BilateralZTransform[expr,n,z]
gives the bilateral Z transform of expr.
BilateralZTransform[expr,{n1,…,nk},{z1,…,zk}]
gives the multidimensional bilateral Z transform of expr.


BilateralZTransform
BilateralZTransform[expr,n,z]
gives the bilateral Z transform of expr.
BilateralZTransform[expr,{n1,…,nk},{z1,…,zk}]
gives the multidimensional bilateral Z transform of expr.
Details and Options

- The bilateral Z transform is the discrete analog of the bilateral Laplace transform and plays an important role in digital signal processing and other fields.
- The bilateral Z transform for a discrete function
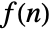 is given by
is given by 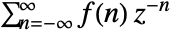 .
. - The multidimensional bilateral Z transform is given by
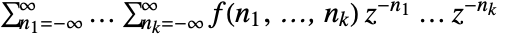 .
. - The sum is computed using numerical methods if the third argument, z, is given a numerical value.
- The bilateral Z transform of
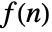 exists only for complex values of
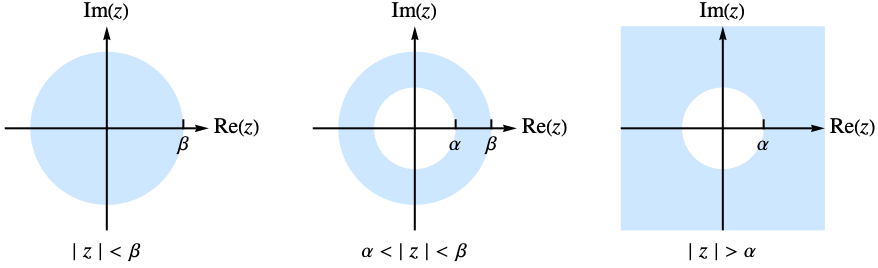
exists only for complex values of 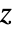 in an annulus given by
in an annulus given by ![alpha<TemplateBox[{z}, Abs]<beta alpha<TemplateBox[{z}, Abs]<beta](Files/BilateralZTransform.en/6.png) . In some cases, the annulus of definition may extend to the exterior or the interior of a disk.
. In some cases, the annulus of definition may extend to the exterior or the interior of a disk. - The following options can be given:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic digits of absolute accuracy sought Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions True whether to generate answers that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic method to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to optimize PrecisionGoal Automatic digits of precision sought WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (8)
Bilateral Z transform of the UnitStep function:
Combination of power functions:
Discrete-time, finite support function:
Calculate the bilateral Z transform at a single point:
Alternatively, calculate the transform symbolically:
Then evaluate it for a specific value of ![]() :
:
For some functions, the bilateral Z transform can be evaluated only numerically:
Options (3)
Assumptions (1)
Specify the range for a parameter using Assumptions:
GenerateConditions (1)
Set GenerateConditions to False to obtain a result without conditions:
WorkingPrecision (1)
Use WorkingPrecision to obtain a result with arbitrary precision:
Applications (2)
Define finite duration signals:
Plot the signals in the time domain:
To find the convolution, first calculate the product of the transforms:
Then, perform inversion back to the time domain:
Plot the convolution in the time domain:
Alternatively, find the convolution using DiscreteConvolve:
Define infinite duration signals:
Plot the signals in the time domain:
To find the convolution, first calculate product of the transforms:
Perform the inversion back to the time domain:
Plot the convolution in the time domain:
Alternatively, find the convolution using DiscreteConvolve:
Properties & Relations (7)
BilateralZTransform and InverseBilateralZTransform are mutual inverses:
BilateralZTransform is closely related to FourierSequenceTransform:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), BilateralZTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BilateralZTransform.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "BilateralZTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BilateralZTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). BilateralZTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BilateralZTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_bilateralztransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BilateralZTransform}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BilateralZTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_bilateralztransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BilateralZTransform}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BilateralZTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}