)
Show the Import elements available in this file:
Get the list of all XML tags that occur in this sample file:
Import Elements (7)
"XMLElement" (1)
Import nested XMLElement objects:
Import Options (18)
"AllowRemoteDTDAccess" (1)
By default, Import tries to retrieve an external DTD over a network:
Disable network access for an external DTD. This file does not have an external DTD, so the result is the same:
"AllowUnrecognizedEntities" (3)
"IncludeDefaultedAttributes" (2)
"IncludeEmbeddedObjects" (2)
"NormalizeWhitespace" (2)
"PreserveCDATASections" (2)
"ReadDTD" (2)
By default, Import reads external DTD file and uses it for validation:

"ValidateAgainstDTD" (2)
By default, Import reports validation errors when DTD file is present:

Export Options (1)
"AttributeQuoting" (1)
Compare Export to XML with different delimiters for attribute values:
