Sunrise[]
gives the time of the next sunrise for the current date and location.
Sunrise[datespec]
gives the times of the next sunrise for the specified dates.
Sunrise[locationspec]
gives the times of the next sunrise for the specified locations.
Sunrise[locationspec,datespec]
gives the time of the next sunrise for the specified date and location.
Sunrise[{{location1,date1},{location2,date2},…}]
gives the times of the next sunrise for all specified locations on the specified dates.
Sunrise[locationspec,datespec,func]
uses func to determine what to return for extended locations.


Sunrise
Sunrise[]
gives the time of the next sunrise for the current date and location.
Sunrise[datespec]
gives the times of the next sunrise for the specified dates.
Sunrise[locationspec]
gives the times of the next sunrise for the specified locations.
Sunrise[locationspec,datespec]
gives the time of the next sunrise for the specified date and location.
Sunrise[{{location1,date1},{location2,date2},…}]
gives the times of the next sunrise for all specified locations on the specified dates.
Sunrise[locationspec,datespec,func]
uses func to determine what to return for extended locations.
Details and Options




- Sunrise, also known as sunup, is defined as the instant of time when the upper rim of the Sun's disk appears to make contact with the horizon as it is rising.
- The observation location can be any point on the surface of a body in the solar system, defining the local horizon.
- Locations can be specified as Entity objects, assuming they represent objects with geographic coordinates, or they can be latitude/longitude pairs, assuming degrees as units.
- Sunrise[] makes use of $GeoLocation and $TimeZone to determine your location and time zone.
- datespec can be a DateObject expression, a TimeObject expression, a date string or a {y,m,d,h,m,s} date list.
- datespec is assumed to be in $TimeZone, unless it is a DateObject or TimeObject expression with an explicit TimeZone option value.
- locationspec and datespec can be either individual items or lists of them.
- If datespec is a list of dates, then the results will contain EventSeries objects.
- datespec can be specified as {start,end,increment} for compatibility with DateRange specifications.
- Sunrise[…,func] is used to specify the format of output when extended locations are specified.
- Possible settings for func include:
-
Automatic returns intervals for extended locations only Interval returns intervals for all specified locations Mean returns mean value for extended locations Min returns minimum values for extended locations Max returns maximum values for extended locations StandardDeviation returns standard deviation for extended locations - Sunrise[TimeZone->z] gives the date of the next sunrise with date and time inferred for time zone z by assuming that your computer is set for the time zone specified by $TimeZone.
- Sunrise[TimeDirection->-1] gives the date of the last sunrise.
- Sunrise can accept the following options:
-
ReferenceAltitude Automatic altitude value defining the instant of rise/set TimeDirection 1 whether to return the next or last Sunrise TimeZone $TimeZone time zone to be used for dates - Possible settings for TimeDirection include:
-
1 returns the next sunrise from the specified date -1 returns the last sunrise from the specified date - Possible values of the ReferenceAltitude option include:
-
Automatic upper limb of the Sun crosses zero altitude alt center of the Sun crosses numeric altitude alt {alt,limb} the given limb of the Sun crosses numeric altitude alt - The reference altitude angle alt can be given as a Quantity angle or as a numeric expression interpreted in angular degrees. These are the traditional values of reference altitude:
-
"Civil" the center of the Sun has altitude –6 degrees "Nautical" the center of the Sun has altitude –12 degrees "Astronomical" the center of the Sun has altitude –18 degrees - Possible values for the limb of the Sun include:
-
"UpperLimb" upper limb of the Sun "Center" central point of the Sun "LowerLimb" lower limb of the Sun limb numeric value between –1 (lower limb) and 1 (upper limb) - Calculations are based on atmospheric refraction models that cannot be accurately predicted. This, combined with local topography deviations, can result in errors on the order of several minutes from actual observed times.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Scope (14)
Dates (4)
Dates can be specified as a DateObject:
Dates can be specified as a date string:
Dates can be specified as a TimeObject:
Locations (8)
Locations can be latitude/longitude pairs:
Locations can include elevation:
Cities are treated as single, specific locations:
Results for extended locations are intervals, by default:
The form of the results for extended locations can be overridden:
Locations can also be off Earth:
Generate the next sunrise for multiple locations:
Generate the next sunrise for multiple locations on different dates:
Options (4)
ReferenceAltitude (2)
By default, Sunrise reports the instant when the upper limb of the Sun has altitude zero:
Therefore, the actual center of the body is below the horizon:
Use a specific value of altitude and choice of limb:
Find the next date of sunrise, by default using the horizon and the upper limb of the Sun:
Use the same horizon at zero apparent altitude, but now comparing to the center of the Sun:
Find the starting time of civil, nautical and astronomical twilight, all defined by the center of the Sun:
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (3)
By default, location is specified by $GeoLocation and the date is specified by the current date:
Results are in the form of an EventSeries when a range of dates is specified:
Calculate the next sunrise, defined as when the upper edge of the Sun's apparent disk touches the horizon:
Find the position of the center of the Sun at that time:
The altitude of the Sun corresponds to its angular radius:
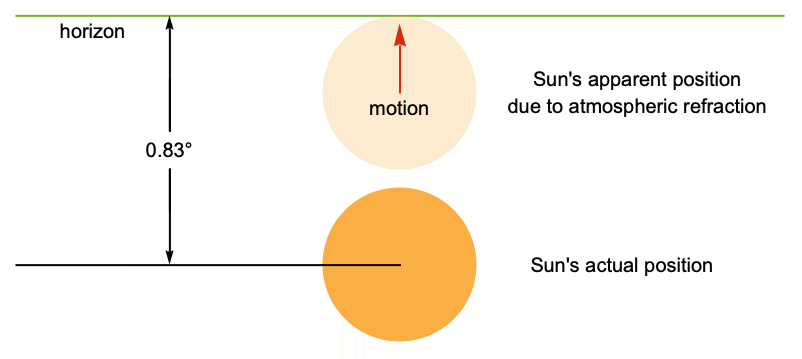
Eliminating atmospheric refraction effects, the true position of the Sun is revealed to be even further below the horizon at sunrise:
Possible Issues (3)
Since the value of $TimeZone may change throughout the year, the results for specified dates may vary depending on when you evaluate the input:
If the above behavior is a concern, the TimeZone option can be used to enforce a consistent value:
With Sunrise[locationspec,Interval], results for specific locations are coerced into intervals:
Sunrise returns values taking into account atmospheric refraction effects:
These effects are especially large near the horizon, but the effects are turned off a few degrees below the horizon:
Use the "TrueAltitude" method to deactivate atmospheric refraction and compare with the previous result:
See Also
Sunset SunPosition DaylightQ MoonPosition StarData SiderealTime
Function Repository: TwilightTimes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), Sunrise, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Sunrise.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "Sunrise." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Sunrise.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). Sunrise. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Sunrise.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_sunrise, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Sunrise}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Sunrise.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_sunrise, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Sunrise}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Sunrise.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}