PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…}]
plots a paired smooth histogram of the values xi and yi.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…},espec]
plots a paired smooth histogram with estimator specification espec.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…},espec,dfun]
plots a paired smooth histogram with distribution function dfun.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{data11,…},{data21,…},…]
plots paired smooth histograms for multiple datasets data1i and data2j.




PairedSmoothHistogram
PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…}]
plots a paired smooth histogram of the values xi and yi.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…},espec]
plots a paired smooth histogram with estimator specification espec.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{x1,x2,…},{y1,y2,…},espec,dfun]
plots a paired smooth histogram with distribution function dfun.
PairedSmoothHistogram[{data11,…},{data21,…},…]
plots paired smooth histograms for multiple datasets data1i and data2j.
Details and Options




- PairedSmoothHistogram[data1,data2] by default plots a paired smooth histogram of the PDF of data1 and data2 using a smooth kernel density estimate.
- The estimator specification espec can be of the form bw or {bw,kernel}.
- The specifications for bandwidth bw and kernel are the same as for SmoothKernelDistribution.
- Possible distribution functions dfun include:
-
"PDF" probability density function "Intensity" count density function "CDF" cumulative distribution function "SF" survival function "HF" hazard function "CHF" cumulative hazard function - The form w[data] provides a wrapper w to be applied to the resulting graphics primitives.
- The following wrappers can be used:
-
Annotation[e,label] provide an annotation Button[e,action] define an action to execute when the element is clicked EventHandler[e,…] define a general event handler for the element Hyperlink[e,uri] make the element act as a hyperlink PopupWindow[e,cont] attach a popup window to the element StatusArea[e,label] display in the status area when the element is moused over Style[e,opts] show the element using the specified styles Tooltip[e,label] attach an arbitrary tooltip to the element - PairedSmoothHistogram[Tabular[…]cspec, …] extracts and plots values from the tabular object using the column specification cspec.
- The following forms of column specifications cspec are allowed for plotting tabular data:
-
col plot values from column col {col1,col2,…,coln} plot columns {col1, …, coln} as a group of values - PairedSmoothHistogram has the same options as Graphics with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of width to height Axes True whether to draw axes ClippingStyle None what to draw where curves are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of curves ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction Filling None filling to insert under each curve FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh points to draw on each curve MeshFunctions {#1&} how to determine the placement of mesh points MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh points Method Automatic methods to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each object PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates Spacings Automatic space between plot axes WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations for symbolic distributions - Possible settings for PlotOrigin include "XAxis" and "YAxis".
- Settings for Spacings are in absolute coordinates. A setting of the form Scaled[s] gives spacing that is a fraction s of the graphic.
- The arguments supplied to RegionFunction, MeshFunctions, and ColorFunction are x and f, where f can be the PDF, CDF, etc. of the distribution.
- With ScalingFunctions->{sx,sy}, the
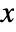 coordinate is scaled using sx and the
coordinate is scaled using sx and the 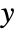 coordinate is scaled using sy.
coordinate is scaled using sy. -
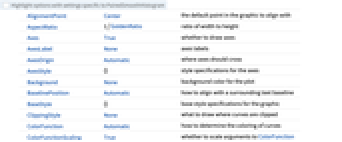
 Highlight options with settings specific to PairedSmoothHistogram
Highlight options with settings specific to PairedSmoothHistogram
-
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of width to height Axes True whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ClippingStyle None what to draw where curves are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of curves ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot Filling None filling to insert under each curve FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh points to draw on each curve MeshFunctions {#1&} how to determine the placement of mesh points MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh points Method Automatic methods to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each object PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates Spacings Automatic space between plot axes Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations for symbolic distributions
List of all options
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (16)
Data (7)
Plot different distribution functions:
PlotRange is selected automatically:
Use PlotRange to focus on areas of interest:
Nonreal data points are ignored:
Specify the number of times to refine the curve:
Override the default tooltips:
Use any object in the tooltip:
Use PopupWindow to provide additional drilldown information:
Tabular Data (1)
Presentation (8)
Options (67)
AspectRatio (2)
Axes (3)
AxesStyle (4)
ClippingStyle (4)
ColorFunction (5)
Color by scaled ![]() and
and ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
Color with a named color scheme:
Fill with the color used for the curve:
ColorFunction has higher priority than PlotStyle for coloring the curve:
Use Automatic in MeshShading to use ColorFunction:
ColorFunctionScaling (2)
Filling (6)
FillingStyle (4)
Fill with red when the first curve is below the second, and blue when the second is below the first:
Use a variable filling style obtained from a ColorFunction:
ImageSize (7)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Allow the width and height to be up to a certain size:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use maximum sizes for the width and height:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Specify the image size as a fraction of the available space:
MaxRecursion (2)
Each level of MaxRecursion will subdivide the initial mesh into a finer mesh:
Mesh (3)
MeshFunctions (2)
MeshShading (6)
Alternate red and blue segments of equal width in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Use None to remove segments:
MeshShading can be used with PlotStyle:
MeshShading has higher priority than PlotStyle for styling the curve:
Use PlotStyle for some segments by setting MeshShading to Automatic:
MeshShading can be used with ColorFunction:
MeshStyle (4)
PerformanceGoal (2)
PlotRange (2)
PlotRange is automatically calculated:
SmoothHistogram automatically chooses the plotting domain:
PlotStyle (6)
Use different style directives:
By default, different styles are chosen for multiple curves:
Explicitly specify the style for different curves:
PlotStyle can be combined with ColorFunction:
PlotStyle can be combined with MeshShading:
RegionFunction (1)
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (1)
PairedSmoothHistogram ignores time stamps of TimeSeries and EventSeries:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2015 (10.2) ▪ 2025 (14.2)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), PairedSmoothHistogram, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PairedSmoothHistogram.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "PairedSmoothHistogram." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PairedSmoothHistogram.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). PairedSmoothHistogram. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PairedSmoothHistogram.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_pairedsmoothhistogram, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PairedSmoothHistogram}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PairedSmoothHistogram.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_pairedsmoothhistogram, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PairedSmoothHistogram}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PairedSmoothHistogram.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}