ChromaticityPlot[colspace]
plots a 2D slice of the color space colspace.
ChromaticityPlot[color]
plots the specific color.
ChromaticityPlot[{col1,col2,…}]
plots multiple colors and color spaces.
ChromaticityPlot[image]
plots the pixels of image as individual colors.
ChromaticityPlot[…,refcolspace]
uses the reference color space refcolspace.




ChromaticityPlot
ChromaticityPlot[colspace]
plots a 2D slice of the color space colspace.
ChromaticityPlot[color]
plots the specific color.
ChromaticityPlot[{col1,col2,…}]
plots multiple colors and color spaces.
ChromaticityPlot[image]
plots the pixels of image as individual colors.
ChromaticityPlot[…,refcolspace]
uses the reference color space refcolspace.
Details and Options



- ChromaticityPlot is also known as chromatic diagram.
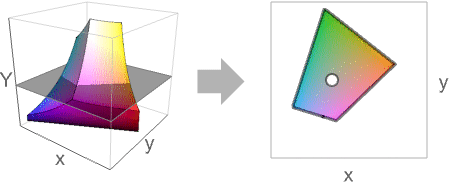
- Typically used to visualize one or several color spaces compared to the visual spectrum. It is also used to visualize one or several colors in an image.
- ChromaticityPlot converts the color coordinates in colspace to coordinates in refcolspace color space and displays a slice given by constant luminance 0.01. For an individual color, the resulting converted color is projected to the slice of constant luminance.
- Color specification color can be any color directive or a color neighborhood given as a ColorsNear object.
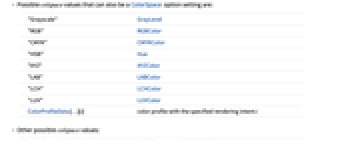
- Possible colspace values that can also be a ColorSpace option setting are:
-
"Grayscale" GrayLevel "RGB" RGBColor "CMYK" CMYKColor "HSB" Hue "XYZ" XYZColor "LAB" LABColor "LCH" LCHColor "LUV" LUVColor ColorProfileData[…][i] color profile with the specified rendering intent 
- Other possible colspace values:
-
"AdobeRGB" Adobe RGB (1998) color space "AppleRGB" Apple RGB color space "CIERGB" CIE RGB color space "ProPhotoRGB" ProPhoto RGB "sRGB" standard sRGB color space "WideGamutRGB" large gamut RGB (a.k.a. Adobe Wide Gamut RGB) - Possible refcolspace specifications include:
-
"CIE31" CIE 1931 xy chromaticity diagram (default) "CIE76" CIE 1976 UCS chromaticity diagram {"ref",l} any of the above spaces at luminance 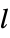
- Luminance is the Y coordinate of the XYZ space.
- Colors or image pixels are rendered as black points if their luminance is the same as the reference luminance and as gray points otherwise.
- ChromaticityPlot accepts all Graphics options with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
Appearance Automatic appearance of visible spectrum BoundaryStyle Automatic the style for the boundary of each region FillingStyle Automatic filling style for each color space Frame True whether to show the frame FrameLabel Automatic frame labels MaxPlotPoints 2000 maximum number of colors or pixels to show PlotLegends Automatic legends for each space PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange Automatic the range of values to include in the plot PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotStyle Automatic specify the style for colors and images PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot WhitePoint Automatic what white point to show - Possible settings for Appearance are:
-
None do not show the visible spectrum Automatic automatically determine appearance "VisibleSpectrum" curve corresponding to the visible spectrum "FilledVisibleSpectrum" filled visible spectrum (default) - Typical settings for PlotLegends include:
-
None add no legend Automatic use automatic legending "Expressions" use colspace name as legend labels {lbl1,lbl2,…} use lbli for the i 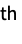 input
inputPlaced[lspec,…] specify placement of legend - Possible settings for WhitePoint include:
-
Automatic automatically determine the white point to use None no white points All all white points "name" use a named white point col use the color col as white point {wp1,…} show several white points wpi -
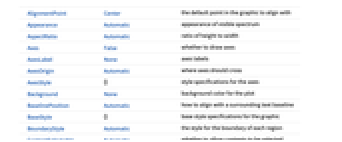
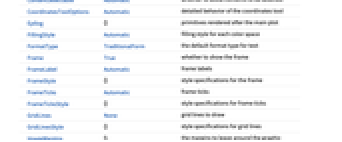
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with Appearance Automatic appearance of visible spectrum AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic BoundaryStyle Automatic the style for the boundary of each region ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FillingStyle Automatic filling style for each color space FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame True whether to show the frame FrameLabel Automatic frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MaxPlotPoints 2000 maximum number of colors or pixels to show Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotLegends Automatic legends for each space PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange Automatic the range of values to include in the plot PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic specify the style for colors and images PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks WhitePoint Automatic what white point to show
List of all options



Examples
open all close allScope (7)
Chromaticity diagram of an ICC profile:
Visualize a random list of RGB colors:
Visualize the pixels of an image:
Visualize the pixels of a 3D image:
Specify the reference color space:
CIE 1976 UCS (uniform chromaticity scale) diagram:
Visualize distribution of an image's pixels as well as a color space:
Options (72)
Appearance (5)
By default, a filled visible spectrum is rendered:
Show the boundary of the visible spectrum only:
Use Appearance->None to remove the visible spectrum:
Use PlotStyle as a suboption to specify a custom style:
Display wavelengths on the visible spectrum using the "Wavelengths"->True suboption:
AspectRatio (3)
By default, ChromaticityPlot determines the height to width ratio from the plot range:
Make the height the same as the width with AspectRatio1:
Make the height half of the width:
AspectRatioFull adjusts the height and width to tightly fit inside other constructs:
Axes (3)
By default, ChromaticityPlot uses a frame instead of axes:
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
BoundaryStyle (2)
By default, the boundary style is automatically chosen:
Use BoundaryStyle->None to show no boundary:
FillingStyle (5)
Frame (4)
ChromaticityPlot uses a frame by default:
Use FrameFalse to turn off the frame:
FrameLabel (5)
FrameTicks (6)
Frame ticks are placed automatically by default:
By default, the top and right edges have tick marks but no tick labels:
Use All to include tick labels on all edges:
Place tick marks at specific positions:
Draw frame tick marks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for tick marks as a fraction of the graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each tick mark:
FrameTicksStyle (3)
PlotLegends (2)
PlotPoints (1)
Automatic setting of PlotPoints might not be sufficient for rendering very small regions:
PlotRange (3)
PlotStyle (1)
PlotTheme (3)
Ticks (6)
Ticks are placed automatically on each axis:
Use TicksNone to draw axes without any tick marks:
Place tick marks at the specified positions:
Draw tick marks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for ticks as a fraction of graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each tick:
TicksStyle (4)
Applications (2)
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), ChromaticityPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "ChromaticityPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). ChromaticityPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_chromaticityplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ChromaticityPlot}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-January-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_chromaticityplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ChromaticityPlot}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-January-2026]}