SnDispersion[list]
gives the ![]() statistic of the elements in list.
statistic of the elements in list.
SnDispersion[list,c]
gives the ![]() statistic with scaling factor c.
statistic with scaling factor c.


SnDispersion
SnDispersion[list]
gives the ![]() statistic of the elements in list.
statistic of the elements in list.
SnDispersion[list,c]
gives the ![]() statistic with scaling factor c.
statistic with scaling factor c.
Details and Options

- SnDispersion is a robust measure of dispersion.
- SnDispersion is a rank-based estimator with its statistic based on absolute pairwise differences. The statistic does not require location estimation.
- For the list {x1,x2,…,xn}, the value of
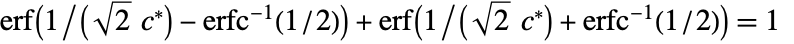 estimator is given by the median of {zi,1≤i≤n} multiplied by a scaling factor c, where zi is the median of {xi– xj,1≤j≤n} over j.
estimator is given by the median of {zi,1≤i≤n} multiplied by a scaling factor c, where zi is the median of {xi– xj,1≤j≤n} over j. - When c is not specified, a positive scaling factor c* that satisfies
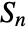 is applied to make
is applied to make  statistic a consistent estimator of the scale parameter for normally distributed data. Also, a finite sample correction is used by default to make the estimator unbiased for small samples.
statistic a consistent estimator of the scale parameter for normally distributed data. Also, a finite sample correction is used by default to make the estimator unbiased for small samples. - SnDispersion[{{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…}] gives {SnDispersion[{x1,x2,…}],SnDispersion[{y1,y2,…}],…}.
- SnDispersion supports a Method option. The following explicit settings can be specified:
-
"FiniteSample" uses finite sample correction (default) "None" no correction - The option Method is ignored if the scaling factor c is specified in the input.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
SnDispersion of a list:
SnDispersion of columns of a matrix:
SnDispersion of a list with scaling factor 1:
SnDispersion of a list of dates:
Scope (8)
Exact input yields exact output when the scaling factor is exact:
SnDispersion with different scaling parameters:
SnDispersion for a matrix gives a columnwise estimate:
SnDispersion of a large array:
Find the SnDispersion of a TimeSeries:
SnDispersion depends only on the values:
SnDispersion works with data involving quantities:
Compute SnDispersion of dates:
Compute SnDispersion of times:
Options (1)
Applications (6)
Obtain a robust estimate of dispersion when extreme values are present:
Sample standard deviation is heavily influenced by extreme values:
Identify periods of high volatility in stock data using a five-year moving ![]() dispersion:
dispersion:
Compute ![]() dispersion for slices of a collection of paths of a random process:
dispersion for slices of a collection of paths of a random process:
Plot ![]() dispersion over these paths:
dispersion over these paths:
Find the ![]() dispersion of the heights for the children in a class:
dispersion of the heights for the children in a class:
Plot the ![]() dispersion with respect to the median:
dispersion with respect to the median:
Consider data from standard normal distribution with outliers modeled by another normal distribution with large spread:
Test the data against standard normal distribution:
Remove outliers by selecting data points that are within three times the ![]() dispersion from the sample median:
dispersion from the sample median:
Test the new data against standard normal distribution:
Generate data from a Student t distribution:
Compute the dispersion of the data with three measures: standard deviation, square root of trimmed variance and ![]() dispersion:
dispersion:
Assess the accuracy of these three dispersion estimators via bootstrapping:
Properties & Relations (2)
SnDispersion is a rank-based dispersion estimator with its statistic based on pairwise absolute differences:
Compute the low median of high medians using RankedMin:
Compare with SnDispersion with scaling factor equal to 1:
QnDispersion, SnDispersion and StandardDeviation are estimators of the scale parameter of NormalDistribution:
Assess the accuracy of the estimators via bootstrapping:
Compute the relative efficiencies with respect to StandardDeviation using the estimated results:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), SnDispersion, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SnDispersion.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "SnDispersion." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SnDispersion.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). SnDispersion. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SnDispersion.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_sndispersion, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SnDispersion}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SnDispersion.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_sndispersion, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SnDispersion}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SnDispersion.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}