- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Manipulating Equations
- Formula Manipulation
- Number Theory
- Computational Geometry
- Polynomial Algebra
- Polynomial Equations
- Diophantine Equations
- Polynomial Systems
- Equation Solving
- Theorem Proving
- Inequalities
- Solvers over Regions
- Solid Geometry
- Plane Geometry
- Finite Fields
- Finite Mathematics
- Polygons
- Polyhedra
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
-
Tech Notes
- Solving Equations
- Inequalities
- Generic and Non‐Generic Solutions
- Equations and Inequalities over Domains
- Solving Logical Combinations of Equations
- The Representation of Solution Sets
- Complex Polynomial Systems
- Real Polynomial Systems
- Diophantine Polynomial Systems
- Implementation notes: Algebra and Calculus
-
- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Manipulating Equations
- Formula Manipulation
- Number Theory
- Computational Geometry
- Polynomial Algebra
- Polynomial Equations
- Diophantine Equations
- Polynomial Systems
- Equation Solving
- Theorem Proving
- Inequalities
- Solvers over Regions
- Solid Geometry
- Plane Geometry
- Finite Fields
- Finite Mathematics
- Polygons
- Polyhedra
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
-
Tech Notes
- Solving Equations
- Inequalities
- Generic and Non‐Generic Solutions
- Equations and Inequalities over Domains
- Solving Logical Combinations of Equations
- The Representation of Solution Sets
- Complex Polynomial Systems
- Real Polynomial Systems
- Diophantine Polynomial Systems
- Implementation notes: Algebra and Calculus




Reduce
Details and Options




- The statement expr can be any logical combination of:
-
lhs==rhs equations lhs!=rhs inequations lhs>rhs or lhs>=rhs inequalities expr∈dom domain specifications {x,y,…}∈reg region specification ForAll[x,cond,expr] universal quantifiers Exists[x,cond,expr] existential quantifiers - The result of Reduce[expr,vars] always describes exactly the same mathematical set as expr.
- Reduce[{expr1,expr2,…},vars] is equivalent to Reduce[expr1&&expr2&&…,vars].
- Reduce[expr,vars] assumes by default that quantities appearing algebraically in inequalities are real, while all other quantities are complex.
- Reduce[expr,vars,dom] restricts all variables and parameters to belong to the domain dom.
- If dom is Reals, or a subset such as Integers or Rationals, then all constants and function values are also restricted to be real.
- Reduce[expr&&vars∈Reals,vars,Complexes] performs reductions with variables assumed real, but function values allowed to be complex.
- Reduce[expr,vars,Integers] reduces Diophantine equations over the integers.
- Reduce[…,x∈reg,Reals] constrains x to be in the region reg. The different coordinates for x can be referred to using Indexed[x,i].
- Reduce[expr,{x1,x2,…},…] effectively writes expr as a combination of conditions on x1, x2, … where each condition involves only the earlier
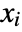 .
. - Algebraic variables in expr free of the
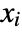 and of each other are treated as independent parameters.
and of each other are treated as independent parameters. - Applying LogicalExpand to the results of Reduce[expr,…] yields an expression of the form
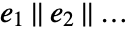 , where each of the
, where each of the 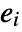 can be thought of as representing a separate component in the set defined by expr.
can be thought of as representing a separate component in the set defined by expr. - The
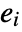 may not be disjoint and may have different dimensions. After LogicalExpand, each of the
may not be disjoint and may have different dimensions. After LogicalExpand, each of the 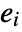 has the form
has the form 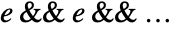 .
. - Without LogicalExpand, Reduce by default returns a nested collection of conditions on the
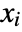 , combined alternately by Or and And on successive levels.
, combined alternately by Or and And on successive levels. - When expr involves only polynomial equations and inequalities over real or complex domains, then Reduce can always in principle solve directly for all the
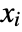 .
. - When expr involves transcendental conditions or integer domains, Reduce will often introduce additional parameters in its results.
- When expr involves only polynomial conditions, Reduce[expr,vars,Reals] gives a cylindrical algebraic decomposition of expr.
- Reduce can give explicit representations for solutions to all linear equations and inequalities over the integers and can solve a large fraction of Diophantine equations described in the literature.
- When expr involves only polynomial conditions over real or complex domains, Reduce[expr,vars] will always eliminate quantifiers, so that quantified variables do not appear in the result.
- The following options can be given:
-
Backsubstitution False whether to give results unwound by backsubstitution » Cubics False whether to use explicit radicals to solve all cubics » GeneratedParameters C how to name parameters that are generated » Modulus 0 modulus to assume for integers » Quartics False whether to use explicit radicals to solve all quartics » - Reduce[expr,{x1,x2,…},Backsubstitution->True] yields a form in which values from equations generated for earlier
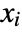 are backsubstituted so that the conditions for a particular
are backsubstituted so that the conditions for a particular 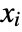 have only minimal dependence on earlier
have only minimal dependence on earlier 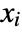 . »
. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (83)
Basic Uses (5)
Find an explicit description of the solution set of a system of equations:
Use ToRules and ReplaceRepeated (//.) to list the solutions:
Find an explicit description of the solution set of a system of inequalities:
Find solutions over specified domains:
The solution set may depend on symbolic parameters:
Representing solutions may require introduction of new parameters:
Complex Domain (16)
A univariate polynomial equation:
A multivariate polynomial equation:
Systems of polynomial equations and inequations can always be reduced:
A quantified polynomial system:
Transcendental equations solvable in terms of inverse functions:
In this case there is no solution:
Equations involving elliptic functions:
Equations solvable using special function zeros:
Solving this system does not require the Riemann hypothesis:
Elementary function equation in a bounded region:
Holomorphic function equation in a bounded region:
Here Reduce finds some solutions but is not able to prove there are no other solutions:
Equation with a purely imaginary period over a vertical stripe in the complex plane:
Doubly periodic transcendental equation:
A system of transcendental equations solvable using inverse functions:
Real Domain (26)
A univariate polynomial equation:
A univariate polynomial inequality:
A multivariate polynomial equation:
A multivariate polynomial inequality:
Systems of polynomial equations and inequalities can always be reduced:
A quantified polynomial system:
Transcendental equations, solvable using inverse functions:
Transcendental inequalities, solvable using inverse functions:
Inequalities involving elliptic functions:
Transcendental equation, solvable using special function zeros:
Transcendental inequality, solvable using special function zeros:
High-degree sparse polynomial equation:
Algebraic equation involving high-degree radicals:
Equation involving irrational real powers:
Elementary function equation in a bounded interval:
Holomorphic function equation in a bounded interval:
Meromorphic function inequality in a bounded interval:
Periodic elementary function equation over the reals:
Transcendental systems solvable using inverse functions:
Systems exp-log in the first variable and polynomial in the other variables:
Systems elementary and bounded in the first variable and polynomial in the other variables:
Systems analytic and bounded in the first variable and polynomial in the other variables:
Integer Domain (13)
Modular Domains (5)
Finite Field Domains (4)
Mixed Domains (4)
Mixed real and complex variables:
Find real values of ![]() and complex values of
and complex values of ![]() for which
for which ![]() is real and less than
is real and less than ![]() :
:
Reduce an inequality involving Abs[x]:
Geometric Regions (10)
Constrain variables to basic geometric regions in 2D:
Constrain variables to basic geometric regions in 3D:
Project a 3D region onto the ![]() -
-![]() plane:
plane:
A parametrically defined region:
The solution of ![]() restricted to the intersection:
restricted to the intersection:
Eliminate quantifiers over a Cartesian product of regions:
Regions dependent on parameters:
Options (6)
Backsubstitution (1)
Cubics (1)
GeneratedParameters (1)
Reduce may introduce new parameters to represent the solution:
Use GeneratedParameters to control how the parameters are generated:
Quartics (1)
WorkingPrecision (1)
Finding the solution with exact computations takes a long time:
With WorkingPrecision->100, Reduce finds a solution fast, but it may be incorrect:
Applications (9)
Basic Applications (1)
Polynomial Root Problems (1)
Find conditions for a quartic to have all roots equal:
Using Subresultants:
Parametrization Problems (1)
Integer Problems (3)
Find a sequence of Pythagorean triples:
Find how to pay $2.27 postage with 10-, 23- and 37-cent stamps:
The same task can be accomplished with IntegerPartitions:
Show that there are only five regular polyhedrons:
Each face for a regular ![]() -gon contributes
-gon contributes ![]() edges, but they are shared, so they are counted twice:
edges, but they are shared, so they are counted twice:
Each face for a regular ![]() -gon contributes
-gon contributes ![]() vertices, but they are shared, so they are counted
vertices, but they are shared, so they are counted ![]() times:
times:
Using Euler's formula ![]() , find the number of faces:
, find the number of faces:
For this last formula to be well defined, the denominator needs to be positive and an integer:
Hence the following five cases:
Compare this to the actual counts in PolyhedronData:
Geometry Problems (3)
The region ℛ is a subset of if ![]() is true. Show that Disk[{0,0},{2,1}] is a subset of Rectangle[{-2,-1},{2,1}]:
is true. Show that Disk[{0,0},{2,1}] is a subset of Rectangle[{-2,-1},{2,1}]:
Show that Cylinder[]⊆Ball[{0,0,0},2]:
For a finite point set ![]() , the Voronoi cell for a point
, the Voronoi cell for a point ![]() can be defined by
can be defined by ![]() , which corresponds to all points closer to
, which corresponds to all points closer to ![]() than any other point
than any other point ![]() for
for ![]() . Find a simple formula for a Voronoi cell, using Reduce:
. Find a simple formula for a Voronoi cell, using Reduce:
The Voronoi cell associated with pts〚1〛 is given by:
The resulting cell is given by an intersection of half-spaces:
Properties & Relations (10)
The result of reduction is equivalent to the original system:
ToRules and ReplaceRepeated can be used to backsubstitute finite solution sets:
Use Expand to simplify a result of substitution involving simple radicals:
To simplify expressions involving algebraic numbers,, use RootReduce:
To find solution instances, use FindInstance:
Solve represents solutions of complex equations in terms of replacement rules:
Solve omits solutions involving equations on parameters:
For transcendental equations, Solve may not give all solutions:
Using inverse functions allows Solve to find some solutions fast:
Finding the complete solution may take much longer, and the solution may be large:
This finds the values of ![]() for which x 2 is a solution:
for which x 2 is a solution:
SolveAlways gives the values of parameters for which complex equations are always true:
This solves the same problem using Reduce:
Resolve eliminates quantifiers, possibly without solving the resulting quantifier‐free system:
Eliminate eliminates variables from systems of complex equations:
This solves the same problem using Resolve:
Reduce additionally solves the resulting equations:
Possible Issues (3)
Because ![]() appears in an inequality, it is assumed to be real;
appears in an inequality, it is assumed to be real; ![]() is allowed to be complex:
is allowed to be complex:
When domain Reals is specified, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and Sqrt[x] are required to be real:
, and Sqrt[x] are required to be real:
This allows complex values of ![]() for which both sides of the inequality are real:
for which both sides of the inequality are real:
Reduce does not solve equations that depend on branch cuts of Wolfram Language functions:

Plot the region where the first condition is nonzero:
Removable singularities of input equations are generally not considered valid solutions:
However, solutions may include removable singularities that are cancelled by automatic simplification:
The removable singularity at ![]() is cancelled by evaluation:
is cancelled by evaluation:
Here the removable singularity at ![]() is cancelled by Together, which is used to preprocess the equation:
is cancelled by Together, which is used to preprocess the equation:
Tech Notes
-
▪
- Solving Equations ▪
- Inequalities ▪
- Generic and Non‐Generic Solutions ▪
- Equations and Inequalities over Domains ▪
- Solving Logical Combinations of Equations ▪
- The Representation of Solution Sets ▪
- Complex Polynomial Systems ▪
- Real Polynomial Systems ▪
- Diophantine Polynomial Systems ▪
- Implementation notes: Algebra and Calculus
Related Guides
-
▪
- Manipulating Equations ▪
- Formula Manipulation ▪
- Number Theory ▪
- Computational Geometry ▪
- Polynomial Algebra ▪
- Polynomial Equations ▪
- Diophantine Equations ▪
- Polynomial Systems ▪
- Equation Solving ▪
- Theorem Proving ▪
- Inequalities ▪
- Solvers over Regions ▪
- Solid Geometry ▪
- Plane Geometry ▪
- Finite Fields ▪
- Finite Mathematics ▪
- Polygons ▪
- Polyhedra ▪
- Symbolic Vectors, Matrices and Arrays
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2003 (5.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2024 (14.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Reduce, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Reduce.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Reduce." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Reduce.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Reduce. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Reduce.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_reduce, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Reduce}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Reduce.html}", note=[Accessed: 07-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_reduce, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Reduce}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Reduce.html}, note=[Accessed: 07-February-2026]}