DominantColors[image]
returns dominant colors in image.
DominantColors[image,n]
returns at most n dominant colors in image.
DominantColors[image,n,prop]
returns the specified property prop for the regions that belong to the same dominant color.
DominantColors[image,n,prop,format]
returns the output in the specified format.
DominantColors[{image1,image2,…},…]
returns dominant colors in each imagei.


DominantColors
DominantColors[image]
returns dominant colors in image.
DominantColors[image,n]
returns at most n dominant colors in image.
DominantColors[image,n,prop]
returns the specified property prop for the regions that belong to the same dominant color.
DominantColors[image,n,prop,format]
returns the output in the specified format.
DominantColors[{image1,image2,…},…]
returns dominant colors in each imagei.
Details and Options


- DominantColors[image] returns a list of colors that represent clusters of colors that appear in the image. The colors are represented by GrayLevel or RGBColor.
- DominantColors works with arbitrary 2D and 3D images.
- The returned colors are ordered based on the size of the clusters they represent.
- DominantColors uses the LABColor to find color clusters.
- The following properties can be used to return dominant colors in different forms:
-
"Color" color for each cluster given in RGB or grayscale (default) "HexRGBColor" RGB color in the hexadecimal form "LABColor" CIELAB color "NearestHTMLColor" name of the nearest HTML color - Other supported properties include:
-
"Count" total number of pixels covered by each cluster "Coverage" fraction of the whole image covered by each cluster "CoverageImage" image representing the region covered by each cluster "MaskCoverage" fraction of the specified mask covered by each cluster - DominantColors[image,n,{"prop1","prop2",…}] computes multiple properties.
- DominantColors[image,n,"Properties"] returns a list of supported properties.
- The format argument specifies the output format. Possible settings are:
-
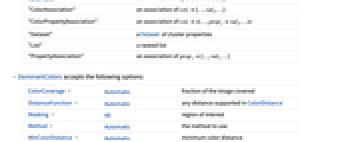
Automatic determine the output automatically "ColorAssociation" an association of coli{…,valj,…} "ColorPropertyAssociation" an association of coli<|…,propjvalj,…|> "Dataset" a Dataset of cluster properties "List" a nested list "PropertyAssociation" an association of propj{…,vali,…} - DominantColors accepts the following options:
-
ColorCoverage Automatic fraction of the image covered DistanceFunction Automatic any distance supported in ColorDistance Masking All region of interest Method Automatic the method to use MinColorDistance Automatic minimum color distance - With MinColorDistance->d, clusters represented by colors c1 and c2 are merged if ColorDistance[c1,c2]<d. The color with the larger coverage is assigned to the new cluster.
- With ColorCoverage->f, colors that cover less than a fraction f of the image are returned. With ColorCoverage->{fmin,fmax} a range of coverage fractions can be specified.
- With Masking->roi, "CoverageImage" and "MaskCoverage" return properties with respect to the specified region of interest roi. »
- Possible settings for Method include:
-
"KMeans" 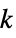 -means clustering algorithm
-means clustering algorithm"KMedoids" partitioning around medoids "MedianCut" recursively split the color space based on median pixel values "MinVariance" recursively split the color space so that the sum of variances in new subregions is minimal (Wu's algorithm) "Octree" create an octree from all image pixels and merge leaves until the most representative remain

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (12)
Basic Uses (4)
Options (8)
ColorCoverage (1)
By default, an automatic threshold is used for ColorCoverage:
Return all colors regardless of their coverage:
If no color covers the minimum coverage specified, an empty list is returned:
DistanceFunction (1)
Masking (2)
By default, dominant colors in the whole image are returned:
This is equivalent to the setting Masking->All:
Compute the dominant colors of the image foreground:
With Masking->All, "Coverage" and "MaskCoverage" are the same:
With a given mask, "MaskCoverage" returns the fraction of mask covered by each cluster:
Method (2)
By default, DominantColors automatically picks the most suitable method to generate color clusters:
Use the Method option to choose a specific method:
MinColorDistance (2)
By default, the minimum color distance is automatically chosen:
With MinColorDistance->d, clusters with color representatives closer than d are merged:
Use MinColorDistance->0 to avoid any color merging:
Avoid color merging by computing all dominant colors using MinColorDistance->0:
Applications (4)
Properties & Relations (4)
Dominant colors are sorted based on their area coverage:
The alpha channel is taken into account in computing dominant colors:
Blend the partially transparent image with the background to get a result similar to the visual appearance of the image:
ColorQuantize represents the image with the existing color tones in an image:
Colors generated by DominantColors:
Replace pixels by the closest common color in the RGB color space:
Perform the color replacement in the CIELAB color space:
List of supported properties that can be computed for any dominant color:
Neat Examples (1)
Use ArrayPlot to show the colors and their relative frequency in one plot:
See Also
FindMatchingColor ColorDetect ColorQuantize ColorReplace ColorDistance ClusteringComponents FindClusters
Function Repository: ImageColorFunction VideoColorMap
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2016 (10.4) ▪ 2016 (11.0) ▪ 2019 (12.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), DominantColors, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DominantColors.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "DominantColors." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DominantColors.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). DominantColors. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DominantColors.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_dominantcolors, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DominantColors}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DominantColors.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_dominantcolors, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DominantColors}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DominantColors.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}