AstroGraphics[primitives,options]
represents a two-dimensional view of space and the celestial sphere.




AstroGraphics
AstroGraphics[primitives,options]
represents a two-dimensional view of space and the celestial sphere.
Details and Options
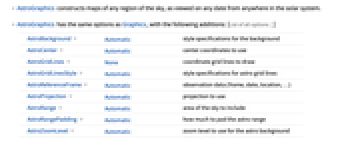
- AstroGraphics constructs maps of any region of the sky, as viewed on any date from anywhere in the solar system.
- AstroGraphics has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions: [List of all options]
-
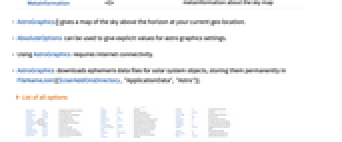
AstroBackground Automatic style specifications for the background AstroCenter Automatic center coordinates to use AstroGridLines None coordinate grid lines to draw AstroGridLinesStyle Automatic style specifications for astro grid lines AstroReferenceFrame Automatic observation data (frame, date, location, …) AstroProjection Automatic projection to use AstroRange Automatic area of the sky to include AstroRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the astro range AstroZoomLevel Automatic zoom level to use for the astro background MetaInformation <||> metainformation about the sky map PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize - AstroGraphics[] gives a map of the sky above the horizon at your current geo location.
- AbsoluteOptions can be used to give explicit values for astro graphics settings.
- Using AstroGraphics requires internet connectivity.
- AstroGraphics downloads ephemeris data files for solar system objects, storing them permanently in FileNameJoin[{$UserAddOnsDirectory,"ApplicationData","Astro"}].
-
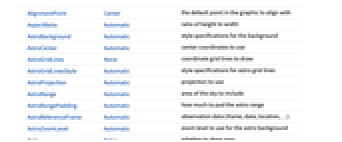
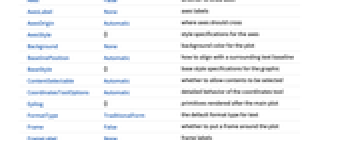
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width AstroBackground Automatic style specifications for the background AstroCenter Automatic center coordinates to use AstroGridLines None coordinate grid lines to draw AstroGridLinesStyle Automatic style specifications for astro grid lines AstroProjection Automatic projection to use AstroRange Automatic area of the sky to include AstroRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the astro range AstroReferenceFrame Automatic observation data (frame, date, location, …) AstroZoomLevel Automatic zoom level to use for the astro background Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MetaInformation <||> metainformation about the sky map Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
List of all options
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Show a map of the current sky above you, showing the equatorial, ecliptic, galactic and horizon planes:
Show the sky above you on a given date, adding a background image:
Show an area of the sky around the star Betelgeuse:
Add constellation illustrations and remove the equatorial, ecliptic and galactic planes:
Visualize the neighborhood of the galactic center:
Compute weekly positions of Mars from January 2022 to July 2023:
Options (16)
AstroBackground (3)
AstroGraphics uses the "BlackSky" style by default:
Use the "WhiteSky" style, with white background and dark colors for the stars:
AstroGridLines (2)
AstroRange (1)
AstroRangePadding (1)
AstroReferenceFrame (5)
By default, AstroGraphics uses the local horizon frame and the "Stereographic" projection:
Show the full sky, using the equatorial frame, in the "Equirectangular" projection:
Show the full sky, using the ecliptic frame, in the "Equirectangular" projection:
Show the full sky, using the galactic frame, with the result using the "Mollweide" projection:
Compute the position of the North Celestial Pole every 1000 years for the past 14000 years:
Applications (6)
Construct the analemma of the Sun, formed by its positions every day at a fixed time for a year:
Draw weekly positions, here shown over the sky of a date close to the vernal equinox:
Show the same analemma over the sky of a date close to the summer solstice:
Plot the positions of Venus at noon, every day over a period of 8 years:
Show the southern sky at 2pm at your location:
Observe the transit of Venus in front of Jupiter, November 22, 2065, better viewed near the South Pole:
| |
Visualize an annular solar eclipse:
Visualize the famous eclipse used by Eddington to confirm Einstein's prediction of light deflection:
Possible Issues (1)
Compute the position of Mars on this date:
By default, the background in AstroGraphics shows the current region of the sky corresponding to the computed coordinates of Mars, which is not the region of the sky where Mars was on the observation date:
Specify the date of observation to show the correct region of the sky, near the ecliptic, where Mars was on that date, with the automatic background label for Mars now appearing:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2022), AstroGraphics, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AstroGraphics.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2022. "AstroGraphics." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AstroGraphics.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2022). AstroGraphics. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AstroGraphics.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_astrographics, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AstroGraphics}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AstroGraphics.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_astrographics, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AstroGraphics}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AstroGraphics.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}