HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m]
represents Hotelling's ![]() distribution with dimensionality parameter p and m degrees of freedom.
distribution with dimensionality parameter p and m degrees of freedom.


HotellingTSquareDistribution
HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m]
represents Hotelling's ![]() distribution with dimensionality parameter p and m degrees of freedom.
distribution with dimensionality parameter p and m degrees of freedom.
Details
- The probability density for value
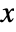 in Hotelling's T-square distribution is proportional to
in Hotelling's T-square distribution is proportional to 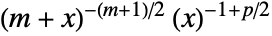 for
for 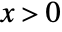 .
. - HotellingTSquareDistribution allows p and m to be any positive real numbers such that
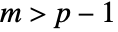 .
. - HotellingTSquareDistribution allows p and m to be dimensionless quantities.
- HotellingTSquareDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate.
Background & Context
- HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m] represents a continuous statistical distribution defined over the interval
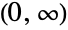 and parameterized by two positive real numbers p and m>p-1. Here, p is called a "dimensionality parameter" and m a degrees of freedom parameter. The parameter m determines the height and steepness of the probability density function (PDF) of a Hotelling
and parameterized by two positive real numbers p and m>p-1. Here, p is called a "dimensionality parameter" and m a degrees of freedom parameter. The parameter m determines the height and steepness of the probability density function (PDF) of a Hotelling 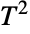 distribution. The general behavior of the PDF is determined by p and may be either monotonically decreasing with a potential singularity approaching the lower boundary of its domain (when
distribution. The general behavior of the PDF is determined by p and may be either monotonically decreasing with a potential singularity approaching the lower boundary of its domain (when 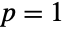 ) or unimodal (for
) or unimodal (for 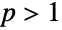 ). In addition, the tails of the PDF are "fat," in the sense that the PDF decreases algebraically rather than exponentially for large values of
). In addition, the tails of the PDF are "fat," in the sense that the PDF decreases algebraically rather than exponentially for large values of 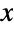 . (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.)
. (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) - The Hotelling
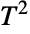 distribution dates to the early 1930s work of American mathematician Harold Hotelling that generalized the Student
distribution dates to the early 1930s work of American mathematician Harold Hotelling that generalized the Student 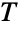 -distribution (StudentTDistribution) to cases involving hypothesis testing of p random variates. The Hotelling
-distribution (StudentTDistribution) to cases involving hypothesis testing of p random variates. The Hotelling 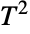 distribution forms the basis of the Hotelling test, which is a multivariate hypothesis test for the null hypothesis of equality among two unknown vectors of normally distributed variates having unknown covariance matrices. Since its creation, the Hotelling
distribution forms the basis of the Hotelling test, which is a multivariate hypothesis test for the null hypothesis of equality among two unknown vectors of normally distributed variates having unknown covariance matrices. Since its creation, the Hotelling 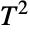 distribution has been used to model phenomena in agriculture, process control, principal component analysis, and quality control.
distribution has been used to model phenomena in agriculture, process control, principal component analysis, and quality control. - RandomVariate can be used to give one or more machine- or arbitrary-precision (the latter via the WorkingPrecision option) pseudorandom variates from a Hotelling
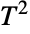 distribution. Distributed[x,HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m]], written more concisely as xHotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m], can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a Hotelling
distribution. Distributed[x,HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m]], written more concisely as xHotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m], can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a Hotelling 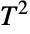 distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation.
distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation. - The probability density and cumulative distribution functions may be given using PDF[HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m],x] and CDF[HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m],x]. The mean, median, variance, raw moments, and central moments may be computed using Mean, Median, Variance, Moment, and CentralMoment, respectively.
- DistributionFitTest can be used to test if a given dataset is consistent with a Hotelling
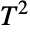 distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a Hotelling
distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a Hotelling 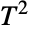 parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a Hotelling
parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a Hotelling 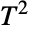 distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic Hotelling
distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic Hotelling 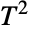 distribution and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic Hotelling
distribution and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic Hotelling 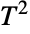 distribution.
distribution. - TransformedDistribution can be used to represent a transformed Hotelling
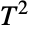 distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a Hotelling
distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a Hotelling 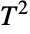 distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving Hotelling
distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving Hotelling 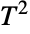 distributions.
distributions. - Hotelling's
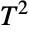 distribution is related to a number of other distributions. As previously noted, HotellingTSquareDistribution is linked to statistical testing involving NormalDistribution and MultinormalDistribution. It was devised as a generalization of StudentTDistribution and in particular, HotellingTSquareDistribution[1,m] is proportional to StudentTDistribution[m]. Under appropriate assumptions, HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m] is a special case of both PearsonDistribution (in the sense that its PDF is identical to that of PearsonDistribution[6,1,-((m(p-2))/(3+m-p)),2/(3+m-p),(2 m)/(3+m-p), 0]) and FRatioDistribution (in the sense that the CDF of HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m] is precisely CDF[FRatioDistribution[p,1 - p + m], x (m - p + 1)/(m p)]). HotellingTSquareDistribution is also related to ChiDistribution, ChiSquareDistribution, BetaDistribution, FisherZDistribution, and LaplaceDistribution.
distribution is related to a number of other distributions. As previously noted, HotellingTSquareDistribution is linked to statistical testing involving NormalDistribution and MultinormalDistribution. It was devised as a generalization of StudentTDistribution and in particular, HotellingTSquareDistribution[1,m] is proportional to StudentTDistribution[m]. Under appropriate assumptions, HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m] is a special case of both PearsonDistribution (in the sense that its PDF is identical to that of PearsonDistribution[6,1,-((m(p-2))/(3+m-p)),2/(3+m-p),(2 m)/(3+m-p), 0]) and FRatioDistribution (in the sense that the CDF of HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,m] is precisely CDF[FRatioDistribution[p,1 - p + m], x (m - p + 1)/(m p)]). HotellingTSquareDistribution is also related to ChiDistribution, ChiSquareDistribution, BetaDistribution, FisherZDistribution, and LaplaceDistribution.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (7)
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a Hotelling's T-square distribution:
Compare its histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare the density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Different moments with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Applications (1)
Hotelling's ![]() ‐statistic is used to test whether multivariate data has a given mean:
‐statistic is used to test whether multivariate data has a given mean:
For multivariate normal data of length ![]() with mean
with mean ![]() , the test statistic follows a HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,n-1] where
, the test statistic follows a HotellingTSquareDistribution[p,n-1] where ![]() is the dimension of the data:
is the dimension of the data:
Obtain the test statistic and ![]() -value for some data:
-value for some data:
Alternatively, use TTest:
Properties & Relations (3)
Relationships to other distributions:
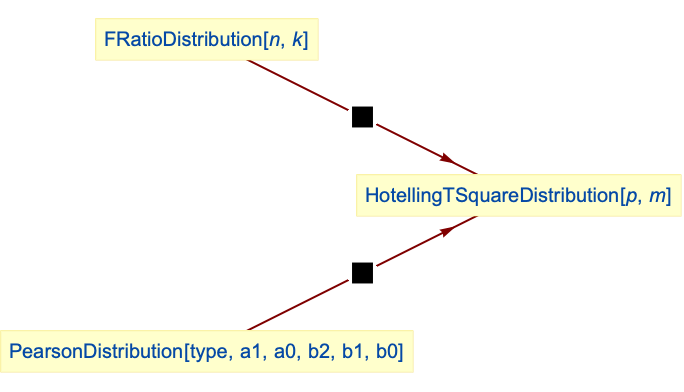
Hotelling's T-square distribution is a special case of FRatioDistribution:
Hotelling's T-square distribution is a special case of type 6 PearsonDistribution:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), HotellingTSquareDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HotellingTSquareDistribution.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "HotellingTSquareDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HotellingTSquareDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). HotellingTSquareDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HotellingTSquareDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hotellingtsquaredistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HotellingTSquareDistribution}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HotellingTSquareDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hotellingtsquaredistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HotellingTSquareDistribution}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HotellingTSquareDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}