InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess[μ,d]
represents an inhomogeneous Poisson point process with density function ![]() in
in ![]() .
.


InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess
InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess[μ,d]
represents an inhomogeneous Poisson point process with density function ![]() in
in ![]() .
.
Details


- InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess is also known as a nonstationary Poisson point process or an independent scattering point process.
- Typical uses include modeling varying density that depends only on the location
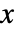 , such as varying growth conditions.
, such as varying growth conditions. - InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess generates points in a region according to the specified density function μ with no point interactions.
- With density function μ, the point count in an observation region
 is distributed as PoissonDistribution with mean
is distributed as PoissonDistribution with mean 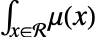 .
. - Density function μ can be given as:
-
func a function of vectors geofunc a function of geo locations PointDensityFunction density function from point collections - The number of points
 in disjoint regions
in disjoint regions 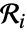 for a Poisson point process are independent
for a Poisson point process are independent 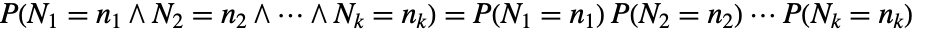 , where
, where 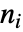 are non-negative integers.
are non-negative integers. - A point configuration
 with density function μ in an observation region
with density function μ in an observation region 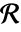 with volume
with volume  has density function
has density function  with respect to PoissonPointProcess[1,d].
with respect to PoissonPointProcess[1,d]. - The Papangelou conditional density
 for adding a point
for adding a point 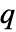 to a point configuration
to a point configuration  is
is 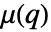 for an inhomogeneous Poisson point process with density function μ.
for an inhomogeneous Poisson point process with density function μ. - The density function
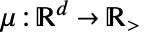 can be any positive integrable function in
can be any positive integrable function in 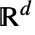 and d can be any positive integer.
and d can be any positive integer. - InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess can be used with such functions as RipleyK and RandomPointConfiguration.

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Sample from an InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess:
Sample from an InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess defined on the surface of the Earth:
Sample from a nonparametric point density:
Define a point process with the computed point density function and check if it is valid:
Scope (4)
Simulate several realizations:
Sample from any valid RegionQ, whose RegionEmbeddingDimension is equal to its RegionDimension:
Gaussian scattering is an example of isotropic inhomogeneous Poisson point process:
Simulate the process over a rectangle:
PointCountDistribution is invariant with respect to a rotation about the origin:
Point count distribution in the rotated region:
The distributions are the same as identified by equal means:
Options (1)
Method (1)
Sample from an InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess using different methods:
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (5)
Inhomogeneous Poisson point process with constant density autoevaluates to PoissonPointProcess:
The expected number of points in a region for InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess follows a PoissonDistribution:
Compute the point count distribution over a rectangle:
Compute void probabilities for an inhomogeneous Poisson point process:
Inhomogeneous Poisson point process is not stationary—the density depends on the location:
Point count distribution in a subregion:
Point count distribution in the translated subregion:
The region measures are the same:
The densities as expressed via PointCountDistribution differ:
InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess with a constant density function is PoissonPointProcess:
The point count distribution in a disk:
Point count distribution for a corresponding Poisson point process in the same region:
The point count distribution in a ball:
Point count distribution for a corresponding Poisson point process in the same region:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_inhomogeneouspoissonpointprocess, author="Wolfram Research", title="{InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_inhomogeneouspoissonpointprocess, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}