

Minimize
Details and Options


- Minimize is also known as infimum, symbolic optimization and global optimization (GO).
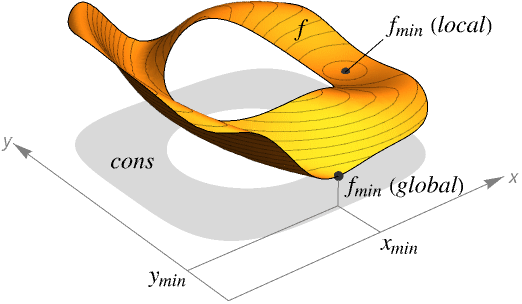
- Minimize finds the global minimum of f subject to the constraints given.
- Minimize is typically used to find the smallest possible values given constraints. In different areas, this may be called the best strategy, best fit, best configuration and so on.
- Minimize returns a list of the form {fmin,{x->xmin,y->ymin,…}}.
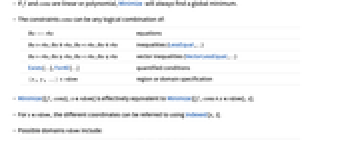
- If f and cons are linear or polynomial, Minimize will always find a global minimum.
- The constraints cons can be any logical combination of:
-
lhs==rhs equations lhs>rhs, lhs≥rhs, lhs<rhs, lhs≤rhs inequalities (LessEqual,…) lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs vector inequalities (VectorLessEqual,…) Exists[…], ForAll[…] quantified conditions {x,y,…}∈rdom region or domain specification - Minimize[{f,cons},x∈rdom] is effectively equivalent to Minimize[{f,cons∧x∈rdom},x].
- For x∈rdom, the different coordinates can be referred to using Indexed[x,i].
- Possible domains rdom include:
-
Reals real scalar variable Integers integer scalar variable Vectors[n,dom] vector variable in 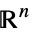
Matrices[{m,n},dom] matrix variable in 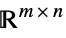
ℛ vector variable restricted to the geometric region 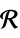
- By default, all variables are assumed to be real.
- Minimize will return exact results if given exact input. With approximate input, it automatically calls NMinimize.
- Minimize will return the following forms:
-
{fmin,{xxmin,…}} finite minimum {∞,{xIndeterminate,…}} infeasible, i.e. the constraint set is empty {-∞,{xxmin,…}} unbounded, i.e. the values of f can be arbitrarily small - If the minimum is achieved only infinitesimally outside the region defined by the constraints, or only asymptotically, Minimize will return the infimum and the closest specifiable point.
- Even if the same minimum is achieved at several points, only one is returned.
- N[Minimize[…]] calls NMinimize for optimization problems that cannot be solved symbolically.
- Minimize[f,x,WorkingPrecision->n] uses n digits of precision while computing a result. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Scope (36)
Basic Uses (7)
Univariate Problems (7)
Unconstrained univariate polynomial minimization:
Constrained univariate polynomial minimization:
Analytic functions over bounded constraints:
Combination of trigonometric functions with commensurable periods:
Combination of periodic functions with incommensurable periods:
Unconstrained problems solvable using function property information:
Multivariate Problems (9)
Multivariate linear constrained minimization:
Linear-fractional constrained minimization:
Unconstrained polynomial minimization:
Constrained polynomial optimization can always be solved:
The minimum value may not be attained:
The objective function may be unbounded:
There may be no points satisfying the constraints:
Quantified polynomial constraints:
Bounded transcendental minimization:
Minimize convex objective function ![]() such that
such that ![]() is positive semidefinite and
is positive semidefinite and ![]() :
:
Parametric Problems (4)
Optimization over Integers (3)
Optimization over Regions (6)
Find the minimum distance between two regions:
Find the minimum ![]() such that the triangle and ellipse still intersect:
such that the triangle and ellipse still intersect:
Find the disk of minimum radius that contains the given three points:
Using Circumsphere gives the same result directly:
Use ![]() to specify that
to specify that ![]() is a vector in
is a vector in ![]() :
:
Options (1)
WorkingPrecision (1)
Finding the exact solution takes a long time:
With WorkingPrecision->100, you get an exact minimum value, but it might be incorrect:
Applications (10)
Basic Applications (3)
Geometric Distances (6)
The shortest distance of a point in a region ℛ to a given point p and a point q realizing the shortest distance is given by Minimize[EuclideanDistance[p,q],q∈ℛ]. Find the shortest distance and the nearest point to {1,1} in the unit Disk[]:
Find the shortest distance and the nearest point to {1,3/4} in the standard unit simplex Simplex[2]:
Find the shortest distance and the nearest point to {1,1,1} in the standard unit sphere Sphere[]:
Find the shortest distance and the nearest point to {-1/3,1/3,1/3} in the standard unit simplex Simplex[3]:
The nearest points p∈ and q∈ and their distance can be found through Minimize[EuclideanDistance[p,q],{p∈,q∈}]. Find the nearest points in Disk[{0,0}] and Rectangle[{3,3}] and the distance between them:
Find the nearest points in Line[{{0,0,0},{1,1,1}}] and Ball[{5,5,0},1] and the distance between them:
Geometric Centers (1)
If ℛ⊆n is a region that is full dimensional, then the Chebyshev center is the center of the largest inscribed ball of ℛ. The center and the radius of the largest inscribed ball of ℛ can be found through Minimize[SignedRegionDistance[ℛ,p], p∈ℛ]. Find the Chebyshev center and the radius of the largest inscribed ball for Rectangle[]:
Find the Chebyshev center and the radius of the largest inscribed ball for Triangle[]:
Properties & Relations (6)
Minimize gives an exact global minimum of the objective function:
NMinimize attempts to find a global minimum numerically, but may find a local minimum:
FindMinimum finds local minima depending on the starting point:
The minimum point satisfies the constraints, unless messages say otherwise:
The given point minimizes the distance from the point {2,![]() }:
}:
When the minimum is not attained, Minimize may give a point on the boundary:
Here the objective function tends to the minimum value when y tends to infinity:
Minimize can solve linear programming problems:
LinearProgramming can be used to solve the same problem given in matrix notation:
This computes the minimum value:
Use RegionDistance and RegionNearest to compute the distance and the nearest point:
Both can be computed using Minimize:
Use RegionBounds to compute the bounding box:
Possible Issues (1)
Minimize requires that all functions present in the input be real-valued:
Values for which the equation is satisfied but the square roots are not real are disallowed:
See Also
MinValue ArgMin Maximize NMinimize FindMinimum Min MinimalBy D FindInstance LeastSquares RegionDistance
Function Repository: GlobalMinima LocalMinima GlobalExtrema LocalExtrema StationaryPoints VariationalBound
Related Guides
-
▪
- Optimization ▪
- Discrete Mathematics ▪
- Solvers over Regions ▪
- Discrete Calculus ▪
- Calculus ▪
- Graph Programming ▪
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays ▪
- Boolean Computation ▪
- Finite Mathematics ▪
- Solid Geometry ▪
- Plane Geometry ▪
- Convex Optimization ▪
- Geometric Computation ▪
- Polygons ▪
- Scientific Models ▪
- Polyhedra
History
Introduced in 2003 (5.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2021 (12.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2003), Minimize, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Minimize.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2003. "Minimize." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Minimize.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2003). Minimize. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Minimize.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_minimize, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Minimize}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Minimize.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_minimize, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Minimize}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Minimize.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}