PearsonChiSquareTest[data]
tests whether data is normally distributed using the Pearson ![]() test.
test.
PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist]
tests whether data is distributed according to dist using the Pearson ![]() test.
test.
PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist,"property"]
returns the value of "property".


PearsonChiSquareTest
PearsonChiSquareTest[data]
tests whether data is normally distributed using the Pearson ![]() test.
test.
PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist]
tests whether data is distributed according to dist using the Pearson ![]() test.
test.
PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist,"property"]
returns the value of "property".
Details and Options



- PearsonChiSquareTest performs the Pearson
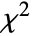 goodness-of-fit test with null hypothesis
goodness-of-fit test with null hypothesis 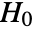 that data was drawn from a population with distribution dist, and alternative hypothesis
that data was drawn from a population with distribution dist, and alternative hypothesis 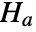 that it was not.
that it was not. - By default, a probability value or
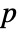 -value is returned.
-value is returned. - A small
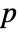 -value suggests that it is unlikely that the data came from dist.
-value suggests that it is unlikely that the data came from dist. - The dist can be any symbolic distribution with numeric and symbolic parameters or a dataset.
- The data can be univariate {x1,x2,…} or multivariate {{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…}.
- The Pearson
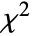 test effectively compares a histogram of data to a theoretical histogram based on dist. The bins are chosen to have equal probability in dist. »
test effectively compares a histogram of data to a theoretical histogram based on dist. The bins are chosen to have equal probability in dist. » - For univariate data, the test statistic is given by
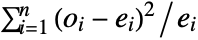 , where
, where 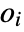 and
and 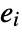 are the observed and expected counts for the
are the observed and expected counts for the 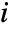
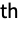 histogram bin, respectively.
histogram bin, respectively. - For multivariate tests, the sum of the univariate marginal
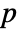 -values is used and is assumed to follow a UniformSumDistribution under
-values is used and is assumed to follow a UniformSumDistribution under 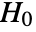 .
. - PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist,"HypothesisTestData"] returns a HypothesisTestData object htd that can be used to extract additional test results and properties using the form htd["property"].
- PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist,"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
- Properties related to the reporting of test results include:
-
"DegreesOfFreedom" the degrees of freedom used in a test "PValue" 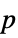 -value
-value"PValueTable" formatted version of "PValue" "ShortTestConclusion" a short description of the conclusion of a test "TestConclusion" a description of the conclusion of a test "TestData" test statistic and 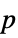 -value
-value"TestDataTable" formatted version of "TestData" "TestStatistic" test statistic "TestStatisticTable" formatted "TestStatistic" - The following properties are independent of which test is being performed.
- Properties related to the data distribution include:
-
"FittedDistribution" fitted distribution of data "FittedDistributionParameters" distribution parameters of data - The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic the method to use for computing 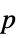 -values
-valuesSignificanceLevel 0.05 cutoff for diagnostics and reporting - For a test for goodness of fit, a cutoff
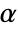 is chosen such that
is chosen such that 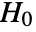 is rejected only if
is rejected only if 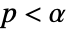 . The value of
. The value of 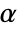 used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. By default,
used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. By default, 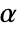 is set to 0.05.
is set to 0.05. - With the setting Method->"MonteCarlo",
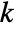 datasets of the same length as the input
datasets of the same length as the input 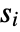 are generated under
are generated under 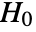 using the fitted distribution. The EmpiricalDistribution from PearsonChiSquareTest[si,dist,"TestStatistic"] is then used to estimate the
using the fitted distribution. The EmpiricalDistribution from PearsonChiSquareTest[si,dist,"TestStatistic"] is then used to estimate the 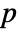 -value.
-value.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (9)
Testing (6)
Perform a Pearson ![]() test for normality:
test for normality:
The ![]() -value for the normal data is large compared to the
-value for the normal data is large compared to the ![]() -value for the non-normal data:
-value for the non-normal data:
Test the goodness of fit to a particular distribution:
Compare the distributions of two datasets:
The two datasets do not have the same distribution:
Test for multivariate normality:
Test for goodness of fit to any multivariate distribution:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for repeated property extraction:
Options (3)
Method (3)
Use Monte Carlo-based methods or a computation formula:
Set the number of samples to use for Monte Carlo-based methods:
The Monte Carlo estimate converges to the true ![]() -value with increasing samples:
-value with increasing samples:
Set the random seed used in Monte Carlo-based methods:
The seed affects the state of the generator and has some effect on the resulting ![]() -value:
-value:
Applications (2)
A power curve for the Pearson ![]() test:
test:
Visualize the approximate power curve:
Estimate the power of the Pearson ![]() test when the underlying distribution is UniformDistribution[{-4,4}], the test size is 0.05, and the sample size is 12:
test when the underlying distribution is UniformDistribution[{-4,4}], the test size is 0.05, and the sample size is 12:
The number of auto accidents was recorded for a city over the course of 30 days. The city council is planning on lowering speed limits in the city and wants a model of the accident rate as a baseline for later comparison:
Count data is often modeled well by PoissonDistribution:
Suppose the city collected data over another 30-day period after reducing the speed limit. Compare the distributions before and after the reduction:
Properties & Relations (10)
By default, univariate data is compared to NormalDistribution:
The parameters have been estimated from the data:
Multivariate data is compared to MultinormalDistribution by default:
The parameters of the test distribution are estimated from the data if not specified:
Specified parameters are not estimated:
Maximum likelihood estimates are used for unspecified parameters of the test distribution:
PearsonChiSquareTest effectively compares the observed and expected histograms:
The data is binned into approximately ![]() bins that are equiprobable under
bins that are equiprobable under ![]() :
:
Under ![]() , each bin will contain an equal number of points:
, each bin will contain an equal number of points:
Observed histograms for when ![]() is true and false, respectively:
is true and false, respectively:
The degrees of freedom are equal to the number of non-empty bins minus one:
One degree of freedom is removed for each parameter that is estimated from the data:
If the parameters are unknown, PearsonChiSquareTest corrects the degrees of freedom:
No correction is applied when the parameters are specified:
The fitted distribution is equivalent, but the degrees of freedom and ![]() -value are corrected:
-value are corrected:
The Pearson ![]() statistic asymptotically follows ChiSquareDistribution under
statistic asymptotically follows ChiSquareDistribution under ![]() :
:
Independent marginal densities are assumed in tests for multivariate goodness of fit:
The test statistic is identical when independence is assumed:
The Pearson ![]() test works with the values only when the input is a TimeSeries:
test works with the values only when the input is a TimeSeries:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), PearsonChiSquareTest, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PearsonChiSquareTest.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "PearsonChiSquareTest." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PearsonChiSquareTest.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). PearsonChiSquareTest. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PearsonChiSquareTest.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_pearsonchisquaretest, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PearsonChiSquareTest}", year="2010", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PearsonChiSquareTest.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_pearsonchisquaretest, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PearsonChiSquareTest}, year={2010}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PearsonChiSquareTest.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}