NMinimize[f,x]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically with respect to x.
NMinimize[f,{x,y,…}]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically with respect to x, y, ….
NMinimize[{f,cons},{x,y,…}]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically subject to the constraints cons.
NMinimize[…,x∈rdom]
constrains x to be in the region or domain rdom.






NMinimize
NMinimize[f,x]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically with respect to x.
NMinimize[f,{x,y,…}]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically with respect to x, y, ….
NMinimize[{f,cons},{x,y,…}]
searches for a global minimum in f numerically subject to the constraints cons.
NMinimize[…,x∈rdom]
constrains x to be in the region or domain rdom.
Details and Options




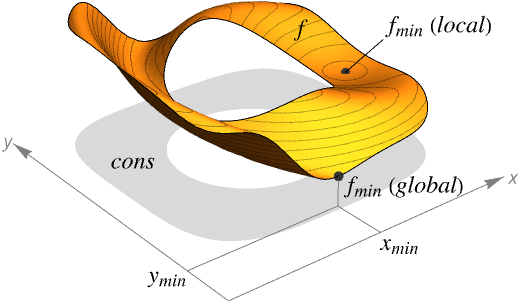
- NMinimize is also known as global optimization (GO).
- NMinimize always attempts to find a global minimum of f subject to the constraints given.
- NMinimize is typically used to find the smallest possible values given constraints. In different areas, this may be called the best strategy, best fit, best configuration and so on.
- NMinimize returns a list of the form {fmin,{x->xmin,y->ymin,…}}.
- If f and cons are linear or convex, the result given by NMinimize will be the global minimum, over both real and integer values; otherwise, the result may sometimes only be a local minimum.
- If NMinimize determines that the constraints cannot be satisfied, it returns {Infinity,{x->Indeterminate,…}}.
- NMinimize supports a modeling language where the objective function f and constraints cons are given in terms of expressions depending on scalar or vector variables. f and cons are typically parsed into very efficient forms, but as long as f and the terms in cons give numerical values for numerical values of the variables, NMinimize can often find a solution.
- The constraints cons can be any logical combination of:
-
lhs==rhs equations lhs>rhs, lhs≥rhs, lhs<rhs, lhs≤rhs inequalities (LessEqual, …) lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs, lhsrhs vector inequalities (VectorLessEqual, …) {x,y,…}∈rdom region or domain specification - NMinimize[{f,cons},x∈rdom] is effectively equivalent to NMinimize[{f,cons&&x∈rdom},x].
- For x∈rdom, the different coordinates can be referred to using Indexed[x,i].
- Possible domains rdom include:
-
Reals real scalar variable Integers integer scalar variable Vectors[n,dom] vector variable in 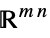
Matrices[{m,n},dom] matrix variable in 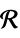
ℛ vector variable restricted to the geometric region 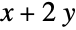
- By default, all variables are assumed to be real.
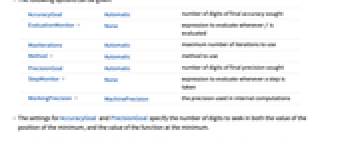
- The following options can be given:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic number of digits of final accuracy sought EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate whenever f is evaluated MaxIterations Automatic maximum number of iterations to use Method Automatic method to use PrecisionGoal Automatic number of digits of final precision sought StepMonitor None expression to evaluate whenever a step is taken WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations - The settings for AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal specify the number of digits to seek in both the value of the position of the minimum, and the value of the function at the minimum.
- NMinimize continues until either of the goals specified by AccuracyGoal or PrecisionGoal is achieved.
- The methods for NMinimize fall into two classes.The first class of guaranteed methods uses properties of the problem so that, when the method converges, the minimum found is guaranteed to be global. The second class of heuristic methods uses methods that may include multiple local searches, commonly adjusted by some stochasticity, to home in on a global minimum. These methods often do find the global minimum, but are not guaranteed to do so.
- Methods that are guaranteed to give a global minimum when they converge to a solution include:
-
"Convex" use only convex methods "MOSEK" use the commercial MOSEK library for convex problems "Gurobi" use the commercial Gurobi library for convex problems "Xpress" use the commercial Xpress library for convex problems - Heuristic methods include:
-
"NelderMead" simplex method of Nelder and Mead "DifferentialEvolution" use differential evolution "SimulatedAnnealing" use simulated annealing "RandomSearch" use the best local minimum found from multiple random starting points "Couenne" use the Couenne library for non-convex mixed-integer nonlinear problems
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (40)
Basic Uses (12)
Minimize ![]() subject to constraints
subject to constraints ![]() :
:
Several linear inequality constraints can be expressed with VectorGreaterEqual:
Use ![]() v>=
v>=![]() or \[VectorGreaterEqual] to enter the vector inequality sign :
or \[VectorGreaterEqual] to enter the vector inequality sign :
An equivalent form using scalar inequalities:
The inequality ![]() may not be the same as
may not be the same as ![]() due to possible threading in
due to possible threading in ![]() :
:
To avoid unintended threading in ![]() , use Inactive[Plus]:
, use Inactive[Plus]:
Use constant parameter equations to avoid unintended threading in ![]() :
:
VectorGreaterEqual represents a conic inequality with respect to the "NonNegativeCone":
To explicitly specify the dimension of the cone, use {"NonNegativeCone",n}:
Minimize ![]() subject to the constraint
subject to the constraint ![]() :
:
Specify the constraint ![]() using a conic inequality with "NormCone":
using a conic inequality with "NormCone":
Minimize the function ![]() subject to the constraint
subject to the constraint ![]() :
:
Use Indexed to access components of a vector variable, e.g. ![]() :
:
Use Vectors[n,dom] to specify the dimension and domain of a vector variable when it is ambiguous:
Specify non-negative constraints using NonNegativeReals (![]() ):
):
An equivalent form using vector inequality ![]() :
:
Specify non-positive constraints using NonPositiveReals (![]() ):
):
An equivalent form using vector inequalities:
Or constraints can be specified:
Domain Constraints (4)
Specify integer domain constraints using Integers:
Specify integer domain constraints on vector variables using Vectors[n,Integers]:
Specify non-negative integer domain constraints using NonNegativeIntegers (![]() ):
):
Specify non-positive integer domain constraints using NonPositiveIntegers (![]() ):
):
Region Constraints (5)
Find the minimum distance between two regions:
Find the minimum ![]() such that the triangle and ellipse still intersect:
such that the triangle and ellipse still intersect:
Find the disk of minimum radius that contains the given three points:
Using Circumsphere gives the same result directly:
Linear Problems (5)
With linear objectives and constraints, when a minimum is found it is global:
The constraints can be equality and inequality constraints:
Use Equal to express several equality constraints at once:
An equivalent form using several scalar equalities:
Use VectorLessEqual to express several LessEqual inequality constraints at once:
Use ![]() v<=
v<=![]() to enter the vector inequality in a compact form:
to enter the vector inequality in a compact form:
An equivalent form using scalar inequalities:
Use Interval to specify bounds on variable:
Convex Problems (7)
Use "NonNegativeCone" to specify linear functions of the form ![]() :
:
Use ![]() v>=
v>=![]() to enter the vector inequality in a compact form:
to enter the vector inequality in a compact form:
Minimize a convex quadratic function subject to linear constraints:
Plot the region and minimizing point:
Minimize a convex quadratic function subject to a set of convex quadratic constraints:
Plot the region and the minimizing point:
Find the minimum distance between two convex regions:
Minimize ![]() such that
such that ![]() is positive semidefinite:
is positive semidefinite:
Show the minimizer on a plot of the objective function:
Minimize the convex objective function ![]() such that
such that ![]() is positive semidefinite and
is positive semidefinite and ![]() :
:
Plot the region and the minimizing point:
Minimize a convex objective function over a 4-norm unit disk:
Transformable to Convex (4)
Minimize the perimeter of a rectangle such that the area is 1 and the height is at most half the width:
This problem is log-convex and is solved by making a transformation {hExp[],wExp[ ]} and taking logarithms to get the convex problem:
Minimize the quasi-convex function ![]() subject to inequality and norm constraints. The objective is quasi-convex because it is a product of a non-negative function and a non-positive function over the domain:
subject to inequality and norm constraints. The objective is quasi-convex because it is a product of a non-negative function and a non-positive function over the domain:
Quasi-convex problems can be solved as a parametric convex optimization problem for the parameter ![]() :
:
Plot the objective as a function of the level-set ![]() :
:
For a level-set value between the interval ![]() , the smallest objective is found:
, the smallest objective is found:
The problem becomes infeasible when the level-set value is increased:
Minimize ![]() subject to the constraint
subject to the constraint ![]() . The objective is not convex but can be represented by a difference of convex function
. The objective is not convex but can be represented by a difference of convex function ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are convex functions:
are convex functions:
Plot the region and the minimizing point:
Minimize ![]() subject to the constraints
subject to the constraints ![]() . The constraint
. The constraint ![]() is not convex but can be represented by a difference of convex constraint
is not convex but can be represented by a difference of convex constraint ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are convex functions:
are convex functions:
Options (10)
AccuracyGoal & PrecisionGoal (2)
This enforces a convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
This enforces a convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() , which is not achievable with the default machine-precision computation:
, which is not achievable with the default machine-precision computation:
Setting a high WorkingPrecision makes the process convergent:
EvaluationMonitor (1)
Method (5)
Some methods may give suboptimal results for certain problems:
The automatically chosen method gives the optimal solution for this problem:
The automatic method choice for this nonconvex problem is method "Couenne":
Plot the solution along with the global minima:
Find the global minimum of a function containing multiple local minima using method "Couenne":
Plot the minimizing function and the global minimum solution:
Use method "NelderMead" for problems with many variables when speed is essential:
Use method "Convex" or Except["Convex"] to specify if a convex method should be used or not:
Use method "Couenne" or Except["Couenne"] to choose or exclude the Couenne solver:
StepMonitor (1)
Steps taken by NMinimize in finding the minimum of the classic Rosenbrock function:
WorkingPrecision (1)
With the working precision set to ![]() , by default AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal are set to
, by default AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal are set to ![]() :
:
Applications (19)
Geometry Problems (4)
Find the minimum distance between two disks of radius 1 centered at ![]() and
and ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be a point on disk 1. Let
be a point on disk 1. Let ![]() be a point on disk 2. The objective is to minimize
be a point on disk 2. The objective is to minimize ![]() subject to constraints
subject to constraints ![]() :
:
Visualize the positions of the two points:
Find the radius ![]() and center
and center ![]() of a minimal enclosing ball that encompasses a given region:
of a minimal enclosing ball that encompasses a given region:
Minimize the radius ![]() subject to the constraints
subject to the constraints ![]() :
:
The minimal enclosing ball can be found efficiently using BoundingRegion:
Find the smallest ellipsoid parametrized as ![]() that encompasses a set of points in 3D by minimizing the volume:
that encompasses a set of points in 3D by minimizing the volume:
For each point ![]() , the constraint
, the constraint ![]() must be satisfied:
must be satisfied:
Minimizing the volume is equivalent to minimizing ![]() :
:
Convert the parametrized ellipse into the explicit form ![]() :
:
A bounding ellipsoid, not necessarily minimum volume, can also be found using BoundingRegion:
Find the smallest square that can contain ![]() circles of given radius
circles of given radius ![]() for
for ![]() that do not overlap. Specify the number of circles and the radius of each circle:
that do not overlap. Specify the number of circles and the radius of each circle:
If ![]() is the center of circle
is the center of circle ![]() , then the objective is to minimize
, then the objective is to minimize ![]() . The objective can be transformed so as to minimize
. The objective can be transformed so as to minimize ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Data-Fitting Problems (3)
Minimize ![]() subject to the constraints
subject to the constraints ![]() for a given matrix a and vector b:
for a given matrix a and vector b:
Fit a cubic curve to discrete data such that the first and last points of the data lie on the curve:
Construct the matrix using DesignMatrix:
Define the constraint so that the first and last points must lie on the curve:
Find the coefficients ![]() by minimizing
by minimizing ![]() :
:
Find a fit less sensitive to outliers to nonlinear discrete data by minimizing ![]() :
:
Fit the data using the bases ![]() . The interpolating function will be
. The interpolating function will be ![]() :
:
Compare the interpolating function with the reference function:
Classification Problems (5)
Find a line ![]() that separates two groups of points
that separates two groups of points ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
For separation, set 1 must satisfy ![]() and set 2 must satisfy
and set 2 must satisfy ![]() :
:
The objective is to minimize ![]() , which gives twice the thickness between
, which gives twice the thickness between ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Find a quadratic polynomial that separates two groups of 3D points ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Construct the quadratic polynomial data matrices for the two sets using DesignMatrix:
For separation, set 1 must satisfy ![]() and set 2 must satisfy
and set 2 must satisfy ![]() :
:
Find the separating polynomial by minimizing ![]() :
:
The polynomial separating the two groups of points is:
Plot the polynomial separating the two datasets:
Separate a given set of points ![]() into different groups. This is done by finding the centers
into different groups. This is done by finding the centers ![]() for each group by minimizing
for each group by minimizing ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a given local kernel and
is a given local kernel and ![]() is a given penalty parameter:
is a given penalty parameter:
The kernel ![]() is a
is a ![]() -nearest neighbor (
-nearest neighbor (![]() ) function such that
) function such that ![]() , else
, else ![]() . For this problem,
. For this problem, ![]() nearest neighbors are selected:
nearest neighbors are selected:
For each data point, there exists a corresponding center. Data belonging to the same group will have the same center value:
Extract and plot the grouped points:
Given a list of positive integers, partition the list into two non-overlapping subsets such that the difference between the sums of the two subsets is minimized. Define the list:
Define a binary variable that takes the values –1 or 1. If an element from the list belongs to subset 1, then the binary variable associated with it is given a value of –1. For subset 2, the associated binary variable is 1:
The objective is to minimize the difference of sums of the two subsets:
Given a collection of objects with different weights and two bags, find the objects with a maximum combined weight that can go into the two bags without exceeding the weight capacity of the bags. Define the number of objects and weights:
Use binary variables to decide if an object goes into bag 1 or 2, or neither:
The weight capacity of each bag is 5000:
The objective is to maximize the weights of the objects in the two bags:
The binary variable ![]() is associated with the objects that go into bag 1. The variable
is associated with the objects that go into bag 1. The variable ![]() is the complement of
is the complement of ![]() . The weights in the bags are:
. The weights in the bags are:
Image Processing (1)
Facility Location Problems (1)
Find the positions of various cell towers ![]() and the range
and the range ![]() needed to serve clients located at
needed to serve clients located at ![]() :
:
Each cell tower consumes power proportional to its range, which is given by ![]() . The objective is to minimize the power consumption:
. The objective is to minimize the power consumption:
Let ![]() be a decision variable indicating that
be a decision variable indicating that ![]() if client
if client ![]() is covered by cell tower
is covered by cell tower ![]() :
:
Each cell tower must be located such that its range covers some of the clients:
Each cell tower can cover multiple clients:
Each cell tower has a minimum and maximum coverage:
Find the cell tower positions and their ranges:
Extract cell tower position and range:
Visualize the positions and ranges of the towers with respect to client locations:
Portfolio Optimization (1)
Find the distribution of capital ![]() to invest in six stocks to maximize return while minimizing risk:
to invest in six stocks to maximize return while minimizing risk:
The return is given by ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a vector of expected return value of each individual stock:
is a vector of expected return value of each individual stock:
The risk is given by ![]() ;
; ![]() is a risk-aversion parameter and
is a risk-aversion parameter and ![]() :
:
The objective is to maximize return while minimizing risk for a specified risk-aversion parameter:
The effect on market prices of stocks due to the buying and selling of stocks is modeled by ![]() :
:
The weights ![]() must all be greater than 0 and the weights plus market impact costs must add to 1:
must all be greater than 0 and the weights plus market impact costs must add to 1:
Compute the returns and corresponding risk for a range of risk-aversion parameters:
The optimal ![]() over a range of
over a range of ![]() gives an upper-bound envelope on the tradeoff between return and risk:
gives an upper-bound envelope on the tradeoff between return and risk:
Compute the weights for a specified number of risk-aversion parameters:
By accounting for the market costs, a diversified portfolio can be obtained for low risk aversion, but when the risk aversion is high, the market impact cost dominates, due to purchasing a less diversified stock:
Trajectory Optimization (1)
Find a path through circular obstacles such that the distance between the start and end points is minimized:
The path is discretized into ![]() different points with distance of
different points with distance of ![]() between points, where
between points, where ![]() is the trajectory length being minimized:
is the trajectory length being minimized:
The points cannot be inside the circular objects:
The start and end points are known:
Manufacturing Problems (3)
Find the number of teeth ![]() needed in the gears
needed in the gears ![]() , respectively, to produce a specified gear ratio:
, respectively, to produce a specified gear ratio:
Each gear can have between ![]() and
and ![]() teeth:
teeth:
For the given gear train configuration, the gear ratio is given by ![]() :
:
Find the number of teeth in each gear to achieve the gear ratio of ![]() :
:
Minimize the manufacturing cost of a pressure vessel. The vessel is a cylindrical shell of length ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() with a hemisphere cap at each end of the tube:
with a hemisphere cap at each end of the tube:
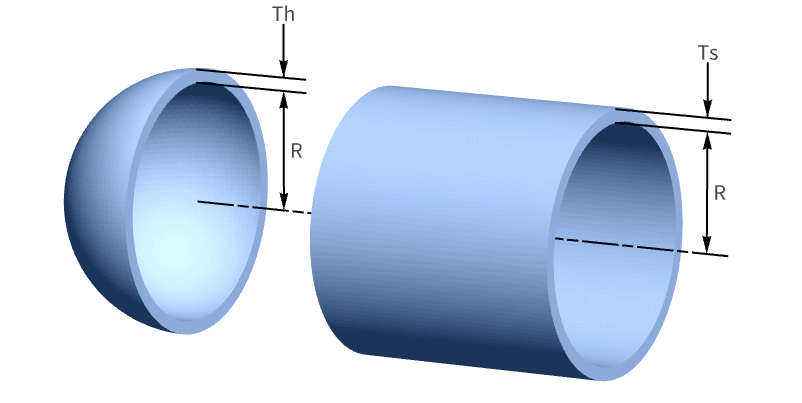
The volume constraint of the vessel is:
The shell has a thickness ![]() and the sphere cap has a thickness
and the sphere cap has a thickness ![]() . The shell and cap thicknesses have specified upper and lower limits and must be greater than a fraction of the radius:
. The shell and cap thicknesses have specified upper and lower limits and must be greater than a fraction of the radius:
The thickness of the shell and cap have additional constraints:
The vessel dimension constraints are:
The shell and cap material has density ![]() . The material cost is:
. The material cost is:
The cost to weld the shell and cap is:
The total manufacturing cost is a total of welding and material costs:
Find the dimensions of the vessel that minimize the manufacturing cost:
Design a minimum-volume helical compression spring of winding diameter ![]() , spring wire diameter
, spring wire diameter ![]() and number of spring coils
and number of spring coils ![]() subjected to an axial load:
subjected to an axial load:
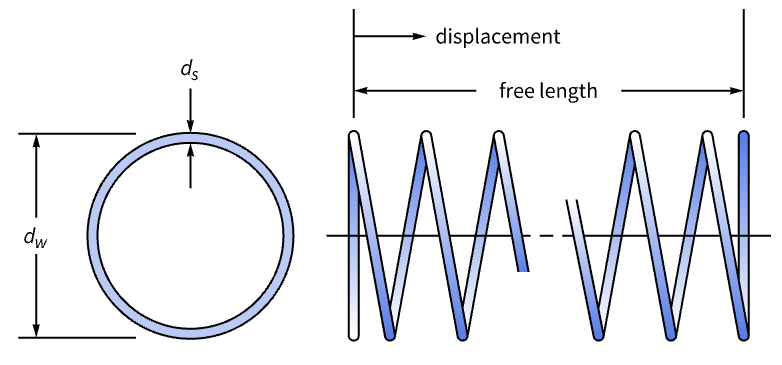
The shear stress on the spring is dependent on the maximum allowable axial load ![]() and must be below the maximum allowable stress
and must be below the maximum allowable stress ![]() :
:
The deflection of the spring is defined as:
The spring free length must be less than the maximum allowable length ![]() :
:
The wire diameter must not exceed the specified minimum diameter:
The outside diameter of the spring must be less than the maximum specified diameter ![]() :
:
The winding diameter ![]() must be at least three times the wire diameter
must be at least three times the wire diameter ![]() to avoid tightly wound springs:
to avoid tightly wound springs:
The deflection under pre-load must be between a specified ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
The load induced from the deflection and pre-load ![]() must not exceed the maximum load
must not exceed the maximum load ![]() :
:
The coil spring is to be manufactured from music wire spring steel ASTM A228 and the wire diameter must be chosen from a set of predetermined diameters:
The wire diameter ![]() is chosen from the predetermined set using binary variables:
is chosen from the predetermined set using binary variables:
Properties & Relations (9)
NMinimize gives the minimum value and rules for the minimizing values of the variables:
NArgMin gives a list of the minimizing values:
NMinValue gives only the minimum value:
Maximizing a function f is equivalent to minimizing -f:
For convex problems, ConvexOptimization may be used to obtain additional solution properties:
For convex problems with parameters, using ParametricConvexOptimization gives a ParametricFunction:
The ParametricFunction may be evaluated for values of the parameter:
Define a function for the parametric problem using NMinimize:
Compare the speed of the two approaches:
Derivatives of the ParametricFunction can also be computed:
For convex problems with parametric constraints, RobustConvexOptimization finds an optimum that works for all possible values of the parameters:
NMinimize may find a smaller value for particular values of the parameters:
This minimizer does not satisfy the constraints for all allowed values of α and β:
The minimum value found for particular values of the parameters is less than or equal to the robust minimum:
NMinimize aims to find a global minimum, while FindMinimum attempts to find a local minimum:
FindFit can use NMinimize to find the global optimal fit. This sets up a model:
Create a function from the model and parameters, and generate sample points:
By default, FindFit only finds the local optimal fit:
Using the NMinimize method finds the global optimal fit:
Use RegionDistance and RegionNearest to compute the distance and the nearest point:
Both can be computed using NMinimize:
Use RegionBounds to compute the bounding box:
Possible Issues (3)
For nonlinear functions, NMinimize may sometimes find only a local minimum for certain methods:
Plot the solution along with the local minima:
Specifying a starting interval can help in achieving a better local minimum:
Automatic method gives a better solution:
NMinimize finds a local minimum of a two-dimensional function on a disk for certain methods:
Specifying a starting interval helps in achieving the global minimum:
Define a function that does numerical integration for a given parameter:
Compute with a parameter value of 2:
Applying the function to a symbolic parameter generates a message from NIntegrate:
This can also lead to warnings when the function is used with other numerical functions like NMinimize:
Define a function that only evaluates when its argument is a numerical value to avoid these messages:
Compute with a numerical value:
The function does not evaluate when its argument is non-numerical:
The function can now be used with other numerical functions such as NMinimize:
Related Guides
-
▪
- Optimization ▪
- Convex Optimization ▪
- Solvers over Regions ▪
- Calculus ▪
- Graph Programming ▪
- Numerical Evaluation & Precision ▪
- Solid Geometry ▪
- Geometric Computation ▪
- Plane Geometry ▪
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays ▪
- Scientific Models ▪
- Polygons ▪
- System Model Analytics & Design ▪
- Polyhedra
History
Introduced in 2003 (5.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2021 (12.3) ▪ 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2022 (13.2) ▪ 2024 (14.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (2003), NMinimize, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NMinimize.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2003. "NMinimize." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NMinimize.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2003). NMinimize. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NMinimize.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_nminimize, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NMinimize}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NMinimize.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_nminimize, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NMinimize}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NMinimize.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}