FourierTransform[f[t],t,ω]
给出 f[t] (变量为 t )的符号傅里叶变换 F[ω] (变量为 ω ).
FourierTransform[f[t],t,![]() ]
]
给出 ![]() 处的数值傅里叶变换.
处的数值傅里叶变换.
FourierTransform[f[t1,…,tn],{t1,…,tn},{ω1,…,ωn}]
给出 f[t1,…,tn] 的多维傅立叶变换.




FourierTransform
FourierTransform[f[t],t,ω]
给出 f[t] (变量为 t )的符号傅里叶变换 F[ω] (变量为 ω ).
FourierTransform[f[t],t,![]() ]
]
给出 ![]() 处的数值傅里叶变换.
处的数值傅里叶变换.
FourierTransform[f[t1,…,tn],{t1,…,tn},{ω1,…,ωn}]
给出 f[t1,…,tn] 的多维傅立叶变换.
更多信息和选项



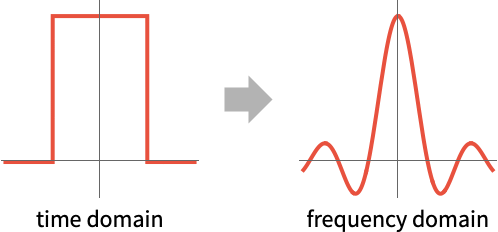
- 傅立叶变换及其逆变换是一种在时域和频域之间转换的方式.
- 傅立叶变换通常用于将常微分方程和偏微分方程分别简化为代数方程或常微分方程. 它们还广泛应用于控制理论和信号处理领域. 此外,它们在研究量子力学现象、噪声过滤等方面也有应用.
- 时域函数
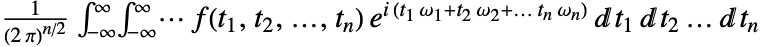 的傅立叶变换是频域函数
的傅立叶变换是频域函数 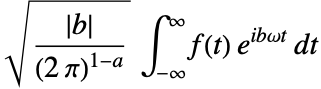 :
: - 在缺省情况下,函数
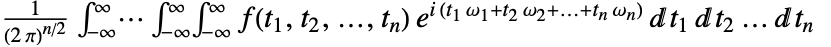 的傅立叶变换的定义为
的傅立叶变换的定义为 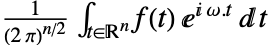 .
. - 函数
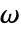 的多维傅立叶变换默认定义为
的多维傅立叶变换默认定义为 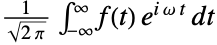 或向量表示形式
或向量表示形式 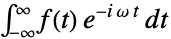 .
. - 不同的定义选择可以使用选项 FourierParameters 指定.
- 如果第三个参数
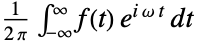 被赋予数值,则积分会通过数值方法计算.
被赋予数值,则积分会通过数值方法计算. - 渐近傅立叶变换可以通过 Asymptotic 方法计算.
- 以下是几种相关的傅立叶变换:
-
FourierTransform 无限连续时间函数 (FT) FourierSequenceTransform 无限离散时间函数 (DTFT) FourierCoefficient 有限连续时间函数 (FS) Fourier 有限离散时间函数 (DFT) - 傅立叶变换是函数在施瓦茨向量空间上的一个自同构,其导数快速降低,因此在其对偶空间(缓和分布空间)中也诱导出一个自同构. 这些空间包括绝对可积函数、多项式增长的良好函数以及紧支撑分布.
- 因此,FourierTransform 不仅可以处理绝对可积函数,还可以处理诸如 DiracDelta 函数等各种缓增分布,从而扩大了它可以有效变换的函数或广义函数的范围.
- 可以给出下列选项:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic 绝对精度的目标位数 Assumptions $Assumptions 所做的参数假定 FourierParameters {0,1} 定义傅立叶变换的参数 GenerateConditions False 是否生成涉及参数条件的答案 PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal 优化的性能方面 PrecisionGoal Automatic 精度的目标位数 WorkingPrecision Automatic 内部计算使用的精度 - 常见的 FourierParameters 设置包括:
-
{0,1} 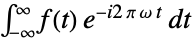
默认设置/物理学 {1,-1} 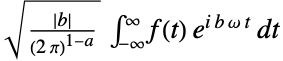
系统工程/数学 {-1,1} 
经典物理学 {0,-2Pi} 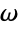
普通频率 {a,b} 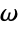
通用设置 - 在 TraditionalForm 中,FourierTransform 用 ℱ 输出. »
范例
打开所有单元 关闭所有单元基本范例 (6)
范围 (44)
基本用法 (4)
初等函数 (8)
特殊函数 (5)
分段函数和分布 (7)
周期函数 (5)
广义函数 (5)
多元函数 (5)
选项 (7)
AccuracyGoal (1)
选项 AccuracyGoal 设置精度的位数:
Assumptions (1)
使用 Assumptions 指定变量的范围:
GenerateConditions (1)
使用 GenerateConditionsTrue 获取结果有效时的参数条件:
PrecisionGoal (1)
选项 PrecisionGoal 设置积分的相对误差:
WorkingPrecision (1)
如果指定了 WorkingPrecision,则计算按该工作精度进行:
应用 (11)
信号与系统 (3)
与 Convolve 比较:
常微分方程 (1)
偏微分方程 (1)
与 DSolveValue 比较:
积分计算 (1)
其它应用 (5)
平面中径向对称函数的傅立叶变换可以表示为汉克尔变换. 验证由下面定义的函数的这种关系:
用 HankelTransform 得到同样的结果:
计算平稳 OrnsteinUhlenbeckProcess 的功率谱:
考虑一个固定面积的盒框函数作为粒子的位置空间波函数. 它的傅立叶变换给出粒子的动量空间波函数:
当 ![]() 较小时,固定面积盒框的高度较大,粒子的位置几乎可以确定. 动量空间波函数在其两个最接近零的根之间的值约为
较小时,固定面积盒框的高度较大,粒子的位置几乎可以确定. 动量空间波函数在其两个最接近零的根之间的值约为 ![]() ,这使得几乎无法确定其动量. 同样地,反之亦然,如下所示:
,这使得几乎无法确定其动量. 同样地,反之亦然,如下所示:
属性和关系 (6)
与 FourierTransform 比较:
用 Asymptotic 计算渐近逼近:
FourierTransform 和 InverseFourierTransform 是互逆的:
对奇函数,FourierTransform 和 FourierCosTransform 是相等的:
对偶函数,FourierTransform 和 FourierSinTransform 的差异为 :
技术笔记
相关链接
历史
1999年引入 (4.0) | 在以下年份被更新:2025 (14.2)
文本
Wolfram Research (1999),FourierTransform,Wolfram 语言函数,https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierTransform.html (更新于 2025 年).
CMS
Wolfram 语言. 1999. "FourierTransform." Wolfram 语言与系统参考资料中心. Wolfram Research. 最新版本 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram 语言. (1999). FourierTransform. Wolfram 语言与系统参考资料中心. 追溯自 https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierTransform.html 年
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_fouriertransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FourierTransform}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_fouriertransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FourierTransform}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}