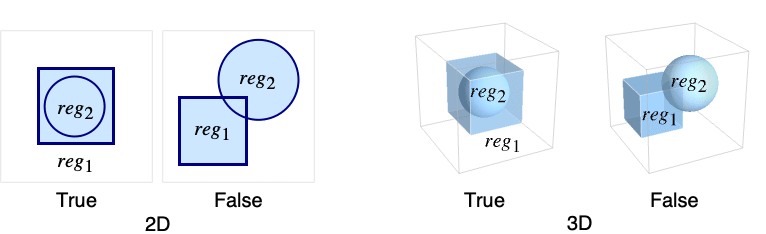
RegionWithin[reg1,reg2]
returns True if reg2 is contained within reg1.


RegionWithin
RegionWithin[reg1,reg2]
returns True if reg2 is contained within reg1.
Details and Options

- The region reg2 is contained within reg1 if every point that belongs to reg2 also belongs to reg1.
- If all regi are parameter-free regions, i.e. ConstantRegionQ[regi] is True, the regions are point sets, and typically True or False is returned.
- If some regi depend on parameters, i.e. ConstantRegionQ[regi] is False, then regi represents a family of regions, and RegionWithin will attempt to compute conditions on parameters such that reg2 is contained within reg1.
- The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate conditions on parameters
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (15)
Basic Uses (3)
Basic Regions (4)
Regions in ![]() including Line and Interval:
including Line and Interval:
Ball:
Regions in ![]() including Point:
including Point:
Line:
Rectangle and RegularPolygon:
Regions in ![]() including Point:
including Point:
Line:
Cuboid and Hexahedron:
Tetrahedron and Simplex:
Regions in ![]() including Cuboid and Parallelepiped in
including Cuboid and Parallelepiped in ![]() :
:
Formula Regions (4)
Mesh Regions (3)
Compare MeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Compare BoundaryMeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Compare MeshRegion with BoundaryMeshRegion in ![]() :
:
Derived Regions (1)
Compare BooleanRegion:
Options (2)
Applications (7)
All convex combinations of points lie within their convex hull:
Find the largest disk contained in a given triangle:
Approximate the largest axes-aligned ellipse contained in the triangle:
Find the smallest disk that contains a given triangle:
Find the smallest axes-aligned ellipse that contains the triangle:
Find all countries that lie completely within the Caribbean Sea:
Select the countries whose polygons lie within the Caribbean Sea:
View these countries on a map:
Find and visualize all positions where a unit rectangle lies within an annulus:
Perform a random walk inside a region:
Define a function to walk a point in a random direction, staying inside a region:
Simulate a random walk from an initial point:
Use RegionWithin as a partial ordering to visualize concentric disks:
Disks with larger radii can completely cover other disks:
Properties & Relations (5)
Use RegionMember to test the membership of a point:
Use RegionWithin to test the membership of a region:
When ℛ2 is within ℛ1, all points in ℛ2 are members of ℛ1:
Check if two regions are equal:
For non‐empty regions, RegionDisjoint returns False when RegionWithin returns True:
Use FindInstance to find points that violate the subset condition:
Use RandomPoint to find a uniform sampling of points that violate the subset condition:
Use Reduce to find where the subset condition is violated:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), RegionWithin, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionWithin.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "RegionWithin." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionWithin.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). RegionWithin. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionWithin.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_regionwithin, author="Wolfram Research", title="{RegionWithin}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionWithin.html}", note=[Accessed: 05-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_regionwithin, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={RegionWithin}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionWithin.html}, note=[Accessed: 05-February-2026]}