ComplexStreamPlot[f,{z,zmin,zmax}]
generates a streamline plot of the vector field {Re[f],Im[f]} over the complex rectangle with corners zmin and zmax.




ComplexStreamPlot
ComplexStreamPlot[f,{z,zmin,zmax}]
generates a streamline plot of the vector field {Re[f],Im[f]} over the complex rectangle with corners zmin and zmax.
Details and Options
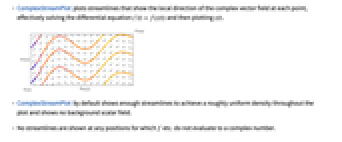


- ComplexStreamPlot plots streamlines that show the local direction of the complex vector field at each point, effectively solving the differential equation
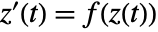 and then plotting
and then plotting 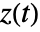 .
. - ComplexStreamPlot by default shows enough streamlines to achieve a roughly uniform density throughout the plot and shows no background scalar field.
- No streamlines are shown at any positions for which f etc. do not evaluate to a complex number.
- ComplexStreamPlot[f,{z,n}] is equivalent to ComplexStreamPlot[f,{z,-n-n I,n+n I}].
- ComplexStreamPlot has attribute HoldAll and evaluates f etc. only after assigning specific numerical values to z. In some cases, it may be more efficient to use Evaluate to evaluate f symbolically first.
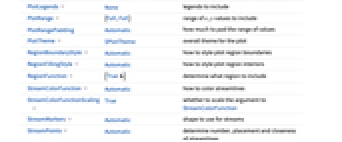
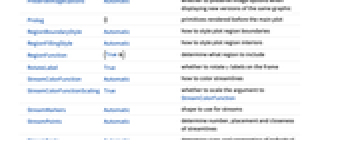
- ComplexStreamPlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio 1 ratio of height to width EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation Frame True whether to draw a frame around the plot FrameTicks Automatic frame tick marks Method Automatic methods to use for the plot PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLegends None legends to include PlotRange {Full,Full} range of x, y values to include PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot RegionBoundaryStyle Automatic how to style plot region boundaries RegionFillingStyle Automatic how to style plot region interiors RegionFunction (True&) determine what region to include StreamColorFunction Automatic how to color streamlines StreamColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the argument to StreamColorFunction StreamMarkers Automatic shape to use for streams StreamPoints Automatic determine number, placement and closeness of streamlines StreamScale Automatic determine sizes and segmenting of individual streamlines StreamStyle Automatic how to draw streamlines WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision precision to use in internal computations - Common stream markers include:
-

"Segment" line segment aligned in the field direction 
"PinDart" pin dart aligned along the field 
"Dart" dart-shaped marker 
"Drop" drop-shaped marker - The arguments supplied to functions in RegionFunction are
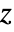 ,
, 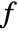 . Functions in ColorFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of Re[z], Im[z], Abs[z], Arg[z], Re[f], Im[f], Abs[f], Arg[f].
. Functions in ColorFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of Re[z], Im[z], Abs[z], Arg[z], Re[f], Im[f], Abs[f], Arg[f]. -
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio 1 ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame True whether to draw a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame tick marks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels Method Automatic methods to use for the plot PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotLegends None legends to include PlotRange {Full,Full} range of x, y values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RegionBoundaryStyle Automatic how to style plot region boundaries RegionFillingStyle Automatic how to style plot region interiors RegionFunction (True&) determine what region to include RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame StreamColorFunction Automatic how to color streamlines StreamColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the argument to StreamColorFunction StreamMarkers Automatic shape to use for streams StreamPoints Automatic determine number, placement and closeness of streamlines StreamScale Automatic determine sizes and segmenting of individual streamlines StreamStyle Automatic how to draw streamlines Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision precision to use in internal computations
List of all options


Examples
open all close allScope (22)
Sampling (8)
Plot a complex functions with streamlines placed with specified densities:
Plot the streamlines that go through a set of complex seed points:
Use both automatic and explicit seeding with styles for explicitly seeded streamlines:
Plot streamlines over a specified complex region:
Use a specific number of mesh lines:
Use Evaluate to evaluate the vector field symbolically before numeric assignment:
Presentation (14)
Specify different dashings and arrowheads by setting to StreamScale:
Plot the streamlines with arrows colored according to the modulus of the function:
Apply a variety of streamline markers:
Use a theme with axes and a different default color:
Override the style from the theme:
Specify a uniform color for the streamlines:
Specify mesh lines with different styles:
Specify global mesh line styles:
Shade mesh regions cyclically:
Apply a variety of styles to region boundaries:
Add a legend indicating the modulus of the function:
Options (60)
EvaluationMonitor (2)
PerformanceGoal (2)
PlotLegends (7)
PlotRange (5)
PlotTheme (3)
RegionBoundaryStyle (1)
RegionFunction (3)
StreamColorFunction (5)
Color streamlines according to the modulus of the function:
Use any named color gradient from ColorData:
Use ColorData for predefined color gradients:
Specify a color function that blends two colors by ![]() :
:
Use StreamColorFunctionScalingFalse to get unscaled values:
StreamColorFunctionScaling (3)
By default, scaled values are used:
Use StreamColorFunctionScalingFalse to get unscaled values:
Explicitly specify the scaling for each color function argument:
StreamMarkers (8)
StreamPoints (5)
Specify a specific maximum number of streamlines:
Use symbolic names to specify the number of streamlines:
Use both automatic and explicit seeding with styles for explicitly seeded streamlines:
Specify the minimum distance between streamlines:
Specify the minimum distance between streamlines at the start and end of a streamline:
StreamScale (9)
Create full streamlines without segmentation:
Use symbolic names to control the lengths of streamlines:
Specify an explicit dashing pattern for streamlines:
Specify the number of points rendered on each streamline segment:
Specify absolute aspect ratios relative to the longest line segment:
Specify relative aspect ratios relative to each line segment:
StreamStyle (5)
StreamColorFunction has precedence over StreamStyle for colors:
Use StreamColorFunctionNone to specify colors with StreamStyle:
Applications (10)
Basic Applications (1)
Other Applications (9)
Streamlines that diverge from a point indicate a simple zero:
Streamlines can also converge at a simple zero:
With ![]() , the real vector field corresponding to the complex function
, the real vector field corresponding to the complex function ![]() is
is ![]() , and the trajectories that follow the field satisfy the differential equation
, and the trajectories that follow the field satisfy the differential equation ![]() . The implicit solution is
. The implicit solution is ![]() for real
for real ![]() , which corresponds to a family of circles that are tangent to the real axis at the origin:
, which corresponds to a family of circles that are tangent to the real axis at the origin:
In polar coordinates, the trajectories are ![]() for any real
for any real ![]() :
:
More generally, for ![]() where
where ![]() is an integer, the streamlines follow
is an integer, the streamlines follow ![]() for constant
for constant ![]() :
:
Near a zero of order ![]() , the streamlines form loops that start and end at the zero in
, the streamlines form loops that start and end at the zero in ![]() directions:
directions:
Near a pole of order ![]() , the streamlines converge to the pole from
, the streamlines converge to the pole from ![]() directions and diverge from the pole from
directions and diverge from the pole from ![]() directions:
directions:
The function ![]() has simple zeros at
has simple zeros at ![]() and
and ![]() , poles of order 1 at
, poles of order 1 at ![]() , and a pole of order 2 at
, and a pole of order 2 at ![]() :
:
Near an essential singularity, the streamlines vary wildly:
Plot a function and its derivatives:
Let ![]() be a complex potential for an ideal fluid flow. Then
be a complex potential for an ideal fluid flow. Then ![]() is the velocity potential,
is the velocity potential, ![]() is the stream function, and the fluid velocity field is
is the stream function, and the fluid velocity field is ![]() . By the Cauchy–Riemann equations,
. By the Cauchy–Riemann equations, ![]() , so you can generate a stream plot with the conjugate of
, so you can generate a stream plot with the conjugate of ![]() . Show streamlines for flow around a cylinder with circulation:
. Show streamlines for flow around a cylinder with circulation:
Properties & Relations (15)
ComplexStreamPlot is a special case of StreamPlot:
ComplexVectorPlot plots complex numbers as vectors:
ComplexVectorPlot is a special case of VectorPlot:
Use VectorDisplacementPlot to visualize the effect of a complex function on a specified region:
Use VectorPlot3D and StreamPlot3D to visualize 3D vector fields:
ComplexContourPlot plots curves over the complexes:
ComplexRegionPlot plots regions over the complexes:
ComplexPlot shows the argument and magnitude of a function using color:
Use ComplexPlot3D to use the ![]() axis for the magnitude:
axis for the magnitude:
Use ComplexArrayPlot for arrays of complex numbers:
Use ReImPlot and AbsArgPlot to plot complex values over the real numbers:
Use ComplexListPlot to show the location of complex numbers in the plane:
Use ListVectorPlot for plotting data:
Use ListStreamPlot to plot streams instead of vectors:
Use VectorDensityPlot to add a density plot of a scalar field:
Use StreamDensityPlot to use streams instead of vectors:
Use ListVectorDensityPlot to generate a density plot of a scalar field based on data:
Use ListStreamDensityPlot to plot streams instead of vectors:
Use LineIntegralConvolutionPlot to plot the line integral convolution of a vector field:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), ComplexStreamPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ComplexStreamPlot.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "ComplexStreamPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ComplexStreamPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). ComplexStreamPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ComplexStreamPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_complexstreamplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ComplexStreamPlot}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ComplexStreamPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 14-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_complexstreamplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ComplexStreamPlot}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ComplexStreamPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 14-February-2026]}