FindDistribution[data]
finds a simple functional form to fit the distribution of data.
FindDistribution[data,n]
finds up to n best distributions.
FindDistribution[data,n,prop]
returns up to n best distributions associated with property prop.
FindDistribution[data,n,{prop1,prop2,…}]
returns up to n best distributions associated with properties prop1, prop2, etc.


FindDistribution
FindDistribution[data]
finds a simple functional form to fit the distribution of data.
FindDistribution[data,n]
finds up to n best distributions.
FindDistribution[data,n,prop]
returns up to n best distributions associated with property prop.
FindDistribution[data,n,{prop1,prop2,…}]
returns up to n best distributions associated with properties prop1, prop2, etc.
Details and Options


- The data must be a list of possible outcomes from a univariate distribution.
- FindDistribution[data,n,All] creates a Dataset object with all possible properties.
- Properties supported include:
-
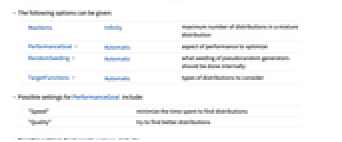
"BIC" Bayesian information criterion "AIC" Akaike information criterion "HQIC" Hannan–Quinn information criterion "Score" internal score "Complexity" complexity of the distribution "LogLikelihood" LogLikelihood value "PearsonChiSquare" PearsonChiSquareTest p-value "CramerVonMises" CramerVonMisesTest p-value All all the previous properties - The following options can be given:
-
MaxItems Infinity maximum number of distributions in a mixture distribution PerformanceGoal Automatic aspect of performance to optimize RandomSeeding Automatic what seeding of pseudorandom generators should be done internally TargetFunctions Automatic types of distributions to consider - Possible settings for PerformanceGoal include:
-
"Speed" minimize the time spent to find distributions "Quality" try to find better distributions - Possible settings for TargetFunctions include:
-
Automatic automatically chosen distributions All all built-in distributions "Continuous" all continuous distributions "Discrete" all discrete distributions {dist1, 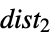 ,
, }
}distributions disti { 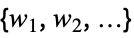 {dist1,
{dist1,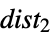 ,
, }}
}}distributions disti using weights wi - Possible settings for RandomSeeding include:
-
Automatic automatically reseed every time the function is called Inherited use externally seeded random numbers seed use an explicit integer or strings as a seed - Possible continuous distributions for TargetFunctions are: BetaDistribution, CauchyDistribution, ChiDistribution, ChiSquareDistribution, ExponentialDistribution, ExtremeValueDistribution, FrechetDistribution, GammaDistribution, GumbelDistribution, HalfNormalDistribution, InverseGaussianDistribution, LaplaceDistribution, LevyDistribution, LogisticDistribution, LogNormalDistribution, MaxwellDistribution, NormalDistribution, ParetoDistribution, RayleighDistribution, StudentTDistribution, UniformDistribution, WeibullDistribution, HistogramDistribution.
- Possible discrete distributions for TargetFunctions are: BenfordDistribution, BinomialDistribution, BorelTannerDistribution, DiscreteUniformDistribution, GeometricDistribution, LogSeriesDistribution, NegativeBinomialDistribution, PascalDistribution, PoissonDistribution, WaringYuleDistribution, ZipfDistribution, HistogramDistribution, EmpiricalDistribution.
- The internal information criterion uses a Bayesian information criterion together with priors over TargetFunctions.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a list of uniformly distributed random integers:
Find the underlying distribution from the data:
Generate data sampled from an exponential distribution:
Find the best distribution from the data:
Compare the PDFs for the original and estimated distributions:
Return the best three distributions:
Compare their Bayesian information criterion and Akaike information criterion values:
Scope (3)
Generate data sampled from a mixture distribution:
Estimate the best distribution from this data:
Compare the PDFs for the original and estimated distributions:
Estimate parameters for a particular distribution:
By default, FindDistribution returns a simpler distribution:
Specify the type of distribution to look for:
Generate data sampled from an exponential distribution:
Generate a Dataset object containing all properties for the top 2 distributions:
Options (5)
TargetFunctions (3)
Generate data samples from a mixture distribution:
Estimate parameters for specific distributions:
Compare the PDFs for the original and estimated distributions:
Time between geyser eruptions:
Estimate the distribution of the data:
Estimate the distribution of the data when treated as continuous:
Estimate the distribution of the data when treated as continuous using GammaDistribution:
Compare the histogram of the data to the PDF of the estimated distributions:
Estimate parameters for specific distributions, assuming priors over them:
The magnitudes of earthquakes in the United States in the years 1935–1989 have two modes:
Estimate the best fit without using TargetFunctions:
Estimate the best fit using priors over distributions:
Compare the histogram to the PDFs of the estimated distributions:
PerformanceGoal (1)
Generate data samples from a mixture distribution:
Estimate the best fit for a big dataset and compare the AbsoluteTiming for different settings of PerformanceGoal:
Compare the LogLikelihood of the solutions:
RandomSeeding (1)
Generate data samples from a mixture distribution:
Compare different rounds of FindDistribution and notice how they differ:
Use the option RandomSeeding to avoid having different results:
Applications (5)
Lengths of Words Beginning with a Particular Letter (1)
Text Frequency (1)
Melanoma in Denmark (1)
Infection Time for AIDS (1)
Properties & Relations (1)
By default, FindDistributionParameters uses maximum likelihood to estimate distribution parameters for a fixed distribution. FindDistribution uses a full Bayesian approach by combining the Bayesian information criterion with priors over distributions to select both the best distribution and the best parameters for it.
Generate data sampled from a StudentTDistribution:
Use FindDistribution to estimate the best distribution that fits the data:
Use FindDistributionParameters to estimate the best parameters, assuming a StudentTDistribution:
Even though the StudentTDistribution minimized the log likelihood, the LogisticDistribution has larger prior and smaller complexity compared to it.
Compare the corresponding LogLikelihood:
The option TargetFunctions can be used if you want to find roughly the same parameters as FindDistributionParameters:
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), FindDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindDistribution.html (updated 2017).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "FindDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2017. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). FindDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_finddistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FindDistribution}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 20-November-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_finddistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FindDistribution}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 20-November-2025]}