

LLMGraph
Details





- An LLMGraph can be used to efficiently schedule and combine multiple LLM generation steps for an optimal evaluation managing LLM submissions' concurrency.
- LLMGraph requires external service authentication, billing and internet connectivity.
- Possible values for the node function funi include:
-
LLMFunction[…] an LLMFunction for LLM submission Function[…] a pure function for Wolfram kernel submission <|key1val1, …|> an Association with detailed node specifications nodespec - Possible node specifications keys in nodespec are:
-
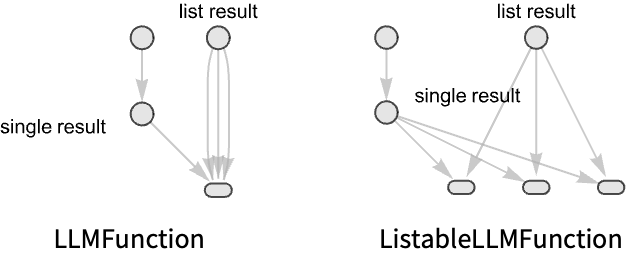
"EvaluationFunction" arbitrary Wolfram Language Function "LLMFunction" LLM evaluation via an LLMFunction "ListableLLMFunction" threaded LLM evaluation on list input values "Input" explicit list of nodes required as function arguments "TestFunction" whether the node should run "TestFunctionInput" explicit list of nodes required as test arguments - Each node must be defined with only one of "EvaluationFunction", "LLMFunction" or "ListableLLMFunction".
- The function specified in "ListableLLMFunction" threads over list input. Non-list input is copied. The output of the node is always a list.
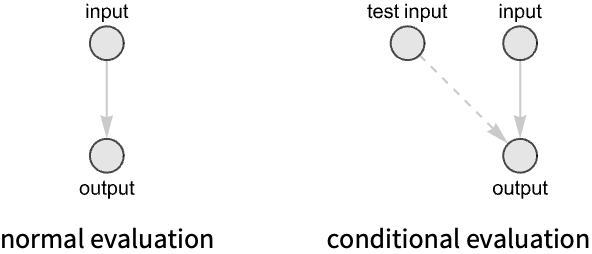
- The "TestFunction" specification makes a node evaluation conditional on other nodes' results.
- Possible "LLMFunction" specifications prompti include:
-
"text" static text {"text1",…} a list of strings LLMPrompt["name"] a repository prompt StringTemplate[…] templated text TemplateObject[…] template for creating a prompt LLMFunction[…] an LLMFunction object - If a prompti is explicitly dependent on the parameter TemplateSlot["namej"], the result from the nodej evaluation will be computed first, then used to build the new prompt.
- Cyclic prompt dependencies are not supported.
- The syntax LLMGraph[…][input] is used to run a graph evaluation.
- Any nodei result can be provided in input. Possible values for input are:
-
val value for the single graph input <|name1val1, …|> values for each of the nodes or inputs namei - Explicitly provided vali will be used in place of the node function result.
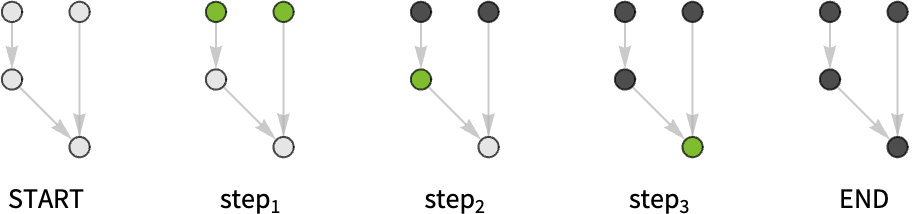
- The computation in a node is started as soon as all its dependencies are available.
- The syntax LLMGraph[…][input,prop] returns specific properties.
- Possible values for prop are:
-
Automatic results for the output nodes All results for all the nodes "LLMGraph" a new LLMGraph annotated with the result - LLMGraph supports the following options:
-
Authentication Automatic fallback authentication LLMEvaluator $LLMEvaluator fallback LLM configuration ProgressReporting $ProgressReporting whether to report the progress of the computation - To evaluate a node, its own LLMConfiguration nconf will be used. LLMEvaluatorgconf can be used to specify defaults for Missing[…] or Automatic values.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Define a basic graph taking an evaluation input:
Evaluate the graph, providing a topic:
Return all the nodes evaluation results:
Return an LLMGraph including computation results:
Scope (23)
Node Specification (9)
LLMFunction (4)
Specify an LLM node and its connections using an Association:
Specify the node using LLMFunction and relying on the automatic dependencies resolution:
Specify the node using a template:
Use any valid LLMFunction prompt specification:
ListableLLMFunction (1)
EvaluationFunction (2)
Evaluation (9)
Node Initialization (4)
Provide input nodes' values to start the graph evaluation:
If a single input is required, it is not necessary to use the Association:
If no input is required, the graph can be evaluated on an empty sequence:
Providing a result for the intermediate nodes will bypass the node function evaluation:
Evaluation Properties (5)
Evaluate output nodes' result of an LLMGraph; they are returned in an Association:
Evaluate a single output node LLMGraph result; it is returned unwrapped:
Request all nodes' results from an LLMGraph evaluation, including input and intermediate nodes:
Request an updated LLMGraph including the computation results:
Request a partially updated LLMGraph; when some dependencies are not satisfied by node initialization, only a subset of the nodes is assigned a result:
Options (6)
LLMEvaluator (2)
Define a graph default LLMConfiguration[…]:
Check the node LLMConfiguration[…]:
Fully specify the node LLMFunction to define a node-specific LLMConfiguration[…]:
The specific node LLMEvaluator is set:
Applications (3)
Style Enforcement (1)
LLM-Based Review (1)
Possible Issues (2)
Node function evaluations are run asynchronously. Side effects are directed to the Messages window:
A failed dependency will prevent the evaluation of a downstream node:
Individual node results can still be recovered from the evaluated LLMGraph:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), LLMGraph, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LLMGraph.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "LLMGraph." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LLMGraph.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). LLMGraph. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LLMGraph.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_llmgraph, author="Wolfram Research", title="{LLMGraph}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LLMGraph.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_llmgraph, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={LLMGraph}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LLMGraph.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}