represents a beta prime distribution with shape parameters p and q.
BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,β]
represents a generalized beta prime distribution with scale parameter β.
BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β]
represents a generalized beta distribution of the second kind with shape parameter α.


BetaPrimeDistribution
represents a beta prime distribution with shape parameters p and q.
BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,β]
represents a generalized beta prime distribution with scale parameter β.
BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β]
represents a generalized beta distribution of the second kind with shape parameter α.
Details
- BetaPrimeDistribution[1,q,1,β] is also known as the Lomax distribution.
- The probability density for value
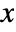 in a beta prime distribution is proportional to
in a beta prime distribution is proportional to 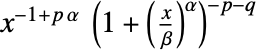 for
for 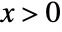 .
. - BetaPrimeDistribution allows p, q, α, and β to be any positive real numbers.
- BetaPrimeDistribution allows β to be a quantity of any unit dimension, and p, q, and α to be dimensionless quantities. »
- BetaPrimeDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate.
Background & Context
- BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β] represents a continuous statistical distribution defined over the interval
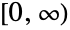 and parametrized by four positive real numbers p, q, α, and β. The parameters p, q, and α are known as "shape parameters", β is known as a "scale parameter", and together, these parameters determine the overall shape of the probability density function (PDF) of the beta prime distribution. Depending on the values of p, q, α, and β, the PDF of the beta prime distribution may be unimodal or monotonic decreasing with potential singularities approaching the lower boundary of its domain. In addition, the tails of the PDF are "fat" in the sense that the PDF decreases algebraically rather than exponentially for large values
and parametrized by four positive real numbers p, q, α, and β. The parameters p, q, and α are known as "shape parameters", β is known as a "scale parameter", and together, these parameters determine the overall shape of the probability density function (PDF) of the beta prime distribution. Depending on the values of p, q, α, and β, the PDF of the beta prime distribution may be unimodal or monotonic decreasing with potential singularities approaching the lower boundary of its domain. In addition, the tails of the PDF are "fat" in the sense that the PDF decreases algebraically rather than exponentially for large values 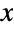 . (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.)
. (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) - BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β] is sometimes referred to as the generalized beta distribution of the second kind, the inverted beta distribution, or the type VI Pearson distribution (PearsonDistribution). The two- and three-argument forms BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q] and BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,β] evaluate to BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,1,1] and BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,1,β], respectively, and are sometimes referred to as the standard beta prime distribution and the generalized beta prime distribution, respectively.
- In Bayesian analysis, the beta prime distribution arises as a prior distribution for binomial proportions expressed as odds. The beta prime distribution has also been found to model many real-world phenomena. For example, the beta prime distribution has proven useful in empirically estimating security returns and in the development of option pricing models. More recently, it has been applied to the modeling of insurance loss processes. Elsewhere, the long tail of the beta prime distribution has been shown to make the distribution particularly well suited to modeling the frequency of behaviors likely to transmit diseases among individuals versus the actual transmission of such diseases.
- RandomVariate can be used to give one or more machine- or arbitrary-precision (the latter via the WorkingPrecision option) pseudorandom variates from a beta prime distribution. Distributed[x,BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β]], written more concisely as xBetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β], can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a beta prime distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation.
- The probability density and cumulative distribution functions may be given using PDF[BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β],x] and CDF[BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,α,β],x]. The mean, median, variance, raw moments, and central moments may be computed using Mean, Median, Variance, Moment, and CentralMoment, respectively.
- DistributionFitTest can be used to test if a given dataset is consistent with a beta prime distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a beta prime parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a beta prime distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic beta prime distribution and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic beta prime distribution.
- TransformedDistribution can be used to represent a transformed beta prime distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a beta prime distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving beta prime distributions.
- BetaPrimeDistribution is related to a number of other distributions. For example, BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,a,b] simplifies to DagumDistribution[p,a,b] when
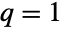 , to SinghMaddalaDistribution[q,a,b] when
, to SinghMaddalaDistribution[q,a,b] when 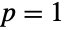 , and to LogLogisticDistribution[a,b] when both
, and to LogLogisticDistribution[a,b] when both 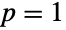 and
and 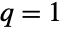 . In addition, the two-parameter form BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q] has the same PDF as the type VI Pearson distribution PearsonDistribution[6,1,f/g,1/g,1/g,0] where
. In addition, the two-parameter form BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q] has the same PDF as the type VI Pearson distribution PearsonDistribution[6,1,f/g,1/g,1/g,0] where 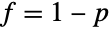 and
and 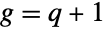 and is related to both type II and type IV versions of ParetoDistribution.The PDF of BetaPrimeDistribution is a transformation of that of BetaDistribution, while the four-parameter version BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,a,1] is the quotient
and is related to both type II and type IV versions of ParetoDistribution.The PDF of BetaPrimeDistribution is a transformation of that of BetaDistribution, while the four-parameter version BetaPrimeDistribution[p,q,a,1] is the quotient 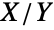 of two independent random variables XGammaDistribution[p,1,a,0] and YGammaDistribution[q,1,a,0]. BetaPrimeDistribution is also related to FRatioDistribution, DirichletDistribution, KumaraswamyDistribution, NoncentralBetaDistribution, and PERTDistribution.
of two independent random variables XGammaDistribution[p,1,a,0] and YGammaDistribution[q,1,a,0]. BetaPrimeDistribution is also related to FRatioDistribution, DirichletDistribution, KumaraswamyDistribution, NoncentralBetaDistribution, and PERTDistribution.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (19)
Probability density function of a generalized beta prime distribution:
Cumulative distribution function of a generalized beta prime distribution:
Mean and variance of a generalized beta prime distribution:
Probability density function of a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Cumulative distribution function of a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Mean and variance of a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a beta prime distribution:
Compare its histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare the density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
For a generalized beta distribution of the second kind, skewness does not depend on β:
For a generalized beta distribution of the second kind, kurtosis does not depend on β:
Different moments with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Closed form for symbolic order:
Different moments for a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Closed form for symbolic order:
Hazard function for a beta prime distribution:
Hazard function for generalized beta prime distribution:
Hazard function for generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Quantile function of a beta prime distribution:
Quantile function of a generalized beta prime distribution:
Quantile function of a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
Consistent use of Quantity in parameters yields QuantityDistribution:
Applications (2)
BetaPrimeDistribution can be used to model losses:
Remove the clear outlier, Andrew, the most destructive hurricane, and attach currency units:
Fit generalized beta distribution to the data:
Compare the histogram of the data with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Find the probability that a loss caused by a hurricane is over 3 billion dollars:
Find the mean hurricane loss in US dollars:
Simulate possible losses in millions of US dollars for the next 30 strong hurricanes:
BetaPrimeDistribution can be used to model state per-capita incomes:
Fit generalized beta distribution of the second kind to the data:
Compare the histogram of the data to the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Find the average income per capita:
Find states with income close to the average:
Find the median income per capita:
Properties & Relations (16)
Parameter influence on the CDF of a generalized beta distribution of the second kind:
BetaPrimeDistribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor:
BetaPrimeDistribution is closed under taking inverse:
Relations to other distributions:
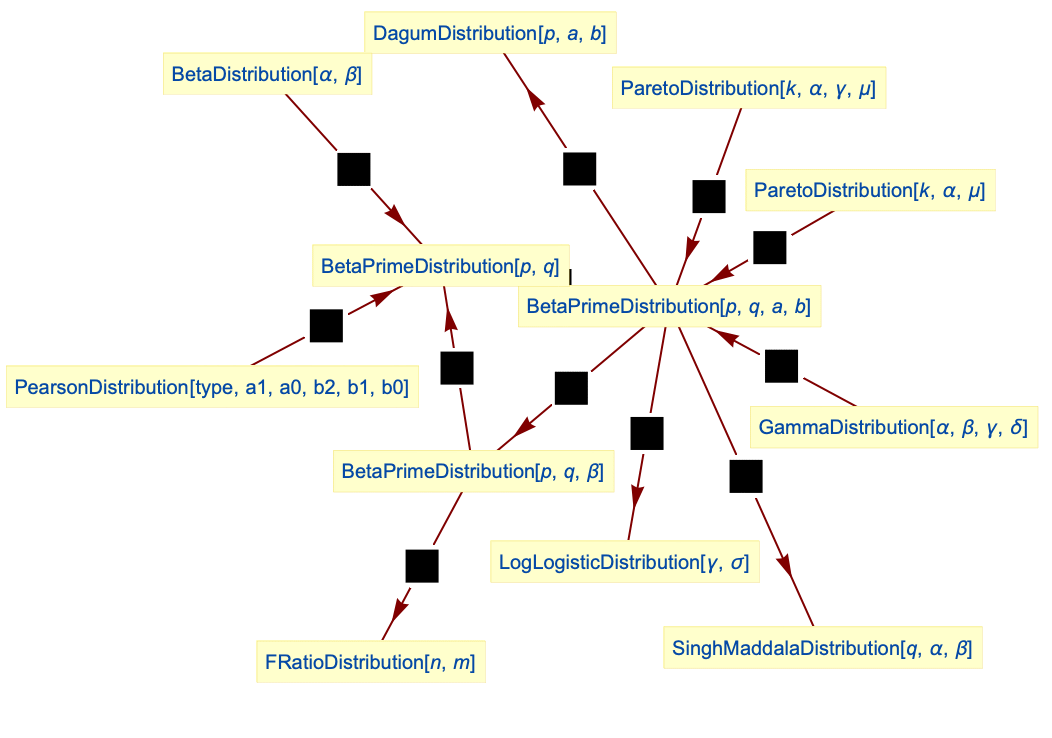
DagumDistribution is a special case of BetaPrimeDistribution:
SinghMaddalaDistribution is a special case of BetaPrimeDistribution:
LogLogisticDistribution is a special case of BetaPrimeDistribution:
FRatioDistribution is a special case of BetaPrimeDistribution:
Beta prime distribution is a special case of the type 6 PearsonDistribution:
ParetoDistribution type II is related to BetaPrimeDistribution:
ParetoDistribution type IV is related to BetaPrimeDistribution:
Beta prime distribution can be obtained as a transformation of BetaDistribution:
Generalized beta distribution of the second kind is the distribution of the ratio of two independent random variables from GammaDistribution:
Generalized beta of the second kind simplifies to beta prime:
Generalized beta prime is a special case of generalized beta of the second kind:
Generalized beta prime simplifies to beta prime distribution:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), BetaPrimeDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BetaPrimeDistribution.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "BetaPrimeDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BetaPrimeDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). BetaPrimeDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BetaPrimeDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_betaprimedistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BetaPrimeDistribution}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BetaPrimeDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_betaprimedistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BetaPrimeDistribution}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BetaPrimeDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}