NSurfaceIntegrate[f,{x,y,…}∈surface]
computes the numerical scalar surface integral of the function f[x,y,…] over the surface.
NSurfaceIntegrate[{p,q,…},{x,y,…}∈surface]
computes the numerical vector surface integral of the vector field {p[x,y,…],q[x,y,…],…}.




NSurfaceIntegrate
NSurfaceIntegrate[f,{x,y,…}∈surface]
computes the numerical scalar surface integral of the function f[x,y,…] over the surface.
NSurfaceIntegrate[{p,q,…},{x,y,…}∈surface]
computes the numerical vector surface integral of the vector field {p[x,y,…],q[x,y,…],…}.
Details and Options




- Surface integrals are also known as flux integrals.
- Scalar surface integrals integrate scalar functions over a hypersurface. They are typically used to compute things like area, mass and charge for a surface.
- Vector surface integrals are used to compute the flux of a vector function through a surface in the direction of its normal. Typical vector functions include a fluid velocity field, an electric field and a magnetic field.
- The scalar surface integral of a function f over a surface
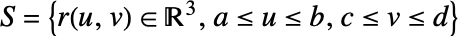 is given by:
is given by: - … where
![TemplateBox[{{{{partial, _, u}, {r, (, {u, ,, v}, )}}, x, {{partial, _, v}, {r, (, {u, ,, v}, )}}}}, Norm] TemplateBox[{{{{partial, _, u}, {r, (, {u, ,, v}, )}}, x, {{partial, _, v}, {r, (, {u, ,, v}, )}}}}, Norm]](Files/NSurfaceIntegrate.en/4.png) is the measure of a parametric surface element.
is the measure of a parametric surface element. - The scalar surface integral of f over a hypersurface
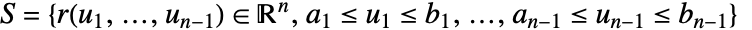 is given by:
is given by: - The scalar surface integral is independent of the parametrization and orientation of the surface. Any
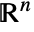 dimensional RegionQ object in
dimensional RegionQ object in 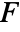 can be use for the surface.
can be use for the surface. - The vector surface integral of a vector function
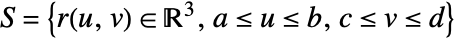 over a surface
over a surface 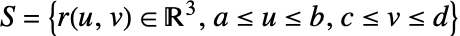 is given by:
is given by: - … where
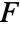 is the projection of the vector function
is the projection of the vector function 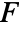 onto the normal direction so only the component in the normal direction gets integrated.
onto the normal direction so only the component in the normal direction gets integrated. - The vector surface integral of
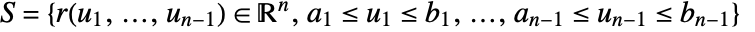 over a a hypersurface
over a a hypersurface 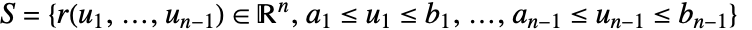 is given by:
is given by: - The vector surface integral is independent of the parametrization, but depends on the orientation.
- The orientation for a hypersurface is given by a normal vector field
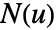 over the surface.
over the surface. - For a parametric hypersurface ParametricRegion[{r1[u1,…,un-1],…,rn[u1,…,un-1]},…], the normal vector field
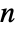 is taken to be Cross[∂u1r[u],…,∂un-1r[u]].
is taken to be Cross[∂u1r[u],…,∂un-1r[u]]. - The RegionQ objects in Wolfram Language are not oriented. However, for the convenience of this function, you can assume the following rules for getting oriented hypersurfaces.
- For solid (of dimension
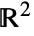 ) and bounded RegionQ objects ℛ, take the surface to be the region boundary (RegionBoundary[ℛ]) and the normal orientation to be pointed outward.
) and bounded RegionQ objects ℛ, take the surface to be the region boundary (RegionBoundary[ℛ]) and the normal orientation to be pointed outward. - Special solids in
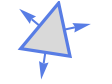 with their assumed boundary surface (edge) normal orientations include:
with their assumed boundary surface (edge) normal orientations include: -
Triangle outward normal 
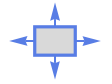
Rectangle outward normal 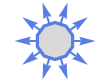
Polygon outward normal 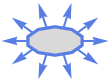
Disk outward normal 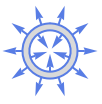
Ellipsoid outward normal 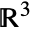
Annulus outward normal - Special solids in
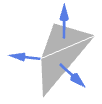 with their assumed boundary surface (face) normal orientations include:
with their assumed boundary surface (face) normal orientations include: -
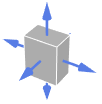
Tetrahedron outward normal 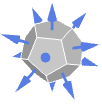
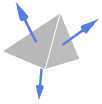
Cuboid outward normal 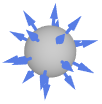
Polyhedron outward normal 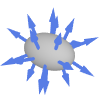
Ball outward normal 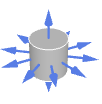
Ellipsoid outward normal 
Cylinder outward normal 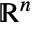
Cone outward normal - Special solids in
 with their assumed surface (facet) and normal orientations:
with their assumed surface (facet) and normal orientations: -
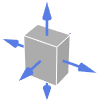
Simplex outward normal 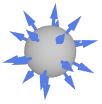
Cuboid outward normal 
Ball outward normal 
Ellipsoid outward normal - The coordinates on the surface can be specified using VectorSymbol. »
- The following options can be given:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic digits of absolute accuracy sought MaxPoints Automatic maximum total number of sample points MaxRecursion Automatic maximum number of recursive subdivisions Method Automatic method to use MinRecursion 0 minimum number of recursive subdivisions PrecisionGoal Automatic digits of precision sought WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations
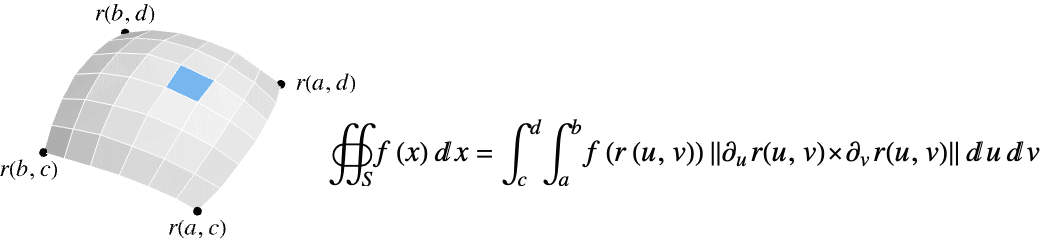
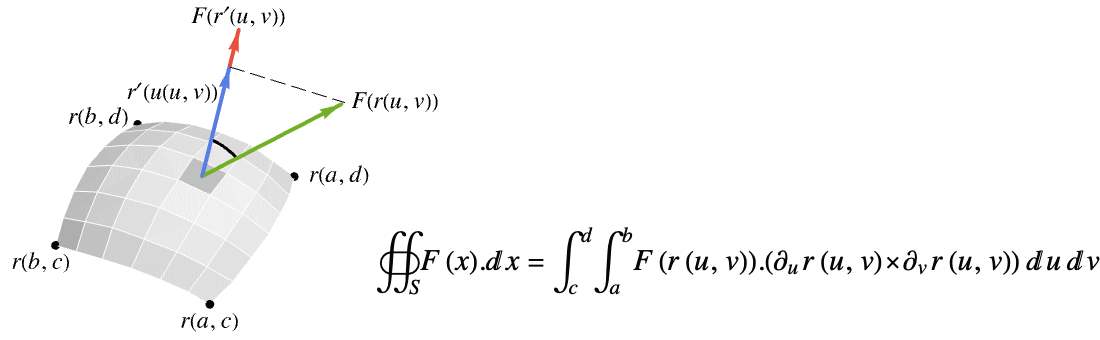
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (7)
Surface integral of a scalar function over a spherical surface:
Surface integral of a vector field over a spherical surface:
Surface integral of a scalar field over a parametric surface:
Surface integral of a vector field over a parametric surface:
Surface integral of a scalar field over a surface:
Visualize the scalar field on the surface:
Surface integral of a vector field over a surface:
Visualize the scalar field on the surface:
Use VectorSymbol:
Scope (32)
Basic Uses (5)
Surface integral of a scalar field over a cube in three dimensions:
Surface integral of a vector field in three dimensions:
SurfaceIntegrate works with many special surfaces:
Surface integral over a parametric surface:
SurfaceIntegrate works in dimensions different from three:
Scalar Functions (5)
Surface integral of a scalar field over a three-dimensional surface:
Surface integral of a scalar field over a triangle:
Surface integral of a scalar field in three dimensions over a sphere:
Surface integral of a scalar field over the surface of a pyramid:
Surface integral of a scalar field over a parametric surface in three dimensions:
Vector Functions (5)
Surface integral of a vector field in three dimensions over a sphere:
Visualize the vector field on the surface:
Surface integral of a vector field in three dimensions over a triangle:
Surface integral of a vector field over a parametric surface in three dimensions:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of an ellipsoid:
Surface integral of a vector field in three dimensions over the boundary of a cone:
Special Surfaces (10)
Surface integral of a vector field over a sphere of radius 1:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a cube of side 2 centered at the origin:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a tetrahedron:
Surface integral of a vector field over a triangle:
Surface integral of a vector field over an ellipsoid:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a cone:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a cylinder:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a parallelepiped:
Surface integral of a vector field over the boundary of a prism:
Surface integral over a polygon in three dimensions:
The orientation of the polygon depends on the order in which the points are given:
Parametric Surfaces (4)
Options (8)
AccuracyGoal (1)
The option AccuracyGoal sets the number of digits of accuracy:
The result with default settings only sets a PrecisionGoal:
MaxPoints (1)
MaxRecursion (1)
The option MaxRecursion specifies the maximum number of recursive steps:
Increasing the number of recursions:
Method (1)
The option Method can take the same values as in NIntegrate. For example:
MinRecursion (1)
PrecisionGoal (1)
WorkingPrecision (2)
If a WorkingPrecision is specified, the calculation is done with that working precision:
Applications (18)
College Calculus (5)
Volumes (3)
Flux (3)
Flux of the electric field generated by a point charge ![]() at the origin over a sphere surrounding it:
at the origin over a sphere surrounding it:
Flux of the uniform magnetic field of an infinite solenoid with ![]() windings per unit length traversed by a current
windings per unit length traversed by a current ![]() over a disk orthogonal to it:
over a disk orthogonal to it:
Electric field due to an infinite charged wire of linear charge density ![]() :
:
Flux across a cylinder of height ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() having the axis on the charged wire:
having the axis on the charged wire:
Centroids (2)
Classical Theorems (2)
Stokes's theorem. The surface integral of the Curl ![]() of a vector field
of a vector field ![]() :
:
The surface integral of ![]() over an open surface is:
over an open surface is:
It is the same as the line integral of ![]() over the boundary of the surface:
over the boundary of the surface:
Divergence theorem. The surface integral of a vector field ![]() (with continuous partial derivatives) over a closed surface is:
(with continuous partial derivatives) over a closed surface is:
It is the same as the integral of Div[f] over the interior of the surface:
Properties & Relations (5)
Apply N[SurfaceIntegrate[…]] to obtain a numerical solution with NSurfaceIntegrate if the symbolic calculation fails:
Find the center of mass of a thin triangular surface of unit mass per unit area:
Find the ![]() component of the center of mass:
component of the center of mass:
Find the ![]() component of the center of mass:
component of the center of mass:
Find the ![]() component of the center of mass:
component of the center of mass:
The center of mass can also be obtained using RegionCentroid:
Find the moment of inertia around the ![]() axis of a thin cylindrical shell of unit area density:
axis of a thin cylindrical shell of unit area density:
The answer can also be computed with MomentOfInertia:
Find the area of a tetrahedron:
The answer can also be computed with SurfaceArea:
Find the volume of an icosahedron:
The answer can also be computed with Volume:
Neat Examples (9)
Volume of a pseudosphere computed using a surface integral:
Plot of a finite part of the pseudosphere:
Volume of a drop-shaped solid using a surface integral:
Flux of a vector field across a part of a Bohemian dome:
Surface integral of a vector field over a portion of a conocuneus of Wallis:
Surface integral of a vector field over a funnel-shaped surface:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), NSurfaceIntegrate, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NSurfaceIntegrate.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "NSurfaceIntegrate." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NSurfaceIntegrate.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). NSurfaceIntegrate. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NSurfaceIntegrate.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_nsurfaceintegrate, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NSurfaceIntegrate}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NSurfaceIntegrate.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_nsurfaceintegrate, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NSurfaceIntegrate}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NSurfaceIntegrate.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}

