

ImageCrop
Details and Options


- Image cropping, also known as image trimming, is the process of removing border pixels from an image and can be used for removing uninteresting regions or extracting regions of interest.
- ImageCrop[image] effectively removes borders from image whose pixel value distribution is almost uniform.
- ImageCrop[image,{width,height}] by default removes pixels symmetrically from image, or if width or height is larger than for image, it adds pixels symmetrically.
- The image size specification size in ImageCrop[image,size] can have the following forms:
-
width particular width; height based on aspect ratio {width,height} particular width and height {width,depth,height} particular width, depth and height in 3D - Specifications for either of the dimensions can be any of the following:
-
d d pixels UpTo[d] maximum d pixels {dmin,dmax} pixel ranges Automatic determine value from aspect ratio Full do no cropping in this dimension - The cropping specification spec in ImageCrop[image,size,spec] can have the following forms:
-
side crop on the specified side; center otherwise {side1,side2} crop on the specified sides {ax,ay} assign a fraction of cropping to each side - Sides can be specified as Left, Right, Bottom or Top. Center indicates symmetrical cropping.
- Cropping fractions are between
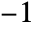 and
and 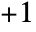 . In the horizontal case,
. In the horizontal case, 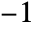 is equivalent to Left,
is equivalent to Left, 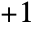 to Right and
to Right and 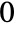 to Center. In the vertical case,
to Center. In the vertical case, 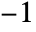 is equivalent to Bottom, and
is equivalent to Bottom, and 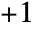 to Top.
to Top. - ImageCrop[image,size] is equivalent to ImageCrop[image,size,Center].
- To obtain an image with an aspect ratio r, use ImageCrop[image,width{1,r}].
- If the final image specified by ImageCrop[image,…] extends beyond image, then pixels are added according to the setting for Padding.

Examples
open all close allScope (7)
Size Specification (2)
Crop an image to a width of 100 pixels, preserving the aspect ratio:
Crop to a 100×100 pixel square:
Do not crop the height of the image:
Crop to a height of 100 pixels, preserving the aspect ratio:
Make the largest dimension not greater than 100 pixels:
Pad the image by using values greater than the image dimensions:
Side Specification (2)
Options (2)
Padding (2)
By default, black padding is used:
Pad the image with a specified color:
Specify a different padding scheme:
Use Padding->None to avoid padding:
The result may be smaller than the given size:
With Padding->Automatic, a color based on the boundary pixel values is chosen:
If the boundary pixels do not have consistent colors, black is used:
Properties & Relations (3)
Possible Issues (2)
Cropping happens if a similar border is present on at least two sides:
If a border is present only on one side, it is not cropped:
Detect the border using BorderDimensions and crop it using ImagePad:
See Also
ImageTrim ImagePad ImageTake BorderDimensions ImagePartition ImageSize ImageAugmentationLayer
Function Repository: ImageSaliencyCrop ImageRegionCrop ArrayCropPad
Tech Notes
Related Workflows
- Crop 2D Images ▪
- Crop 3D Images
History
Introduced in 2008 (7.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2015 (10.3) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), ImageCrop, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageCrop.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "ImageCrop." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageCrop.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). ImageCrop. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageCrop.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_imagecrop, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ImageCrop}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageCrop.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_imagecrop, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ImageCrop}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageCrop.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}