"AudioSTFT" (Net Encoder)
NetEncoder["AudioSTFT"]
represents an encoder that converts an audio file or object into its short-time Fourier transform.
NetEncoder[{"AudioSTFT","param"->val,…}]
represents an encoder with specific parameters for preprocessing.
Details

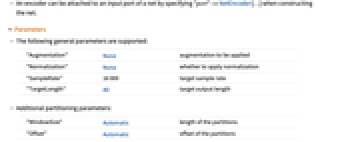


- The "AudioSTFT" encoder partitions the signal, multiplies each partition with a window function and computes the Fourier transform on each of them. The result of a Fourier transform is a complex number, and for each of them the encoder returns a list of the real and imaginary parts. The original signal can be reconstructed from the STFT as there is no loss of information.
- NetEncoder[…][input] applies the encoder to an input to produce a "Real32" output.
- NetEncoder[…][{input1,input2,…}] applies the encoder to a list of inputs to produce a list of outputs.
- When given a NumericArray as input, the output will be a NumericArray.
- The input to the encoder can be an Audio object or a File[…] expression.
- The output of the encoder is a rank-3 tensor of dimensions {n,ws,2}, where n is the number of partitions after the preprocessing is applied and ws is the length of the partitions used for the computation. The last dimension represents the real and imaginary parts of the result.
- An encoder can be attached to an input port of a net by specifying "port"->NetEncoder[…] when constructing the net.
- The following general parameters are supported:
-
"Augmentation" None augmentation to be applied "Normalization" None whether to apply normalization "SampleRate" 16000 target sample rate "TargetLength" All target output length - Additional partitioning parameters:
-
"WindowSize" Automatic length of the partitions "Offset" Automatic offset of the partitions "WindowFunction" Automatic window to be applied to the partitions - The following settings and suboptions can be specified for each encoder parameter.
- "Normalization" can take the following settings:
-
None no normalization "Max" absolute maximum value normalized to 1 {"Max",val} absolute maximum value normalized to val {"RMS",val} RMS of input audio signal normalized to val - "TargetLength" can take the following settings:
-
All same as input signal dur the duration dur specified as a time quantity n the first n partitions - If the specified "TargetLength" does not match the length of the input signal, padding or trimming are applied accordingly.
- "Augmentation" can be specified as a list of rules with the following keys:
-
"Convolution" None convolves an impulse response to the input "Noise" None adds noise to the input "TimeShift" None shifts the input by a specified amount "Volume" None multiplies the input with a constant - Any augmentation parameter that accepts a numeric value can also be specified as a list of two numbers or a univariate distribution. In the first case, the value will be randomized according to a uniform distribution between the given bounds. In the second, the user-provided distribution will be used.
- Possible values for "Convolution" include:
-
None no augmentation signal File or Audio object to be convolved with input {mix,signal} signal to be convolved with input and mix parameter - Possible values for "Noise" include:
-
None no augmentation amp white noise with amplitude amp noise File or Audio object containing the noise signal to be added {amp,noise} - noise signal and its with the specified amplitude
- Use "TimeShift"->t to shift the input by t seconds, padding or trimming if necessary. Use Scaled[s] to shift the input by s×dur seconds, where dur is the duration of the input signal. Use {t1,t2} or Scaled[{ts1,t2}] to randomize the shift between the specified times.
- Use "Volume"->val to specify a constant multiplier.
- With the parameter "WindowSize"->Automatic, a partition length of 25 milliseconds is used. Use "WindowSize"->dur to select a partition length of duration dur. Use "WindowSize"->n to select a partition length of n samples.
- With the parameter "Offset"->Automatic, a partition offset of 8.33 milliseconds is used. Use "Offset"->dur to select a partition offset of duration dur. Use "Offset"->n to select a partition offset of n samples.
- Parameter "WindowFunction" applies a window to each partition. Possible settings are:
-
None no windowing applied to the input audio Automatic 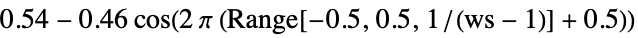
func the window is computed using the function func list the sampled window list is explicitly specified
Parameters
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (3)
NetEncoder["AudioSTFT"] can encode either File or Audio objects. Create an audio STFT encoder:
Apply the encoder to a File object:
Apply the encoder to an in-core Audio object:
Apply the encoder to an out-of-core Audio object:
Create a list of Audio objects:
NetEncoder["AudioSTFT"] maps across a batch of inputs:
Create an audio STFT NetEncoder:
Attach the encoder to the input of a net:
Apply the net to an Audio object:
Parameters (6)
"Normalization" (1)
Create an Audio object:
Use an encoder with "Normalization"->None to avoid any normalization:
Since the normalization is applied to the signal before the short-time Fourier transform is computed, there are no guarantees on the bounds of the result:
Use an encoder with "Normalization"->Automatic to normalize the maximum absolute value of the waveform samples to 1.:
"SampleRate" (2)
Create an Audio object:
Using an encoder with "SampleRate"8000 resamples the signal to 8000Hz before performing the short-time Fourier transform:
The "SampleRate" parameter affects the computation of the default window size:
An encoder with a lower sample rate than the original audio will result in a shorter window length:
An encoder with a higher sample rate than the original audio will result in a longer window length:
"TargetLength" (1)
"WindowSize" (1)
Create an Audio object:
The partition length is automatically computed to be 25ms:
Using an encoder with "WindowSize"600 returns the short-time Fourier transform using partitions of 600 samples:
"Offset" (1)
Create an Audio object:
The partition offset is automatically computed to be 1/3 of the partition length:
Using an encoder with "Offset"10 returns the short-time Fourier transform computed using partitions with an offset of 10 samples:
Properties & Relations (2)
Create an Audio object:
Create an audio STFT NetEncoder:
The length of the result can be computed as Ceiling[length/offset], where length is the length of the signal after resampling and offset is the "Offset" parameter of the encoder:
The equivalent computation for the "AudioSTFT" encoder is based on ShortTimeFourier:
See Also
NetEncoder Audio SpectrogramArray AudioResample ConformAudio NetChain NetGraph NetTrain
Net Encoders: Audio AudioSpectrogram AudioMelSpectrogram AudioMFCC