VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,data2,…}]
tests whether the variances of the datai are equal.
VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},"property"]
returns the value of "property".


VarianceEquivalenceTest
VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,data2,…}]
tests whether the variances of the datai are equal.
VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},"property"]
returns the value of "property".
Details and Options



- VarianceEquivalenceTest performs a hypothesis test on the datai with null hypothesis
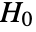 that the true population variances are identical to
that the true population variances are identical to 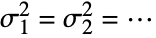 , and alternative hypothesis
, and alternative hypothesis 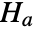 that at least one is different.
that at least one is different. - By default, a probability value or
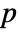 -value is returned.
-value is returned. - A small
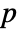 -value suggests that it is unlikely that
-value suggests that it is unlikely that 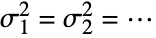 .
. - The datai must be univariate {x1,x2,…}.
- VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…}] will choose the most powerful test that applies to the data.
- VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},All] will choose all tests that apply to the data.
- VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},"test"] reports the
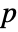 -value according to "test".
-value according to "test". - Most tests require normally distributed datai. If a test is less sensitive to a normality assumption, it is called robust. Some tests assume that datai is symmetric around its medians.
- The following tests can be used:
-
"Bartlett" normality modified likelihood ratio test "BrownForsythe" robust robust Levene test "Conover" symmetry Conover's squared ranks test "FisherRatio" normality based on 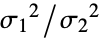
"Levene" robust,symmetry compares individual and group variances - VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},"HypothesisTestData"] returns a HypothesisTestData object htd that can be used to extract additional test results and properties using the form htd["property"].
- VarianceEquivalenceTest[{data1,…},"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
- Properties related to the reporting of test results include:
-
"AllTests" list of all applicable tests "AutomaticTest" test chosen if Automatic is used "DegreesOfFreedom" the degrees of freedom used in a test "PValue" list of 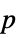 -values
-values"PValueTable" formatted table of 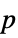 -values
-values"ShortTestConclusion" a short description of the conclusion of a test "TestConclusion" a description of the conclusion of a test "TestData" list of pairs of test statistics and 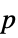 -values
-values"TestDataTable" formatted table of 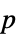 -values and test statistics
-values and test statistics"TestStatistic" list of test statistics "TestStatisticTable" formatted table of test statistics - The following options can be given:
-
SignificanceLevel 0.05 cutoff for diagnostics and reporting VerifyTestAssumptions Automatic set which diagnostic tests to run - For tests of variance, a cutoff
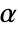 is chosen such that
is chosen such that 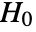 is rejected only if
is rejected only if 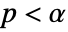 . The value of
. The value of 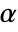 used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. This value
used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. This value 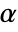 is also used in diagnostic tests of assumptions, including tests for normality and symmetry. By default,
is also used in diagnostic tests of assumptions, including tests for normality and symmetry. By default, 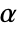 is set to 0.05.
is set to 0.05. - Named settings for VerifyTestAssumptions in VarianceEquivalenceTest include:
-
"Normality" verify that all data is normally distributed "Symmetry" verify that all data is symmetric
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Test variances from two datasets for equivalence:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for further property extraction:
Scope (12)
Testing (8)
Compare the variances of two datasets:
The ![]() -values are typically large when the variances are equal:
-values are typically large when the variances are equal:
The ![]() -values are typically small when the variances are not equal:
-values are typically small when the variances are not equal:
Using Automatic applies the generally most powerful appropriate test:
The property "AutomaticTest" can be used to determine which test was chosen:
Compare the variances of many datasets simultaneously:
Compare the distributions of the datasets visually using SmoothHistogram:
Perform a particular test for equal variance:
Any number of tests can be performed simultaneously:
Perform all tests, appropriate to the data, simultaneously:
Use the property "AllTests" to identify which tests were used:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for repeated property extraction:
The properties available for extraction:
Extract some properties from a HypothesisTestData object:
The ![]() -value and test statistic from a Levene test:
-value and test statistic from a Levene test:
Reporting (4)
Tabulate the results from a selection of tests:
A full table of all appropriate test results:
A table of selected test results:
Retrieve the entries from a test table for customized reporting:
The ![]() -values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject normality at that level:
-values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject normality at that level:
Tabulate ![]() -values for a test or group of tests:
-values for a test or group of tests:
A table of ![]() -values from all appropriate tests:
-values from all appropriate tests:
A table of ![]() -values from a subset of tests:
-values from a subset of tests:
Report the test statistic from a test or group of tests:
Options (6)
SignificanceLevel (3)
VerifyTestAssumptions (3)
Applications (2)
Test whether a group of populations shares a common variance:
The first group of datasets was drawn from populations with very different variances:
Populations represented by the second group all have similar variances:
LocationEquivalenceTest can be used to compare the means of several datasets simultaneously but requires that the datasets have common variance:
Use VarianceEquivalenceTest to determine if the variances are equivalent:
LocationEquivalenceTest can be used to compare the means:
Properties & Relations (5)
The Brown–Forsythe and Levene tests are equivalent but use different standardizing functions:
The Levene test uses Mean to standardize the data:
The Brown–Forsythe test typically uses Median:
For heavy-tailed data, the 10% TrimmedMean is used instead:
For ![]() datasets and
datasets and ![]() total observations, the Brown–Forsythe and Levene test statistics both follow FRatioDistribution[k-1,n-k] under
total observations, the Brown–Forsythe and Levene test statistics both follow FRatioDistribution[k-1,n-k] under ![]() :
:
Under ![]() , the test statistic follows ChiSquareDistribution[k-1]:
, the test statistic follows ChiSquareDistribution[k-1]:
The variance equivalence test ignores the time stamps when the input is a TimeSeries:
The variance equivalence test recognizes the path structure of a TemporalData:
Possible Issues (2)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), VarianceEquivalenceTest, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VarianceEquivalenceTest.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "VarianceEquivalenceTest." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VarianceEquivalenceTest.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). VarianceEquivalenceTest. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VarianceEquivalenceTest.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_varianceequivalencetest, author="Wolfram Research", title="{VarianceEquivalenceTest}", year="2010", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VarianceEquivalenceTest.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_varianceequivalencetest, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={VarianceEquivalenceTest}, year={2010}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VarianceEquivalenceTest.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}