RegionEqual
RegionEqual[reg1,reg2]
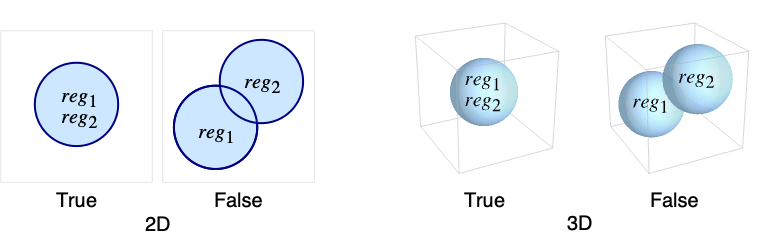
returns True if the regions reg1 and reg2 are equal.
RegionEqual[reg1,reg2,reg3,…]
returns True if the regions reg1, reg2, reg3, … are all equal.
Details and Options

- The regions reg1 and reg2 are equal if all points in reg1 are points in reg2 and vice versa.
- If all regi are parameter-free regions, i.e. ConstantRegionQ[regi] is True, the regions are point sets, and typically True or False is returned.
- If some regi depend on parameters, i.e. ConstantRegionQ[regi] is False, then regi represents a family of regions, and RegionEqual will attempt to compute conditions on parameters such that the regions are equal.
- The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate conditions on parameters
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (16)
Basic Uses (4)
Basic Regions (4)
Regions in ![]() including Line and Interval:
including Line and Interval:
Ball:
Regions in ![]() including Point:
including Point:
Line:
Rectangle and RegularPolygon:
Regions in ![]() including Point:
including Point:
Line:
Cuboid and Hexahedron:
Tetrahedron and Simplex:
Regions in ![]() including Cuboid and Parallelepiped in
including Cuboid and Parallelepiped in ![]() :
:
Formula Regions (4)
Mesh Regions (3)
Compare MeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Compare BoundaryMeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Compare MeshRegion with BoundaryMeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Derived Regions (1)
Compare BooleanRegion:
Options (2)
Applications (6)
Find when two lamina are equal:
Create the unit disk by covering the hole of an annulus with a disk. Find all possible radii:
Create the unit disk by covering the hole of an annulus with a square. Find all possible side lengths:
Find all ways to express the unit rectangle in terms of Parallelogram:
Express an implicitly defined ellipse through Ellipsoid:
Find a value for each parameter:
Properties & Relations (4)
Equivalent regions have all points in common:
RegionEqual can be expressed with RegionWithin:
For non‐empty regions, RegionDisjoint returns False when RegionEqual returns True:
Use FindInstance to find points that lie in one region but not the other:
Use RandomPoint to find a uniform sampling of points that lie in one region but not the other:
Use Reduce to find where two regions differ:
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), RegionEqual, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionEqual.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "RegionEqual." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionEqual.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). RegionEqual. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionEqual.html