MedianDeviation[data]
gives the median absolute deviation from the median ![]() of the elements in data.
of the elements in data.


MedianDeviation
MedianDeviation[data]
gives the median absolute deviation from the median ![]() of the elements in data.
of the elements in data.
Details


- MedianDeviation is also known as MAD.
- MedianDeviation is a robust measure of dispersion, which means it is not very sensitive to outliers.
- For VectorQ data, {x1,x2,…,xn}, the median deviation
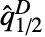 is given by the median of the vector {x1–
is given by the median of the vector {x1–  ,…,xn–
,…,xn– 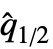 }, where
}, where 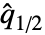 is the median of data.
is the median of data. - For MatrixQ data, the median deviation is computed for each column vector with MedianDeviation[{{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…}] equivalent to {MedianDeviation[{x1,x2,…}],MedianDeviation[{y1,y2,…}],…}. »
- For ArrayQ data, the median deviation is equivalent to ArrayReduce[MedianDeviation,data,1]. »
- MedianDeviation handles both numerical and symbolic data.
- The data can have the following additional forms and interpretations:
-
Association the values (the keys are ignored) » SparseArray as an array, equivalent to Normal[data] » QuantityArray quantities as an array » WeightedData based on the underlying EmpiricalDistribution » EventData based on the underlying SurvivalDistribution » TimeSeries, TemporalData, … vector or array of values (the time stamps ignored) » Image,Image3D RGB channel's values or grayscale intensity value » Audio amplitude values of all channels » DateObject, TimeObject list of dates or list of times »

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
MedianDeviation of a list:
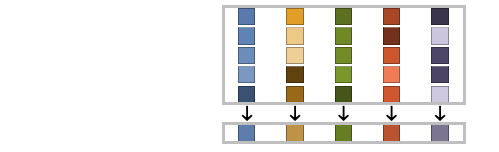
MedianDeviation of columns of a matrix:
MedianDeviation of a list of dates:
Scope (18)
Basic Uses (6)
Exact input yields exact output:
Approximate input yields approximate output:
Find the median deviation of WeightedData:
Find the median deviation of EventData:
Find the median deviation of TimeSeries:
Array Data (5)
MedianDeviation for a matrix works columnwise:
MedianDeviation for a tensor gives the columnwise median deviation at the first level:
When the input is an Association, median deviation works on its values:
SparseArray data can be used just like dense arrays:
Find the median deviation of a QuantityArray:
Image and Audio Data (2)
Channelwise median deviation value of an RGB image:
Median deviation value of a grayscale image:
On audio objects, MedianDeviation works channelwise:
Applications (4)
Obtain a robust estimate of dispersion when extreme values are present:
Measures based on the Mean are heavily influenced by extreme values:
Identify periods of high volatility in stock data using a five-year moving median deviation:
Compute median deviations for slices of a collection of paths of a random process:
Plot median deviations over these paths:
Find the median deviation of the heights for the children in a class:
Properties & Relations (2)
MedianDeviation is the Median of absolute deviations from the Median:
For large uniform datasets, MedianDeviation and MeanDeviation are nearly the same:
Possible Issues (1)
MedianDeviation requires real numeric values:
Neat Examples (1)
Ratio of MedianDeviation to MeanDeviation for increasing sample size:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), MedianDeviation, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MedianDeviation.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "MedianDeviation." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MedianDeviation.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). MedianDeviation. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MedianDeviation.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_mediandeviation, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MedianDeviation}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MedianDeviation.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_mediandeviation, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MedianDeviation}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MedianDeviation.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}