returns the date of the next new moon.
MoonPhaseDate[phase]
returns the date of the next instance of the given phase of the Moon.
MoonPhaseDate[date,phase]
returns the date for the first instance of the given phase after date.




MoonPhaseDate
returns the date of the next new moon.
MoonPhaseDate[phase]
returns the date of the next instance of the given phase of the Moon.
MoonPhaseDate[date,phase]
returns the date for the first instance of the given phase after date.
Details and Options


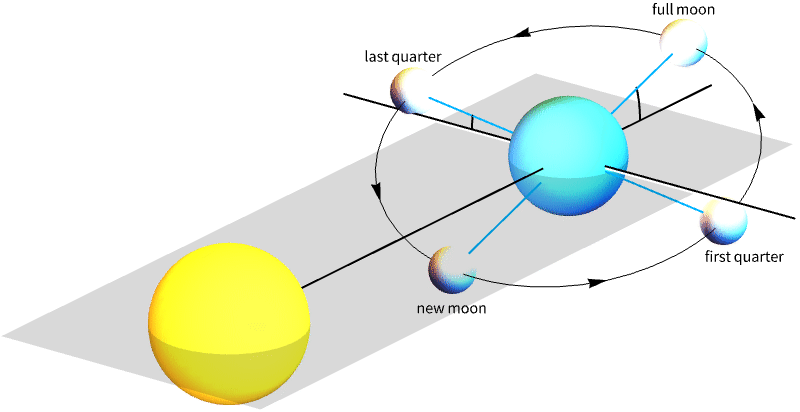
- The phase of the Moon describes the angle between the Moon and Sun, which determines the apparent shape of the Moon, as observed from the Earth.
- MoonPhaseDate reports dates of new moons, full moons or any other phase of the Moon.
- In MoonPhaseDate[phase], the phase can be given as a named case, such as "NewMoon" or "FirstQuarter", an entity such as Entity["MoonPhase","New"], or as a continuous real number with value 0 for a new moon, 0.25 for the first quarter, 0.5 for a full moon, 0.75 for the last quarter and 1 for the following new moon.
- Special named cases of full moons include:
-
"SeasonalBlueMoon" third full moon in a season with four full moons "MonthlyBlueMoon" second full moon in a month with two full moons "HarvestMoon" full moon nearest to the September equinox "HuntersMoon" full moon following the harvest moon - In MoonPhaseDate[date,phase], date can be any DateObject expression.
- Options of MoonPhaseDate include:
-
CalendarType Automatic calendar used to return dates DateFormat Automatic format used to display output dates DateGranularity Automatic calendar granularity of output dates Method "EclipticLongitude" method to define moon phases TimeDirection 1 whether to return the next or last date of a given phase TimeSystem Automatic time system of output dates TimeZone $TimeZone time zone of output dates - Possible settings for the Method option include:
-
"Illumination" phase defined by fraction of illumination of the Moon "EclipticLongitude" phase defined by Moon‐Sun ecliptic longitude difference
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (5)
Specify the same phase of the Moon in different ways:
Find the next seasonal blue moon:
Such a full moon will be the third of four full moons in a season:
Find the next monthly blue moon:
Such a full moon will be the second in the same month, as defined by your local time zone:
The full moon following about one month later is called the hunter's moon:
Options (7)
CalendarType (1)
MoonPhaseDate returns dates in the Gregorian calendar by default:
DateFormat (1)
MoonPhaseDate returns dates in a long format by default:
DateGranularity (1)
MoonPhaseDate returns dates with granularity "Instant" by default:
Method (1)
MoonPhaseDate uses differences of ecliptic longitudes between the Sun and the Moon by default:
Use a value of illumination to define the instant of a given moon phase:
TimeDirection (1)
MoonPhaseDate finds the next new moon by default:
TimeSystem (1)
MoonPhaseDate returns dates in universal time by default:
TimeZone (1)
MoonPhaseDate returns dates in your local time zone by default:
Properties & Relations (8)
At every new moon, the Sun and the Moon have the same ecliptic longitude:
There will be a solar eclipse if the difference in ecliptic latitude is small enough:
MoonPhaseDate gives the date of a given phase of the Moon:
MoonPhase gives illumination fractions and names:
Entity phases can also be used in MoonPhaseDate:
Use the "Illumination" method to find when 50% of the surface of the Moon appears illuminated:
NewMoon is the particular case of MoonPhaseDate for new moons:
FullMoon is the particular case of MoonPhaseDate for full moons:
MoonPhaseDate[date,"phase"] is equivalent to FindAstroEvent[{"MoonPhase","phase"},date]:
Use a numeric specification of phase where a lunation cycle between new moons goes from 0 to 1:
MoonPhaseDate extrapolates the lunation counter, such that this is the following first quarter:
FindAstroEvent interprets phase numbers modulo 1, such that this is the same first quarter:
MoonPhaseDate defines Moon phases as observed from Earth's center:
This is also the default in FindAstroEvent:
FindAstroEvent will take parallax effects into account if an observer location is specified:
New moons are conjunctions of the Moon with the Sun:
Full moons are oppositions of the Moon with respect to the Sun:
First quarters are eastern quadratures of the Moon with respect to the Sun:
Last quarters are western quadratures of the Moon with respect to the Sun:
Find the date of a random Moon phase value p:
This date can also be obtained using FromLunationNumber, using p as the decimal part of the current integer lunation number:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), MoonPhaseDate, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoonPhaseDate.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "MoonPhaseDate." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoonPhaseDate.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). MoonPhaseDate. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoonPhaseDate.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_moonphasedate, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MoonPhaseDate}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoonPhaseDate.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_moonphasedate, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MoonPhaseDate}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoonPhaseDate.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}