ChromaticityPlot3D[colspace]
returns a 3D gamut of the color space colspace.
ChromaticityPlot3D[color]
plots the specific color.
ChromaticityPlot3D[image]
plots the pixels of image as individual colors.
ChromaticityPlot3D[{input1,input2,…}]
plots multiple colors, color spaces and images.
ChromaticityPlot3D[…,refcolspace]
uses the reference color space refcolspace.




ChromaticityPlot3D
ChromaticityPlot3D[colspace]
returns a 3D gamut of the color space colspace.
ChromaticityPlot3D[color]
plots the specific color.
ChromaticityPlot3D[image]
plots the pixels of image as individual colors.
ChromaticityPlot3D[{input1,input2,…}]
plots multiple colors, color spaces and images.
ChromaticityPlot3D[…,refcolspace]
uses the reference color space refcolspace.
Details and Options
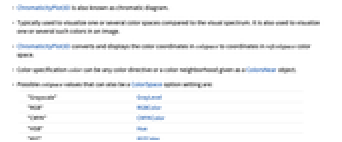


- ChromaticityPlot3D is also known as chromatic diagram.
- Typically used to visualize one or several color spaces compared to the visual spectrum. It is also used to visualize one or several such colors in an image.
- ChromaticityPlot3D converts and displays the color coordinates in colspace to coordinates in refcolspace color space.
- Color specification color can be any color directive or a color neighborhood given as a ColorsNear object.
- Possible colspace values that can also be a ColorSpace option setting are:
-
"Grayscale" GrayLevel "RGB" RGBColor "CMYK" CMYKColor "HSB" Hue "XYZ" XYZColor "LAB" LABColor "LUV" LUVColor "LCH" LCHColor ColorProfileData[…][i] color profile with the specified rendering intent 
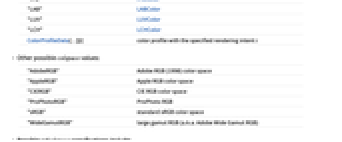
- Other possible colspace values:
-
"AdobeRGB" Adobe RGB (1998) color space "AppleRGB" Apple RGB color space "CIERGB" CIE RGB color space "ProPhotoRGB" ProPhoto RGB "sRGB" standard sRGB color space "WideGamutRGB" large gamut RGB (a.k.a. Adobe Wide Gamut RGB) - Possible refcolspace specifications include:
-
"CIE31" CIE 1931 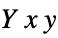 (default)
(default)"CIE76" CIE 1976 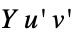
"XYZ" CIE 1931 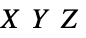
"LAB" CIE 1976 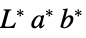
"LCH" CIE 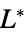
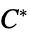
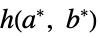
"LUV" CIE 1976 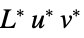
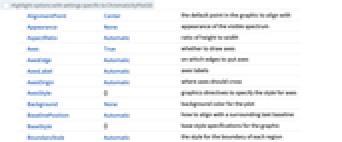
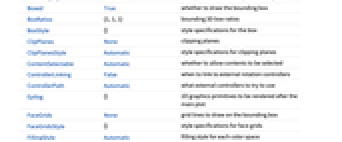
"RGB" RGB cube "HSB" HSB cube - ChromaticityPlot3D accepts all Graphics3D options with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
Appearance None appearance of the visible spectrum Axes True whether to draw axes AxesLabel Automatic axes labels BoundaryStyle Automatic the style for the boundary of each region BoxRatios {1,1,1} bounding 3D box ratios FillingStyle Automatic filling style for each color space MaxPlotPoints 2000 maximum number of colors or pixels to show Mesh None whether to draw a mesh MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh divisions PlotLegends Automatic legends for each space PlotPoints Automatic number of sample points in each dimension PlotStyle Automatic specify the style for colors and images PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot ViewPoint {1,1.5,-2.} viewing position ViewVertical {1,0,0} direction to make vertical WhitePoint Automatic what white point to show - Possible settings for Appearance are:
-
None do not show the visible spectrum "VisibleSpectrum" show the curve corresponding to the visible spectrum - Typical settings for PlotLegends include:
-
None add no legend Automatic use automatic legending "Expressions" use color space name as legend labels {lbl1,lbl2,…} use lbli for the i  input
inputPlaced[lspec,…] specify placement of legend -
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with Appearance None appearance of the visible spectrum AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes AxesEdge Automatic on which edges to put axes AxesLabel Automatic axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} graphics directives to specify the style for axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic BoundaryStyle Automatic the style for the boundary of each region Boxed True whether to draw the bounding box BoxRatios {1,1,1} bounding 3D box ratios BoxStyle {} style specifications for the box ClipPlanes None clipping planes ClipPlanesStyle Automatic style specifications for clipping planes ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected ControllerLinking False when to link to external rotation controllers ControllerPath Automatic what external controllers to try to use Epilog {} 2D graphics primitives to be rendered after the main plot FaceGrids None grid lines to draw on the bounding box FaceGridsStyle {} style specifications for face grids FillingStyle Automatic filling style for each color space FormatType TraditionalForm default format type for text ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels, etc. ImageSize Automatic absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels Lighting Automatic simulated light sources to use MaxPlotPoints 2000 maximum number of colors or pixels to show Mesh None whether to draw a mesh MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh divisions Method Automatic details of 3D graphics methods to use PlotLabel None a label for the plot PlotLegends Automatic legends for each space PlotPoints Automatic number of sample points in each dimension PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic specify the style for colors and images PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} 2D graphics primitives to be rendered before the main plot RotationAction "Fit" how to render after interactive rotation SphericalRegion Automatic whether to make the circumscribing sphere fit in the final display area Ticks Automatic specification for ticks TicksStyle {} style specification for ticks TouchscreenAutoZoom False whether to zoom to fullscreen when activated on a touchscreen ViewAngle Automatic angle of the field of view ViewCenter Automatic point to display at the center ViewMatrix Automatic explicit transformation matrix ViewPoint {1,1.5,-2.} viewing position ViewProjection Automatic projection method for rendering objects distant from the viewer ViewRange All range of viewing distances to include ViewVector Automatic position and direction of a simulated camera ViewVertical {1,0,0} direction to make vertical WhitePoint Automatic what white point to show
List of all options



Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (8)
Visualize the sRGB gamut in the CIE 1931 Yxy reference space:
Visualize the gamut in the CIE 1931 XYZ reference space:
Compare two gamuts in the CIE 1976 ![]() space:
space:
Show a list of RGB colors in the RGB cube:
Visualize color regions in 3D:
Visualize the pixels of an image:
Options (40)
Appearance (1)
AxesLabel (3)
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
BoundaryStyle (3)
BoxRatios (1)
FillingStyle (3)
By default, one space is fully opaque and colored:
Make the plot partially transparent:
With multiple spaces, by default all are partially transparent:
Individually define the appearance for each space:
If the specified list of styles is shorter than the list of color spaces, it is cyclically padded:
MaxPlotPoints (1)
Mesh (6)
By default, no mesh is displayed:
Use five mesh lines in each direction:
The resolution of the full mesh is taken from the PlotPoints option:
Show only the mesh for each space:
Use five mesh lines in each direction for every space:
Specify whether to show the mesh individually for each space:
MeshStyle (1)
PlotLegends (2)
PlotPoints (1)
PlotPoints specifies the density of the grid:
PlotStyle (1)
PlotTheme (3)
Applications (2)
Visualize shades of green in the RGB cube:
Shades of green in the HSB cube:
ImageAdjust rescales RGB values to 0 and 1. Visualize the transformation in the Lab color space:
Properties & Relations (2)
ProPhoto RGB is designed to cover most of the visible portion of the Lab space:
ChromaticityPlot3D can visualize symbolic color regions specified by ColorsNear:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), ChromaticityPlot3D, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot3D.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "ChromaticityPlot3D." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot3D.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). ChromaticityPlot3D. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot3D.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_chromaticityplot3d, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ChromaticityPlot3D}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot3D.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-September-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_chromaticityplot3d, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ChromaticityPlot3D}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChromaticityPlot3D.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-September-2025]}