WinsorizedVariance[list,f]
gives the variance of the elements in list after replacing the fraction f of the smallest and largest elements by the remaining extreme values.
WinsorizedVariance[list,{f1,f2}]
gives the variance when the fraction f1 of the smallest elements and the fraction f2 of the largest elements are replaced by the remaining extreme values.
WinsorizedVariance[list]
gives the 5% winsorized variance WinsorizedVariance[list,0.05].
WinsorizedVariance[dist,…]
gives the winsorized variance of a univariate distribution dist.


WinsorizedVariance
WinsorizedVariance[list,f]
gives the variance of the elements in list after replacing the fraction f of the smallest and largest elements by the remaining extreme values.
WinsorizedVariance[list,{f1,f2}]
gives the variance when the fraction f1 of the smallest elements and the fraction f2 of the largest elements are replaced by the remaining extreme values.
WinsorizedVariance[list]
gives the 5% winsorized variance WinsorizedVariance[list,0.05].
WinsorizedVariance[dist,…]
gives the winsorized variance of a univariate distribution dist.
Details

- WinsorizedVariance gives a robust estimate of the variance, as more extreme values are replaced by less extreme ones.
- The winsorizing fraction is determined by the parameters f1 and f2, which indicate the fraction f1 of the smallest elements and the fraction f2 of the largest elements to be replaced by the remaining extreme values.
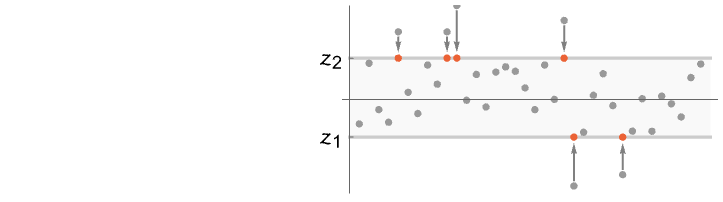
- WinsorizedVariance[list,{f1,f2}] gives the variance of Clip[list,{z1,z2}] where z1 equals RankedMin[list,1+
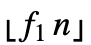 ], z2 equals RankedMax[list,1+
], z2 equals RankedMax[list,1+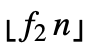 ], and n equals the length of list. »
], and n equals the length of list. » - WinsorizedVariance of a univariate WeightedData data gives the weighted variance of the censored data. »
- WinsorizedVariance[{{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…},f] gives {WinsorizedVariance[{x1,x2,…},f],WinsorizedVariance[{y1,y2,…},f],…}. »
- WinsorizedVariance[dist,{f1,f2}] gives Variance[CensoredDistribution[Quantile[dist,{f1,1-f2}],dist]] for a univariate distribution dist. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (11)
Data (10)
Exact input yields exact output:
Approximate input yields approximate output:
Winsorized variance of a matrix gives columnwise variances:
Winsorized variance of a large array:
SparseArray data can be used just like dense arrays:
WinsorizedVariance of a univariate WeightedData:
Compare with the variance of the unweighted data:
Winsorized variance of a TimeSeries:
The winsorized variance depends only on the values:
Winsorized variance works with data involving quantities:
Compute winsorized variance of dates:
Applications (2)
Obtain a robust estimate of location when outliers are present:
Extreme values have a large influence on the variance:
Find a winsorized variance for the heights of children in a class:
Plot the winsorized variance as a function of the fraction parameter:
Plot the square root of the winsorized variance with respect to the winsorized mean:
Properties & Relations (5)
A 0% WinsorizedVariance is equivalent to Variance:
WinsorizedVariance approaches 0 as f approaches 1/2:
WinsorizedVariance of a distribution is the variance of its CensoredDistribution:
Variance of the CensoredDistribution with appropriate bounds:
WinsorizedVariance of a sample gives an estimate of the variance of a censored distribution:
Variance of the CensoredDistribution with appropriate bounds:
TrimmedVariance drops the data beyond a certain quantile level, then computes the sample mean:
WinsorizedVariance clips the data beyond a certain quantile level, then computes the sample mean:
Plot the sorted data against the sample with elements removed and the clipped sample:
Possible Issues (1)
WinsorizedVariance requires numeric values:
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), WinsorizedVariance, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WinsorizedVariance.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "WinsorizedVariance." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WinsorizedVariance.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). WinsorizedVariance. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WinsorizedVariance.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_winsorizedvariance, author="Wolfram Research", title="{WinsorizedVariance}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WinsorizedVariance.html}", note=[Accessed: 14-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_winsorizedvariance, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={WinsorizedVariance}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WinsorizedVariance.html}, note=[Accessed: 14-March-2026]}