InverseFourierCosTransform
InverseFourierCosTransform[expr,ω,t]
给出 expr 的符号傅立叶余弦逆变换.
InverseFourierCosTransform[expr,{ω1,ω2,…},{t1,t2,…}]
给出 expr 的多维傅立叶余弦逆变换.
更多信息和选项



- The Fourier cosine transform is a particular way of viewing the Fourier transform without the need for complex numbers or negative frequencies.
- Joseph Fourier designed his famous transform using this and the Fourier sine transform, and they are still used in applications like signal processing, statistics and image and video compression.
- The inverse Fourier cosine transform of the frequency domain function
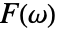 is the time domain function
is the time domain function 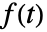 for
for 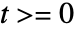 :
: - 一个函数
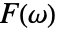 的傅立叶余弦逆变换在缺省情况下定义成
的傅立叶余弦逆变换在缺省情况下定义成 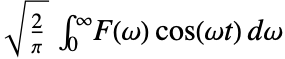 .
. - The multidimensional inverse Fourier cosine transform of a function
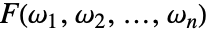 is by default defined as
is by default defined as 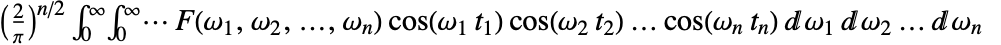 or when using vector notation,
or when using vector notation, ![(2/pi)^(n/2)int_(omega in TemplateBox[{}, PositiveReals]^n)F(omega) cos(omega t)domega (2/pi)^(n/2)int_(omega in TemplateBox[{}, PositiveReals]^n)F(omega) cos(omega t)domega](Files/InverseFourierCosTransform.zh/9.png) .
. - 不同的定义选择可以用选项 FourierParameters 指定.
- The integral is computed using numerical methods if the third argument,
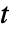 , is given a numerical value.
, is given a numerical value. - The asymptotic inverse Fourier cosine transform can be computed using Asymptotic.
- There are several related Fourier transformations:
-
FourierTransform infinite continuous-time functions (FT) FourierSequenceTransform infinite discrete-time functions (DTFT) FourierCoefficient finite continuous-time functions (FS) Fourier finite discrete-time functions (DFT) - The inverse Fourier cosine transform is an automorphism in the Schwartz vector space of functions whose derivatives are rapidly decreasing and thus induces an automorphism in its dual: the space of tempered distributions. These include absolutely integrable functions, well-behaved functions of polynomial growth and compactly supported distributions.
- Hence, InverseFourierCosTransform not only works with absolutely integrable functions on
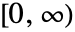 , but it can also handle a variety of tempered distributions such as DiracDelta to enlarge the pool of functions or generalized functions it can effectively transform.
, but it can also handle a variety of tempered distributions such as DiracDelta to enlarge the pool of functions or generalized functions it can effectively transform. - The lower limit of the integral is effectively taken to be
![TemplateBox[{0, -}, Superscript] TemplateBox[{0, -}, Superscript]](Files/InverseFourierCosTransform.zh/12.png) , so that the inverse Fourier cosine transform of the Dirac delta function
, so that the inverse Fourier cosine transform of the Dirac delta function 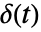 is equal to
is equal to 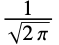 . »
. » - The following options can be given:
-
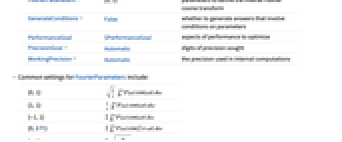
AccuracyGoal Automatic digits of absolute accuracy sought Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters FourierParameters {0,1} parameters to define the inverse Fourier cosine transform GenerateConditions False whether to generate answers that involve conditions on parameters PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to optimize PrecisionGoal Automatic digits of precision sought WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations - Common settings for FourierParameters include:
-
{0,1} 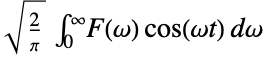
{1,1} 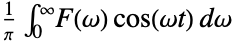
{-1,1} 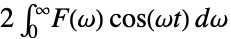
{0,2Pi} 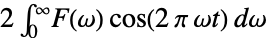
{a,b} 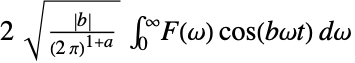
范例
打开所有单元关闭所有单元基本范例 (6)
Compute the inverse Fourier cosine transform of a function:
Plot the function and its inverse cosine transform:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of reciprocal square root:
For a different convention, change the parameters:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of a Gaussian is another Gaussian:
Compute the inverse Fourier cosine transform of a multivariate function:
范围 (43)
Basic Uses (3)
Algebraic Functions (4)
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of power functions:
For integer ![]() , the result is a derivative of DiracDelta:
, the result is a derivative of DiracDelta:
Inverse cosine transforms for rational functions:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of a quotient of two nonlinear polynomials:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of a quotient of quadratic and quartic polynomials:
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions (4)
Trigonometric Functions (5)
Special Functions (9)
Sinc function:
Inverse Fourier cosine transforms of expressions involving ExpIntegralEi:
Expression involving Erfc:
Expression involving SinIntegral:
Inverse cosine transforms for BesselJ functions:
Cosine transforms for BesselY functions:
Cosine transform for a BesselK function:
Inverse cosine transform for a hypergeometric function is a BesselK function:
Piecewise Functions and Distributions (4)
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of a piecewise function:
Restriction of a sine function to a half-period:
Transforms in terms of FresnelC:
Periodic Functions (2)
Generalized Functions (4)
Inverse Fourier cosine transforms of expressions involving HeavisideTheta:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform involving DiracDelta:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform involving HeavisideLambda:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform involving HeavisidePi:
Multivariate Functions (3)
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of rational function in two variables:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of exponential in two variables:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform of product of exponential and SquareWave:
Formal Properties (3)
选项 (8)
AccuracyGoal (1)
The option AccuracyGoal sets the number of digits of accuracy:
Assumptions (1)
用 Assumptions 定来指定感兴趣的参数区域:
FourierParameters (3)
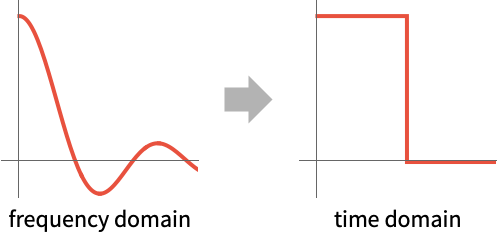
Inverse Fourier cosine transform for the unit box function with different parameters:
To get the original function back, use the same FourierParameters setting:
Set up your particular global choice of parameters to work once per session:
GenerateConditions (1)
当结果有效时,用 GenerateConditions->True 获得参数条件:
PrecisionGoal (1)
The option PrecisionGoal sets the relative tolerance in the integration:
WorkingPrecision (1)
If a WorkingPrecision is specified, the computation is done at that working precision:
应用 (4)
Ordinary Differential Equations (1)
Consider the following ODE with initial condition ![]() :
:
Apply the Fourier cosine transform to the ODE:
Solve for the Fourier cosine transform of ![]() :
:
Find the inverse Fourier cosine transform with ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Compare with DSolveValue:
Partial Differential Equations (1)
Solve the heat equation for ![]() ,
, ![]() :
: ![]() with initial condition
with initial condition ![]() for
for ![]() and Neumann boundary condition
and Neumann boundary condition ![]() for
for ![]() :
:
Apply the Fourier cosine transform to the ODE on ![]() :
:
Compute the inverse cosine transform of the exponential functions:
Convolution property gives the inverse cosine transform of the first summand to get the solution:
Consider the special case with ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Compare with DSolveValue:
Plot the initial conditions and solutions for different values of ![]() .
.
Evaluation of Integrals (2)
Calculate the following definite integral:
Inverse Fourier cosine transform preserves integration of products over ![]() :
:
Compare with Integrate:
Calculate the following definite integral for ![]() :
:
Compute inverse fourier cosine transform of the square root of the integrand:
Solve for the definite integral:
Compare with Integrate:
属性和关系 (4)
By default, the inverse Fourier cosine transform of ![]() is:
is:
For ![]() , the definite integral becomes:
, the definite integral becomes:
Compare with InverseFourierCosTransform:
用 Asymptotic 计算渐近近似:
FourierCosTransform 和 InverseFourierCosTransform 是互逆的:
For even functions results are identical to InverseFourierTransform:
可能存在的问题 (1)
The result from a Fourier cosine transform may not have the same form as the original:
傅立叶余弦逆变换可能需要类似 DiracDelta 的广义函数:
文本
Wolfram Research (1999),InverseFourierCosTransform,Wolfram 语言函数,https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseFourierCosTransform.html (更新于 2025 年).
CMS
Wolfram 语言. 1999. "InverseFourierCosTransform." Wolfram 语言与系统参考资料中心. Wolfram Research. 最新版本 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseFourierCosTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram 语言. (1999). InverseFourierCosTransform. Wolfram 语言与系统参考资料中心. 追溯自 https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseFourierCosTransform.html 年